Abstract
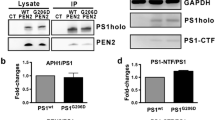
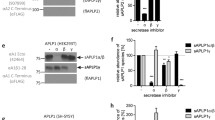
APH-1 is one of the four essential components of presenilin (PS)-γ-secretase complexes. There are three major isoforms of APH-1 in humans: APH-1aS, APH-1aL, and APH-1b. To gain insight into the functional role of APH-1 in γ-secretase complexes, we analyzed the relationship between the three APH-1 forms and characterized APH-1 mutants with a disrupted transmembrane GxxxG motif. We found that overexpression of APH-1aS or APH-1b in human cells significantly reduced the levels of endogenous APH-1aL protein. However, this displacement was not observed in PS-deficient cells, suggesting that it is dependent on PS. In transiently transfected cells, the levels of APH-1aL with G122D or L123D mutations were much lower than wild-type APH-1aL. Also, cycloheximide treatment of stable transfectants revealed that the mutant proteins are much less stable than the wild type. Furthermore, coimmunoprecipitation analysis showed that wild-type but not the mutant APH-1aL is incorporated into PS1 complexes, displacing endogenous APH-1aS. These results collectively indicate that the three forms of APH-1 can replace each other in PS complexes and that the transmembrane GxxxG region is essential for the stability of the APH-1 protein as well as the assembly of PS complexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki W., Yuasa K., Takeda S., Takeda K., Shirotani K., Takahashi K., et al. (2001) Pro-apopototic effect of presenilin 2 (PS2) overexpression is associated with downregulation of Bcl-2 in cultured neurons. J. Neurochem. 79, 1161–1168.
Chui D. H., Shirotani K., Tanahashi H., Akiyama H., Ozawa K., Kunishita T., et al. (1998) Both N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of presenilin 1 colocalize with neurofibrillary tangles in neurons and dystrophic neurites of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 53, 99–106.
Citron M., Westaway D., Xia W., Carlson G., Diehl T., Levesque G., et al. (1997) Mutant presenilins of Alzheimer's disease increase production of 42-residue amyloid beta-protein in both transfected cells and transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 3, 67–72.
Edbauer D., Kaether C., Steiner H., and Haass C. (2004) Co-expression of nicastrin and presenilin rescues a loss of function mutant of APH-1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 37,311–37,315.
Edbauer D., Winkler E., Regula J. T., Pesold B., Steiner H., and Haass C. (2003) Reconstitution of gamma-secretase activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 486–488.
Ephrat L.-L., Wasco W., Poorkaj P., Romano D. M., Oshima J., Pettingell W. H., et al. (1995) Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer's disease locus. Science 269, 973–977.
Fortna R. R., Crystal A. S., Morais V. A., Pijak D. S., Lee V. M., and Doms R. W. (2004) Membrane topology and nicastrin-enhanced endoproteolysis of APH-1, a component of the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 3685–3693.
Francis R., McGrath G., Zhang J., Ruddy D. A., Sym M., Apfeld J., et al. (2002) aph-1 and pen-2 are required for Notch pathway signaling, gamma-secretase cleavage of betaAPP, and presenilin protein accumulation. Dev. Cell 3, 85–97.
Goutte C., Tsunozaki M., Hale V. A., and Priess J. R. (2002) APH-1 is a multipass membrane protein essential for the Notch signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 775–779.
Gu Y., Chen F., Sanjo N., Kawarai T., Hasegawa H., Duthie M., et al. (2003) APH-1 interacts with mature and immature forms of presenilins and nicastrin and may play a role in maturation of presenilin nicastrin complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7374–7380.
Herreman A., Serneels L., Annaert W., Collen D., Schoonjans L., and De Strooper B. (2000) Total inactivation of gamma-secretase activity in presenilin-deficient embryonic stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 461–462.
Hu Y. and Fortini M. E. (2003) Different cofactor activities in gamma-secretase assembly: evidence for a nicastrin-Aph-1 subcomplex. J. Cell Biol. 161, 685–690.
Kimberly W. T. and Wolfe M. S. (2003) Identity and function of gamma-secretase. J. Neurosci. Res. 74, 353–360.
Kimberly W. T., LaVoie M. J., Ostaszewski B. L., Ye W., Wolfe M. S., and Selkoe D. J. (2003) Gamma-secretase is a membrane protein complex comprised of presenilin, nicastrin, Aph-1, and Pen-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 6382–6387.
LaVoie M. J., Fraering P. C., Ostaszewski B. L., Ye W., Kimberly W. T., Wolfe M. S., et al. (2003) Assembly of the gamma-secretase complex involves early formation of an intermediate subcomplex of Aph-1 and nicastrin. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37,213–37,222.
Lee S. F., Shah S., Li H., Yu C., Han W., and Yu G. (2002) Mammalian APH-1 interacts with presenilin and nicastrin and is required for intramembrane proteolysis of amyloid-beta precursor protein and Notch. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 45,013–45,019.
Lee S. F., Shah S., Yu C., Wigley W. C., Li H., Lim M., et al. (2004) A conserved GXXXG motif in APH-1 is critical for assembly and activity of the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 4144–4152.
Ma G., Li T., Price D. L., and Wong P. C. (2005) APH-1a is the principal mammalian APH-1 isoform present in gamma-secretase complexes during embryonic development. J. Neurosci. 25, 192–198.
Morais V. A., Crystal A. S., Pijak D. S., Carlin D., Costa J., Lee V. M., et al. (2003) The transmembrane domain region of nicastrin mediates direct interactions with APH-1 and the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 43,284–43,291.
Niimura M., Isoo N., Takasugi N., Tsuruoka M., Ui-Tei K., Saigo K., et al. (2005) Aph-1 contributes to the stabilization and trafficking of the gamma-secretase complex through mechanisms involving intermolecular and intramolecular interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 12,967–12,975.
Russ W. P. and Engelman D. M. (2000) The GxxxG motif: a framework for transmembrane helix-helix association. J. Mol. Biol. 296, 911–919.
Saito S. and Araki W. (2005) Expression profiles of two human APH-1 genes and their roles in the formation of presenilin complexes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 327, 18–22.
Saito S., Takahasi-Sasaki N., and Araki W. (2005) Identification and characterization of a novel human APH-1b splice variant lacking exon 4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 330, 1068–1072.
Sebastien S., Hebert S. S., Serneels L., Dejaegere T., Horre K., Dabrowski M., et al. (2004) Coordinated and wide-spread expression of gamma-secretase in vivo: evidence for size and molecular heterogeneity. Neurobiol. Dis. 17, 260–272.
Serneels L., Dejaegere T., Craessaerts K., Horre K., Jorissen E., Tousseyn T., et al. (2005) Differential contribution of the three Aph1 genes to gamma-secretase activity in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 1719–1724.
Sherrington R., Rogaev E. I., Liang Y., Rogaeva E. A., Levesque G., Ikeda M., et al. (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature 375, 754–760.
Shiraishi H., Sai X., Wang H. Q., Maeda Y., Kurono Y., Nishimura M., et al. (2004) PEN-2 enhances gamma-cleavage after presenilin heterodimer formation. J. Neurochem. 90, 1402–1413.
Shirotani K., Edbauer D., Kostka M., Steiner H., and Haass C. (2004a) Immature nicastrin stabilizes APH-1 independent of PEN-2 and presenilin: identification of nicastrin mutants that selectively interact with APH-1. J. Neurochem. 89, 1520–1527.
Shirotani K., Edbauer D., Prokop S., Haass C., and Steiner H. (2004b) Identification of distinct gamma-secretase complexes with different APH-1 variants. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41,340–41,345.
Shirotani K., Takahashi K., and Tabira T. (1999) Determination of a cleavage site of presenilin 2 protein in stably transfected SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240, 728–731.
Shirotani K., Takahashi K., Araki W., Maruyama K., and Tabira T. (2000) Mutational analysis of intrinsic regions of presenilin 2 that determine its endoproteolytic cleavage and pathological function. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3681–3686.
Sisodia S. S. and St George-Hyslop P. H. (2002) gamma-Secretase, Notch, Abeta and Alzheimer's disease: where do the presenilins fit in? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 281–290.
Takasugi N., Tomita T., Hayashi I., Tsuruoka M., Niimura M., Takahashi Y., et al. (2003) The role of presenilin cofactors in the gamma-secretase complex. Nature 422, 438–441.
Thinakaran G., Borchelt D. R., Lee M. K., Slunt H. H., Spitzer L., Kim G., et al. (1996) Endoproteolysis of presenilin 1 and accumulation of processed derivatives in vivo. Neuron 17, 181–190.
Yu G., Nishimura M., Arawaka S., Levitan D., Zhang L., Tandon A., et al. (2000) Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and betaAPP processing. Nature 407, 48–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, W., Saito, S., Takahashi-Sasaki, N. et al. Characterization of APH-1 mutants with a disrupted transmembrane GxxxG motif. J Mol Neurosci 29, 35–43 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:29:1:35
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:29:1:35