Abstract
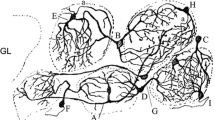
According to the combinatorial receptor and glomerular codes for odors, the fine tuning of the output level from each glomerulus is assumed to be important for information processing in the olfactory system, which may be regulated by numerous elements, such as olfactory nerves (ONs), periglomerular (PG) cells, centrifugal nerves and even various interneurons, such as granule cells, making synapses outside the glomeruli. Recently, structural and physiological analyses at the cellular level started to reveal that the neuronal organization of the olfactory bulb may be more complex than previously thought. In the present paper, we describe the following six points of the structural organization of the glomerulus, revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopy and electron microscopy analyses of rats, mice and other mammals: (i) the chemical heterogeneity of PG cells; (ii) compartmental organization of the glomerulus, with each glomerulus consisting of two compartments, the ON zone and the non-ON zone; (iii) the heterogeneity of PG cells in terms of their structural and synaptic features, whereby type 1 PG cells send their intraglomerular dendrites into both the ON and non-ON zones and type 2 PG cells send their intraglomerular dendrites only into the non-ON zone, thus receiving either few synapses from the ON terminals, if present, or none at all; (iv) the spatial relationship of mitral/tufted cell dendritic processes with ON terminals and PG cell dendrites; (v) complex neuronal interactions via chemical synapses and gap junctions in the glomerulus; and (vi) comparative aspects of the organization of the main olfactory bulb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baimbridge KG, Miller JJ (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of calcium-binding protein in the cerebellum, hippocampal formation and olfactory bulb of the rat. Brain Res 245, 223–9.
Bennett MVL, Zukin RS (2004) Electrical coupling and neuronal synchronization in the mammalian brain. Neuron 41, 495–511.
Bogan N, Brecha N, Gall C, Karten HJ (1982) Distribution of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the rat main olfactory bulb. Neuroscience 7, 895–906.
Briñón JG, Alonso JR, Arévalo R, Garćia-Ojeda E, Lara J, Aijón J (1992) Calbindin-D28K-positive neurons in the rat main olfactory bulb. Cell Tissue Res 269, 289–97.
Buck L, Axel R (1991) A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: A molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell 65, 175–87.
Celio MR (1990) Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience 35, 375–475.
Chao TI, Kasa P, Wolff JR (1997) Distribution of astroglia in glomeruli of the rat main olfactory bulb: Exclusion from the sensory subcompartment of neuropil. J Comp Neurol 388, 191–210.
Crosby EC, Schnitzlein HN (1982) Comparative Correlative Neuroanatomy of the Vertebrate Telencephalon. Macmillan Publishing, New York.
Davis BJ, Macrides F (1983) Tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons and fibers in the olfactory system of the hamster. J Comp Neurol 214, 427–40.
Davis BJ, Burd GD, Macrides F (1982) Localization of methionineenkephalin, substance P, and somatostatin immunoreactivities in the main olfactory bulb of the hamster. J Comp Neurol 204, 377–83.
Dulac C (1997) How does the brain smell? Neuron 19, 477–80.
Friedrich RW, Korsching SI (1997) Combinatorial and chemotopic odorant coding in the zebrafish olfactory bulb visualized by optical imaging. Neuron 18, 737–52.
Gall CM, Hendry SHC, Seroogy KB, Jones EG, Haycock JW (1987) Evidence for coexistence of GABA and dopamine in neurons of the rat olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 266, 307–18.
Halász N (1990) The Vertebrate Olfactory System: Chemical Neuroanatomy, Function and Development. Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest.
Halász N, Hökfelt T, Norman AW, Goldstein M (1985) Tyrosine hydroxylase and 28K-vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein are localized in different subpopulations of periglomerular cells of the rat olfactory bulb. Neurosci Lett 61, 103–7.
Halász N, Ljungdahl Å, Hökfelt T et al. (1977) Transmitter histochemistry of the rat olfactory bulb. I. Immunohistochemical localization of monoamine synthesizing enzymes. Support for intrabulbar, periglomerular dopamine neurons. Brain Res 126, 455–74.
Hildebrand JG, Shepherd GM (1997) Mechanisms of olfactory discrimination: Converging evidence for common principles across phyla. Annu Rev Neurosci 20, 596–631.
Hill WCO (1972) Evolutionary Biology of the Primates. Academic Press, London.
Jacobowitz DM, Winsky L (1991) Immunocytochemical localization of calretinin in the forebrain of the rat. J Comp Neurol 304, 198–218.
Kappers CUA, Huber GC, Crosby EC (1967) The Comparative Anatomy of the Nervous System of Vertebrates, Including Man. Hafner Publishing, New York.
Kasowski HJ, Kim H, Greer CA (1999) Compartmental organization of the olfactory bulb glomerulus. J Comp Neurol 407, 261–74.
Kosaka K, Kosaka T (1999) Distinctive neuronal organization of the olfactory bulb of the laboratory shrew. Neuroreport 10, 267–73.
Kosaka K, Kosaka T (2001) Nidus and Tasseled cell: Distinctive neuronal organization of the main olfactory bulb of the laboratory musk shrew (Suncus murinus). J Comp Neurol 430, 542–61.
Kosaka K, Kosaka T (2004a) Organization of the main olfactory bulbs of some mammals: Musk shrews, moles, hedgehogs, tree shrews, bats, mice, and rats. J Comp Neurol 472, 1–12.
Kosaka K, Hama K, Nagatsu I et al. (1987a) Postnatal development of neurons containing both catecholaminergic and GABAergic traits in the rat main olfactory bulb. Brain Res 403, 355–60.
Kosaka K, Hama K, Nagatsu I, Wu JY, Kosaka T (1988) Possible coexistence of amino acid (γ-aminobutyric acid), amine (dopamine) and peptide (substance P); neurons containing immunoreactivities for glutamic acid decarboxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase and substance P in the hamster main olfactory bulb. Exp Brain Res 71, 633–42.
Kosaka K, Aika Y, Toida K et al. (1995) Chemically defined neuron groups and their subpopulations in the glomerular layer of the rat main olfactory bulb. Neurosci Res 23, 73–88.
Kosaka K, Toida K, Margolis FL, Kosaka T (1997) Chemically defined neuron groups and their subpopulations in the glomerular layer of the rat main olfactory bulb, II. Prominent differences in the intraglomerular dendritic arborization and their relationship to olfactory nerve terminals. Neuroscience 76, 775–86.
Kosaka K, Toida K, Aika Y, Kosaka T (1998) How simple is the organization of the olfactory glomerulus? The heterogeneity of so-called periglomerular cells. Neurosci Res 30, 101–10.
Kosaka K, Aika Y, Toida K, Kosaka T (2001) Structure of intraglomerular dendritic tufts of mitral cells and their contacts with olfactory nerve terminals and calbindin-immunoreactive type 2 periglomerular neurons. J Comp Neurol 440, 219–35.
Kosaka T, Hama K (1982-83) Synaptic organization in the teleost olfactory bulb. J Physiol 78, 707–19.
Kosaka T, Kosaka K (2003) Neuronal gap junctions in the rat main olfactory bulb, with special reference to intraglomerular gap junctions. Neurosci Res 45, 189–209.
Kosaka T, Kosaka K (2004b) Neuronal gap junctions between intraglomerular mitral/tufted cell dendrites in the mouse main olfactory bulb. Neurosci Res 49, 373–8.
Kosaka T, Hataguchi Y, Hama K, Nagatsu I, Wu JY (1985) Coexistence of immunoreactivities for glutamate decarboxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase in some neurons in the periglomerular region of the rat main olfactory bulb: Possible coexistence of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and dopamine. Brain Res 343, 166–71.
Kosaka T, Kosaka K, Heizmann CW et al. (1987b) An aspect of the organization of the GABAergic system in the rat main olfactory bulb: Laminar distribution of immunohistochemically defined subpopulations of GABAergic neurons. Brain Res 411, 373–8.
Kosaka T, Kosaka K, Hataguchi Y et al. (1987c) Catecholaminergic neurons containing GABA-like and/or glutamic acid decarboxylase-like immunoreactivities in various brain regions of the rat. Exp Brain Res 66, 191–210.
Landis DMD, Reese TS, Raviola E (1974) Differences in membrane structure between excitatory and inhibitory components of the reciprocal synapse in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 155, 67–92.
Liu FGR, Miyamoto MM, Freire NP et al. (2001) Molecular and morphological supertrees for eutherian (placental) mammals. Science 291, 1786–9.
López-Mascaraque L, De Carlos J, Valverde F (1990) Structure of the olfactory bulb of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus): A Golgi study of the intrinsic organization of the superficial layers. J Comp Neurol 301, 243–61.
Lowe G (2003) Electrical signaling in the olfactory bulb. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13, 476–81.
Macrides F, Schneider SP (1982) Laminar organization of mitral and tufted cells in the main olfactory bulb of the adult hamster. J Comp Neurol 208, 419–30.
Macrides F, Schoenfeld TA, Marchand JE, Clancy AN (1985) Evidence for morphologically and functionally heterogeneous classes of mitral and tufted cells in the olfactory bulb. Chem Senses 10, 175–202.
Malnic B, Hirono J, Sato T, Buck LB (1999) Combinatorial receptor codes for odors. Cell 96, 713–23.
McLean JH, Shipley MT (1988) Postmitotic, postmigrational expression of tyrosine hydroxylase in olfactory bulb dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 8, 3658–69.
Miragall F, Stimbürger E, Dermietzel R (1996) Mitral and tufted cells of the mouse olfactory bulb possess gap junctions and express connexin43 mRNA. Neurosci Lett 216, 199–202.
Mombaerts P (2004) Odorant receptor gene choice in olfactory sensory neurons: The one receptor-one neuron hypothesis revisited. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14, 31–6.
Mombaerts P, Wang F, Dulac C et al. (1996) Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87, 675–86.
Mori K, Yoshihara Y (1995) Molecular recognition and olfactory processing in the mammalian olfactory system. Prog Neurobiol 45, 585–620.
Mori K, Nagao H, Yoshihara Y (1999) The olfactory bulb: Coding and processing of odor molecule information. Science 286, 711–15.
Mouchaty SK, Gullberg A, Janke A, Arnason U (2000) The phylogenetic position of the Talpidae within Eutheria based on analysis of complete mitochondrial sequences. Mol Biol Evol 17, 60–7.
Mugnaini E, Oertel WH, Wouterlood FG (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of GABAergic neurons and dopaminergic neurons in the rat main and accessory olfactory bulbs. Neurosci Lett 47, 221–6.
Nagayama S, Takahashi YK, Yoshihara Y, Mori K (2004) Mitral and tufted cells differ in the decoding manner of odor maps in the rat olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol 91, 2532–40.
Nieuwenhuys R, Ten Donkelaar HJ, Nicholson C (1998) The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates 3. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Onuma M, Kusakabe T, Kusakabe S (1998) Phylogenetic positions of insectivore in eutheria inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome coxidase subunit II gene. Zool Sci 15, 139–45.
Onuma M, Cao Y, Hasegawa M, Kusakabe S (2000) A close relationship of Chiroptera with Eulipotyphla (core Insectivora) suggested by four mitochondrial genes. Zool Sci 17, 1327–32.
Pinching AJ, Powell TPS (1971a) The neuron types of the glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb. J Cell Sci 9, 305–45.
Pinching AJ, Powell TPS (1971b) The neuropil of the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb. J Cell Sci 9, 347–77.
Ramon y Cajal S (1911) Histologie du Système Nerveux de l’Homme et des Vertébrés, Tome II A. Translated by L Azoulay (1972). Maloine Editions, Paris.
Reesler KJ, Sullivan SL, Buck LB (1994) Information coding in the olfactory system: Evidence for a stereotyped and highly organized epitope map in the olfactory bulb. Cell 79, 1245–55.
Ribak CE, Vaughn JE, Saito K, Barber R, Roberts E (1977) Glutamate decarboxylase localization in neurons of the olfactory bulb. Brain Res 126, 1–18.
Rogers JH (1992) Immunohistochemical markers in rat brain: Colocalization of calretinin and calbindin-D28k with tyrosine hydroxylase. Brain Res 587, 203–10.
Rubin BD, Katz LC (1999) Optical imaging of odorant representations in the mammalian olfactory bulb. Neuron 23, 499–511.
Schoppa NE, Westbrook GL (2001) Glomerulus-specific synchronization of mitral cells in the olfactory bulb. Neuron 31, 639–51.
Seroogy KB, Brecha N, Gall C (1985) Distribution of cholecystokinin-like immunoreactivity in the rat main olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 239, 373–83.
Shepherd GM (1994) Discrimination of the molecular signals by the olfactory receptor neuron. Neuron 13, 771–90.
Shipley MT, Mclean JH, Ennis M (1995) Olfactory system. In: The Rat Nervous System, 2nd edn. (Paxinos G, ed.). Academic Press, New York, 899–926.
Sotelo C, Korn H (1978) Morphological correlates of electrical and other interactions through low-resistance pathways between neurons of the vertebrate central nervous system. Int Rev Cytol 55, 67–107.
Toida K, Kosaka K, Heizmann CW, Kosaka T (1998) Chemically defined neuron groups and their subpopulations in the glomerular layer of the rat main olfactory bulb, III. Structural features of calbindin D28K-immunoreactive neurons. J Comp Neurol 392, 179–98.
Toida K, Kosaka K, Aika Y, Kosaka T (2000) Chemically defined neuron groups and their subpopulations in the glomerular layer of the rat main olfactory bulb, IV. Intraglomerular synapses of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons. Neuroscience 101, 11–17.
Toida K, Kosaka K, Aika Y et al. (2002) Catecholaminergic neurons in the olfactory bulb. In: Catecholamine Metabolism: From Molecular Understanding to Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment (Nagatsu T, Nabeshima R, McCarthy R, Goldstein D, eds). Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 289–92.
Tsuruo Y, Hökfelt T, Visser TJ (1988) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-immunoreactive neuron populations in the rat olfactory bulb. Brain Res 447, 183–7.
Uchida N, Takahashi YK, Tanifuji M, Mori K (2000) Odor maps in the mammalian olfactory bulb: Domain organization and odorant structural features. Nat Neurosci 3, 1035–43.
Urban NN, Sakmann B (2002) Reciprocal intraglomerular excitation and intra- and interglomerular lateral inhibition between mouse olfactory bulb mitral cells. J Physiol 542, 355–67.
Valverde F (1965) Studies on the Piriform Lobe. Harvard University Press, Cambridge.
Vassar R, Chao SK, Sticheran R, Nunñez JM, Vossall LB, Axel R (1994) Topographic organization of sensory projections to the olfactory bulb. Cell 79, 981–91.
Waddell PJ, Okada N, Hasegawa M (1999) Toward resolving the interordinal relationships of placental mammals. SystBiol 48, 1–5.
White E (1973) Synaptic organization of the mammalian olfactory glomerulus: New findings including an intraspecific variation. Brain Res 60, 299–313.
Zippel HP, Reschke CH, Korff V (1999) Simultaneous recordings from two physiologically different types of relay neurons, mitral cells and ruffed cells, in the olfactory bulb of goldfish. Cell Mol Biol 45, 327–37.
Zippel HP, Gloger M, Lüthje L, Nasser S, Wicke S (2000) Pheromone discrimination ability of olfactory bulb mitral and ruffed cells in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Chem Senses 25, 339–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosaka, K., Kosaka, T. Synaptic organization of the glomerulus in the main olfactory bulb: Compartments of the glomerulus and heterogeneity of the periglomerular cells. Anato Sci Int 80, 80–90 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073x.2005.00092.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073x.2005.00092.x