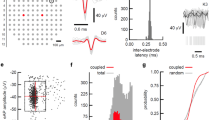
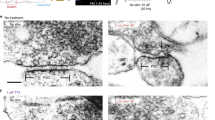
Abstract
Analysis of synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, axonal processing, synaptic timing or electrical coupling requires the simultaneous recording of both the pre- and postsynaptic compartments. Paired-recording technique of monosynaptically connected neurons is also an appropriate technique to probe the function of small molecules (calcium buffers, peptides or small proteins) at presynaptic terminals that are too small to allow direct whole-cell patch-clamp recording. We describe here a protocol for obtaining, in acute and cultured slices, synaptically connected pairs of cortical and hippocampal neurons, with a reasonably high probability. The protocol includes four main stages (acute/cultured slice preparation, visualization, recording and analysis) and can be completed in ∼4 h.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hugues, G. & Tauc, L. A direct synaptic connexion between the left and right giant cells in Aplysia. J. Physiol. 197, 511–527 (1968).
Miles, R. & Poncer, J.C. Paired recording from neurones. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 6, 387–394 (1996).
Miles, R. Synaptic excitation of inhibitory cells by single CA3 hippocampal pyramidal cells of the guinea-pig in vitro . J. Physiol. 428, 64–77 (1990).
Sayer, R.J., Friedlander, M.J. & Redman, S.J. The time course and amplitude of EPSPs evoked at synapses between pairs of CA3/CA1 neurons in the hippocampal slice. J. Neurosci. 10, 826–836 (1990).
Hefft, S. & Jonas, P. Asynchronous GABA release generates long-lasting inhibition at a hippocampal interneuron-principal neuron synapse. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1319–1328 (2005).
Mason, A., Nicoll, A. & Stratford, K. Synaptic transmission between individual pyramidal neurons of the rat visual cortex in vitro . J. Neurosci. 11, 72–84 (1991).
Deuchars, J., West, D.C. & Thomson, A.M. Relationships between morphology and physiology of pyramid-pyramid single axon connections in rat neocortex in vitro . J. Physiol. 478, 423–435 (1994).
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M., Roth, A. & Sakmann, B. Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex. J. Physiol. 500, 409–440 (1997).
Feldmeyer, D., Egger, V., Lübke, J. & Sakmann, B. Reliable synaptic connections between pairs of excitatory layer 4 neurons within a single “barrel” of developing rat somatosensory cortex. J. Physiol. 521, 169–190 (1999).
Barbour, B. & Isope, P. Combining loose cell-attached stimulation and recording. J. Neurosci. Methods 103, 199–208 (2000).
Vincent, P. & Marty, A. Fluctuations of inhibitory postsynaptic currents in Purkinje cells from rat cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. 494, 183–199 (1996).
Orduz, D. & Llano, I. Recurrent axon collaterals underlie facilitating synapses between cerebellar Purkinje cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 17831–17836 (2007).
Freiman, I., Anton, A., Monyer, H., Urbanski, M.J. & Szabo, B. Analysis of the effects of cannabinoids on identified synaptic connections in the caudate-putamen by paired-recordings in transgenic mice. J. Physiol. 575, 789–806 (2006).
Vandercasteel, M., Glowinski, J., Deniau, J.M. & Venance, L. Chemical transmission between dopaminergic neuron pairs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 4904–4909 (2008).
Woodruff, A.R., Monyer, H. & Sah, P. GABAergic excitation in the basolateral amygdala. J. Neurosci. 26, 11881–11887 (2006).
Geracitano, R., Kaufmann, W.A., Szabo, G., Ferraguti, F. & Capogna, M. Synaptic heterogeneity between mouse paracapsular intercalated neurons of the amygdala. J. Physiol. 585, 117–134 (2007).
Urban, N. & Sakmann, B. Reciprocal intraglomerular excitation and intra- and interglomerular lateral inhibition between mouse olfactory bulb mitral cells. J. Physiol. 542, 355–367 (2002).
Christie, J.M. & Westbrook, G.L. Lateral excitation within the olfactory bulb. J. Neurosci. 26, 2269–2277 (2006).
Pressler, R.T. & Strowbridge, B.W. Blanes cells mediate persistent feedforward inhibition onto granule cells in the olfactory bulb. Neuron 49, 889–904 (2006).
Jonas, P., Bischofberger, J. & Sandkühler, J. Corelease of two fast neurotransmitters at a central synapse. Science 281, 419–424 (1998).
Gulyás, A.I. et al. Hippocampal pyramidal cells excite inhibitory neurons through a single release site. Nature 366, 683–387 (1993).
Maccaferri, G., Roberts, J.D.B., Szucs, P., Cottingham, C.A. & Somogyi, P. Cell surface domain specific postsynaptic currents evoked by identified GABAergic neurones in rat hippocampus in vitro . J. Physiol. 524, 91–116 (2000).
Malinow, R. Transmission between pairs of hippocampal slice neurons: quantal levels, oscillations, and LTP. Science 252, 722–724 (1991).
Stricker, C., Field, A.C. & Redman, S.J. Changes in quantal parameters of EPSCs in rat CA1 neurones in vitro after the induction of long-term potentiation. J. Physiol. 490, 443–454 (1996).
Biró, A., Holderith, N.B. & Nusser, Z. Quantal size is independent of the release probability at hippocampal excitatory synapses. J. Neurosci. 25, 223–232 (2005).
Debanne, D., Guérineau, N.C., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Physiology and pharmacology of unitary synaptic connections between pairs of cells in areas CA3 and CA1 of rat hippocampal slice cultures. J. Neurophysiol. 73, 1282–1294 (1995).
Raffaelli, G., Saviane, C., Mohajerani, M.H., Pedarzani, P. & Cherubini, E. BK potassium channels control transmitter release at CA3-CA3 synapses in the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 557, 147–157 (2004).
Capogna, M., McKinney, R.A., O'Connor, V., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Ca2+ or Sr2+ partially rescues synaptic transmission in hippocampal cultures treated with botulinum toxin A and C, but not tetanus toxin. J. Neurosci. 17, 7190–7202 (1997).
Poncer, J.C., McKinney, R.A., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Either N- or P-type calcium channels mediate GABA release at distinct hippocampal inhibitory synapses. Neuron 18, 463–472 (1997).
Scanziani, M., Gähwiler, B.H. & Charpak, S. Target cell-specific modulation of transmitter release at terminals from a single axon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12004–12009 (1998).
Poncer, J.C., McKinney, R.A., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Differential control of GABA release at synapses from distinct interneurons in rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 528, 123–130 (2000).
Neu, A., Földy, C. & Soltesz, I. Postsynaptic origin of CB1-dependent tonic inhibition of GABA release at cholecystokinin-positive basket cell to pyramidal cell synapses in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 578, 233–247 (2007).
Boudkkazi, S. et al. Release-dependent variations in synaptic latency: a putative code for short- and long-term synaptic dynamics. Neuron 56, 1048–1060 (2007).
Miles, R. & Wong, R.K.S. Excitatory synaptic interactions between CA3 neurones in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro . J. Physiol. 373, 397–418 (1986).
Miles, R. & Wong, R.K.S. Unitary inhibitory synaptic potentials in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro . J. Physiol. 356, 97–113 (1984).
Bartos, M., Vida, I., Frotscher, M., Geiger, J.R.P. & Jonas, P. Rapid signalling at inhibitory synapses in a dentate gyrus interneuron network. J. Neurosci. 21, 2687–2698 (2001).
Okun, M. & Lampl, I. Instantaneous correlation of excitation and inhibition during ongoing and sensory-evoked activities. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 535–537 (2008).
Khalilov, I. et al. A novel in vitro preparation: the intact hippocampal formation. Neuron 19, 743–749 (1997).
Schneggenburger, R. & Forsythe, I.D. The calyx of Held. Cell Tissue Res. 326, 311–337 (2006).
Geiger, J.R.P. & Jonas, P. Dynamic control of presynaptic Ca2+ inflow by fast-inactivating K+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber boutons. Neuron 28, 927–939 (2000).
Ohana, O. & Sakmann, B. Transmitter release modulation in nerve terminals of rat neocortical pyramidal cells by intracellular calcium buffers. J. Physiol. 513, 135–148 (1998).
Pavlidis, P. & Madison, D.V. Synaptic transmission in pair recordings from CA3 pyramidal cells in organotypic culture. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 2787–2797 (1999).
Rozov, A., Burnashev, N., Sakmann, B. & Neher, E. Transmitter release modulation by intracellular Ca2+ buffers in facilitating and depressing nerve terminals of pyramidal cells in layer 2/3 of the rat neocortex indicates a target cell-specific difference in presynaptic calcium dynamics. J. Physiol. 531, 807–826 (2001).
Caillard, O. et al. Role of the calcium binding protein parvalbumin in short-term synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 13372–13377 (2000).
Lu, F.M. & Hawkins, R.D. Presynaptic and postsynaptic Ca2+ and CaMKII contribute to long-term potentiation at synapses between individual CA3 neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 4264–4269 (2006).
Blatow, M., Caputi, A., Burnashev, N., Monyer, H. & Rozov, A. Ca2+ buffer saturation underlies paired pulse facilitation in calbindin-D28k-containing terminals. Neuron 38, 79–88 (2003).
Unni, V., Zakharenko, S.S., Zablow, L., DeCostanzo, A.J. & Siegelbaum, S.A. Calcium release from presynaptic ryanodine-sensitive stores is required for long-term depression at hippocampal CA3-CA3 pyramidal neuron synapses. J. Neurosci. 24, 9612–9622 (2004).
Bucurenciu, I., Kulik, A., Schwaller, B., Frotscher, M. & Jonas, P. Nanodomain coupling between Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ sensors promotes fast and efficient transmitter release at a cortical GABAergic synapse. Neuron 57, 536–545 (2008).
Bekkers, J. & Stevens, C.F. Excitatory and inhibitory autaptic currents in isolated hippocampal neurons maintained in cell culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 7834–7838 (1991).
Feldmeyer, D., Lübke, J., Silver, R.A. & Sakmann, B. Synaptic connections between layer 4 spiny neurone-layer 2/3 pyramidal cell pairs in juvenile rat barrel cortex: physiology and anatomy of interlaminar signalling within a cortical column. J. Physiol. 538, 803–822 (2002).
Feldmeyer, D., Roth, A. & Sakmann, B. Monosynaptic connections between pairs of spiny stellate cells in layer 4 and pyramidal cells in layer 5A indicate that lemniscal and paralemniscal afferent pathway converge in the infragranular somatosensory cortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 3423–3441 (2005).
Song, S., Sjöström, P.J., Reigl, M., Nelson, S. & Chklovskii, D.B. Highly non-random features of synaptic connectivity in local cortical circuits. PLoS Biol. 3, e68 (2005).
Kampa, B.M., Letzkus, J.J. & Stuart, G.J. Cortical feed-forward networks for binding different streams of sensory information. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 1472–1473 (2006).
Maffei, A., Nelson, S.B. & Turrigiano, G.G. Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 1353–1359 (2004).
Maffei, A., Nataraj, K., Nelson, S.B. & Turrigiano, G.G. Potentiation of cortical inhibition by visual deprivation. Nature 443, 81–84 (2006).
Bolshakov, V. & Siegelbaum, S.A. Regulation of hippocampal transmitter release during development and long-term potentiation. Science 269, 1730–1734 (1995).
Gähwiler, B.H., Capogna, M., Debanne, D., McKinney, R.A. & Thompson, S.M. Organotypic slice cultures: a technique has come of age. Trends Neurosci. 20, 471–477 (1997).
De Simoni, A., Griesinger, C.B. & Edwards, F.A. Development of rat CA1 neurones in acute versus organotypic slices: role of experience in synaptic morphology and activity. J. Physiol. 550, 135–147 (2003).
Debanne, D., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Cooperative interactions in the induction of long-term potentiation and depression of synaptic excitation between hippocampal CA3-CA1 cell pairs in vitro . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11225–11230 (1996).
Mori, M., Abegg, M.H., Gähwiler, B.H. & Gerber, U. A frequency-dependent switch from inhibition to excitation in a hippocampal unitary circuit. Nature 431, 453–456 (2004).
Galimberti, I. et al. Long-term rearrangements of hippocampal mossy fibre terminal connectivity in the adult regulated by experience. Neuron 50, 749–763 (2006).
Mori, M., Gähwiler, B.H. & Gerber, U. Recruitment of an inhibitory hippocampal network after bursting in a single granule cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7640–7645 (2007).
Debanne, D., Guérineau, N.C., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Paired-pulse facilitation and depression at unitary synapses in rat hippocampus: quantal fluctuation affects subsequent release. J. Physiol. 491, 163–176 (1996).
Angulo, M.C., Staiger, J.F., Rossier, J. & Audinat, E. Distinct local circuits between neocortical pyramidal cells and fast-spiking interneurons in young adult rats. J. Neurophysiol. 89, 943–953 (2003).
Alle, H., Jonas, P. & Geiger, J.R.P. PTP and LTP at a hippocampal mossy fiber-interneuron synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 14708–14713 (2001).
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M. & Sakmann, B. Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275, 213–215 (1997).
Debanne, D., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Long-term synaptic plasticity between pairs of individual CA3 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slice cultures. J. Physiol. 507, 237–247 (1998).
Bi, Q.Q. & Poo, M.M. Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J. Neurosci. 18, 10464–10472 (1998).
Egger, V., Feldmeyer, D. & Sakmann, B. Coincidence detection and changes of synaptic efficacy in spiny stellate neurons in rat barrel cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 1098–1105 (1999).
Sjöström, P.J., Turrigiano, G.G. & Nelson, S.B. Rate, timing, and cooperativity jointly determine cortical synaptic plasticity. Neuron 32, 1149–1164 (2001).
Sjöström, P.J. & Häusser, M. A cooperative switch determines the sign of synaptic plasticity in distal dendrites of neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron 51, 227–238 (2006).
Holmgren, C.D. & Zilberter, Y. Coindicent spiking activity induces long-term changes in inhibition of neocortical pyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. 21, 8270–8277 (2001).
Li, C.Y., Lu, J.T., Wu, C.P., Duan, S.M. & Poo, M.M. Bidirectional modification of presynaptic neuronal excitability accompanying spike timing-dependent synaptic plasticity. Neuron 41, 257–268 (2004).
Debanne, D., Guérineau, N.C., Gähwiler, B.H. & Thompson, S.M. Action-potential propagation gated by an axonal IA-like K+ conductance in hippocampus. Nature 389, 286–289 (1997).
Baccus, S.A. Synaptic facilitation by reflected action potentials: enhancement of transmission when nerve impulses reverse direction at axon branch points. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8345–8350 (1998).
Debanne, D. Information processing in the axon. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 304–316 (2004).
Saviane, C., Mohajerani, M.H. & Cherubini, E. An ID-like current that is downregulated by Ca2+ modulates information coding at CA3-CA1 synapses in the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 552, 513–524 (2003).
Shu, Y., Hasenstaub, A., Duque, A., Yu, Y. & McCormick, D.A. Modulation of intracortical synaptic potentials by presynaptic somatic membrane potential. Nature 441, 761–765 (2006).
Kole, M.H.P., Letzkus, J.J. & Stuart, G.J. Axon initial segment Kv1 channels control axonal action potential waveform and synaptic efficacy. Neuron 55, 633–647 (2007).
Galaretta, M. & Hestrin, S. A network of fast-spiking cells in the neocortex connected by electrical synapses. Nature 402, 72–75 (1999).
Gibson, J.R., Beierlein, M. & Connors, B.W. Two networks of electrically coupled inhibitory neurons in neocortex. Nature 402, 75–79 (1999).
Schmitz, D. et al. Axo-axonal coupling: a novel mechanism for ultrafast neuronal communication. Neuron 31, 831–840 (2001).
Zsiros, V., Aradi, I. & Maccaferri, G. Propagation of postsynaptic currents and potentials via gap junctions in GABAergic networks of the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 578, 527–544 (2007).
Zsiros, V. & Maccaferri, G. Noradrenergic modulation of electrical coupling in GABAergic networks of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 28, 1804–1815 (2008).
Hestrin, S. & Galarreta, M. Electrical synapses define networks of neocortical GABAergic neurons. Trends Neurosci. 28, 304–309 (2004).
Wickersham, I.R. et al. Monosynaptic restriction of transsynaptic tracing from single, genetically targeted neurons. Neuron 53, 639–647 (2007).
Luo, L., Callaway, E.M. & Svoboda, K. Genetic dissection of neural circuits. Neuron 57, 634–660 (2008).
Scharfman, H.E. Evidence from simultaneous intracellular recordings in rat hippocampal slices that area CA3 pyramidal cells innervate dentate hilar mossy cells. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 2167–2180 (1994).
Davie, J.T. et al. Dendritic patch-clamp recording. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1235–1247 (2006).
Bischofberger, J., Engel, D., Li, L.Y., Geiger, J.R.P. & Jonas, P. Patch-clamp recording from mossy fiber terminal in hippocampal slices. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2075–2081 (2006).
De Simoni, A. & Yu, L.M.Y. Preparation of organotypic hippocampal slice cultures: interface method. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1439–1445 (2006).
Castañeda-Castellanos, D.R., Flint, A.C. & Kriegstein, A.R. Blind patch clamp recordings in embryonic and adult mammalian brain slices. Nat. Protoc. 1, 532–542 (2006).
Gogolla, N., Galimberti, I., DePaola, V. & Caroni, P. Preparation of organotypic hippocampal slice cultures for long-term live imaging. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1165–1171 (2006).
Mortensen, M. & Smart, T. Single-channel recording of ligand-gated ion channels. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2826–2841 (2007).
Thompson, S.M., Masukawa, L.M. & Prince, D.A. Temperature dependence of intrinsic membrane properties and synaptic potentials in hippocampal CA1 neurons in vitro . J. Neurosci. 5, 817–824 (1985).
Postlethwaite, M., Hennig, M.H., Steinert, J.R., Graham, B.P. & Forsythe, I.D. Acceleration of AMPA receptor kinetics underlies temperature-dependent changes in synaptic strength at the calyx of Held. J. Physiol. 579, 69–84 (2007).
Saviane, C., Savtchenko, L.P., Raffaelli, G., Voronin, L.L. & Cherubini, E. Frequency-dependent shift from paired-pulse facilitation to paired-pulse depression at unitary CA3-CA3 synapses in the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 544, 469–476 (2002).
Harveit, E. & Veruki, M.L. Studying properties of neurotransmitter receptors by non-stationary noise analysis of spontaneous currents and agonist-evoked responses in outside-out patches. Nat. Protoc. 2, 434–448 (2007).
Reyes, A. et al. Target-cell-specific facilitation and depression in neocortical circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 279–285 (1998).
Silberberg, G. & Markram, H. Disynaptic inhibition between neocortical pyramidal cells mediated by Martinotti cells. Neuron 53, 735–746 (2007).
Sjöström, P.J., Turrigiano, G.G. & Nelson, S.B. Neocortical LTD via coincident activation of presynaptic NMDA and cannabinoid receptors. Neuron 39, 641–654 (2003).
Simon, A., Oláh, S., Molnár, G., Szabadics, J. & Tamás, G. Gap-junctional coupling between neurogliaform cells and various interneuron types in the neocortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 6278–6285 (2005).
Le Bé, J.V. & Markram, H. Spontaneous and evoked synaptic rewiring in the neonatal neocortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13214–13219 (2006).
Gasparini, S., Saviane, C., Voronin, L.L. & Cherubini, E. Silent synapses in the developing hippocampus: lack of functional AMPA receptors or low probability of glutamate release? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9741–9746 (2000).
Montgomery, J.M., Pavlidis, P. & Madison, D.V. Pair recordings reveal all-silent synaptic connections and the post-synaptic expression of long-term potentiation. Neuron 29, 691–701 (2001).
Durand, G.M., Kovalchuk, Y. & Konnerth, A. Long-term potentiation and functional synapse induction in developing hippocampus. Nature 381, 71–75 (1996).
Nowak, L., Bregestowski, P., Ascher, P., Herbet, A. & Prochiantz, A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature 307, 462–465 (1984).
Isaac, J.T., Nicoll, R.A. & Malenka, R.C. Evidence for silent synapses: implications for the expression of LTP. Neuron 15, 427–434 (1995).
Diana, M.A. & Marty, A. Characterization of depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition using paired interneuron-Purkinje cell recordings. J. Neurosci. 23, 5906–5918 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Seagar, O. El Far, J.M. Goaillard, Y. Frégnac and G. Alcaraz for stimulating discussions and F. Dubruc for help with video recordings. This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (Neuroscience, Neurologie and Psychiatrie, 06-Neuro-014-01 to D.D.), the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (to E.C.), the Fondation Française pour la Recherche sur l'Epilepsie (to O.C.), the Ministry of Research (doctoral grant to S.B. & E.C. and ACI Jeunes Chercheurs to D.D.), AFM (to R.C.) and the European Community (LSHM-CT-2004-511995, synaptic scaffolding proteins orchestrating cortical synapse organization during development to D.D.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debanne, D., Boudkkazi, S., Campanac, E. et al. Paired-recordings from synaptically coupled cortical and hippocampal neurons in acute and cultured brain slices. Nat Protoc 3, 1559–1568 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.147
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.147
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.