Abstract
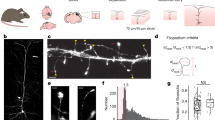
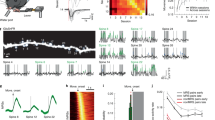
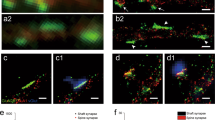
Although new and functional neurons are produced in the adult brain, little is known about how they integrate into mature networks. Here we explored the mechanisms of synaptogenesis on neurons born in the adult mouse hippocampus using confocal microscopy, electron microscopy and live imaging. We report that new neurons, similar to mature granule neurons, were contacted by axosomatic, axodendritic and axospinous synapses. Consistent with their putative role in synaptogenesis, dendritic filopodia were more abundant during the early stages of maturation and, when analyzed in three dimensions, the tips of all filopodia were found within 200 nm of preexisting boutons that already synapsed on other neurons. Furthermore, dendritic spines primarily synapsed on multiple-synapse boutons, suggesting that initial contacts were preferentially made with preexisting boutons already involved in a synapse. The connectivity of new neurons continued to change until at least 2 months, long after the formation of the first dendritic protrusions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lamprecht, R. & LeDoux, J. Structural plasticity and memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 45–54 (2004).
Altman, J. & Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 124, 319–335 (1965).
Eriksson, P.S. et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 4, 1313–1317 (1998).
van Praag, H. et al. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415, 1030–1034 (2002).
Shors, T.J. et al. Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410, 372–376 (2001).
Saxe, M.D. et al. Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17501–17506 (2006).
Madsen, T.M., Kristjansen, P.E., Bolwig, T.G. & Wortwein, G. Arrested neuronal proliferation and impaired hippocampal function following fractionated brain irradiation in the adult rat. Neuroscience 119, 635–642 (2003).
Zhao, C., Teng, E.M., Summers, R.G., Jr., Ming, G.L. & Gage, F.H. Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 26, 3–11 (2006).
Harris, K.M. & Kater, S.B. Dendritic spines: cellular specializations imparting both stability and flexibility to synaptic function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 341–371 (1994).
Petrak, L.J., Harris, K.M. & Kirov, S.A. Synaptogenesis on mature hippocampal dendrites occurs via filopodia and immature spines during blocked synaptic transmission. J. Comp. Neurol. 484, 183–190 (2005).
Dunaevsky, A., Tashiro, A., Majewska, A., Mason, C. & Yuste, R. Developmental regulation of spine motility in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13438–13443 (1999).
Fischer, M., Kaech, S., Knutti, D. & Matus, A. Rapid actin-based plasticity in dendritic spines. Neuron 20, 847–854 (1998).
Portera-Cailliau, C., Pan, D.T. & Yuste, R. Activity-regulated dynamic behavior of early dendritic protrusions: evidence for different types of dendritic filopodia. J. Neurosci. 23, 7129–7142 (2003).
Harris, K.M., Jensen, F.E. & Tsao, B. Three-dimensional structure of dendritic spines and synapses in rat hippocampus (CA1) at postnatal day 15 and adult ages: implications for the maturation of synaptic physiology and long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 12, 2685–2705 (1992).
Matsuzaki, M. et al. Dendritic spine geometry is critical for AMPA receptor expression in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1086–1092 (2001).
Takumi, Y., Ramirez-Leon, V., Laake, P., Rinvik, E. & Ottersen, O.P. Different modes of expression of AMPA and NMDA receptors in hippocampal synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 618–624 (1999).
Fiala, J.C., Feinberg, M., Popov, V. & Harris, K.M. Synaptogenesis via dendritic filopodia in developing hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 8900–8911 (1998).
Ziv, N.E. & Smith, S.J. Evidence for a role of dendritic filopodia in synaptogenesis and spine formation. Neuron 17, 91–102 (1996).
Knott, G.W., Holtmaat, A., Wilbrecht, L., Welker, E. & Svoboda, K. Spine growth precedes synapse formation in the adult neocortex in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 1117–1124 (2006).
Ge, S. et al. GABA regulates synaptic integration of newly generated neurons in the adult brain. Nature 439, 589–593 (2006).
Esposito, M.S. et al. Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J. Neurosci. 25, 10074–10086 (2005).
Laplagne, D.A. et al. Functional convergence of neurons generated in the developing and adult hippocampus. PLoS Biol. 4, e409 (2006).
Harris, K.M. & Stevens, J.K. Dendritic spines of CA 1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus: serial electron microscopy with reference to their biophysical characteristics. J. Neurosci. 9, 2982–2997 (1989).
Schikorski, T. & Stevens, C.F. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J. Neurosci. 17, 5858–5867 (1997).
Wu, G., Malinow, R. & Cline, H.T. Maturation of a central glutamatergic synapse. Science 274, 972–976 (1996).
Kempermann, G., Gast, D., Kronenberg, G., Yamaguchi, M. & Gage, F.H. Early determination and long-term persistence of adult-generated new neurons in the hippocampus of mice. Development 130, 391–399 (2003).
Gould, E., Beylin, A., Tanapat, P., Reeves, A. & Shors, T.J. Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 260–265 (1999).
Cameron, H.A., McEwen, B.S. & Gould, E. Regulation of adult neurogenesis by excitatory input and NMDA receptor activation in the dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 15, 4687–4692 (1995).
Balazs, R., Jorgensen, O.S. & Hack, N. N-methyl-D-aspartate promotes the survival of cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neuroscience 27, 437–451 (1988).
Tashiro, A., Sandler, V.M., Toni, N., Zhao, C. & Gage, F.H. NMDA-receptor-mediated, cell-specific integration of new neurons in adult dentate gyrus. Nature 442, 929–933 (2006).
Okabe, S., Miwa, A. & Okado, H. Spine formation and correlated assembly of presynaptic and postsynaptic molecules. J. Neurosci. 21, 6105–6114 (2001).
Majewska, A.K., Newton, J.R. & Sur, M. Remodeling of synaptic structure in sensory cortical areas in vivo. J. Neurosci. 26, 3021–3029 (2006).
Shepherd, G.M., Raastad, M. & Andersen, P. General and variable features of varicosity spacing along unmyelinated axons in the hippocampus and cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 6340–6345 (2002).
Trachtenberg, J.T. et al. Long-term in vivo imaging of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in adult cortex. Nature 420, 788–794 (2002).
Kirov, S.A. & Harris, K.M. Dendrites are more spiny on mature hippocampal neurons when synapses are inactivated. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 878–883 (1999).
Richards, D.A. et al. Glutamate induces the rapid formation of spine head protrusions in hippocampal slice cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 6166–6171 (2005).
Kullmann, D.M. & Asztely, F. Extrasynaptic glutamate spillover in the hippocampus: evidence and implications. Trends Neurosci. 21, 8–14 (1998).
Harris, K.M. How multiple-synapse boutons could preserve input specificity during an interneuronal spread of LTP. Trends Neurosci. 18, 365–369 (1995).
Chklovskii, D.B., Mel, B.W. & Svoboda, K. Cortical rewiring and information storage. Nature 431, 782–788 (2004).
Schmidt-Hieber, C., Jonas, P. & Bischofberger, J. Enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated granule cells of the adult hippocampus. Nature 429, 184–187 (2004).
Jessberger, S. & Kempermann, G. Adult-born hippocampal neurons mature into activity-dependent responsiveness. Eur. J. Neurosci. 18, 2707–2712 (2003).
De Paola, V. et al. Cell type-specific structural plasticity of axonal branches and boutons in the adult neocortex. Neuron 49, 861–875 (2006).
Shepherd, G.M. & Harris, K.M. Three-dimensional structure and composition of CA3→CA1 axons in rat hippocampal slices: implications for presynaptic connectivity and compartmentalization. J. Neurosci. 18, 8300–8310 (1998).
Toni, N., Buchs, P.A., Nikonenko, I., Bron, C.R. & Muller, D. LTP promotes formation of multiple spine synapses between a single axon terminal and a dendrite. Nature 402, 421–425 (1999).
Geinisman, Y., Berry, R.W., Disterhoft, J.F., Power, J.M. & Van der Zee, E.A. Associative learning elicits the formation of multiple-synapse boutons. J. Neurosci. 21, 5568–5573 (2001).
Friedlander, M.J., Martin, K.A. & Wassenhove-McCarthy, D. Effects of monocular visual deprivation on geniculocortical innervation of area 18 in cat. J. Neurosci. 11, 3268–3288 (1991).
Consiglio, A. et al. Robust in vivo gene transfer into adult mammalian neural stem cells by lentiviral vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 14835–14840 (2004).
van Praag, H., Christie, B.R., Sejnowski, T.J. & Gage, F.H. Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13427–13431 (1999).
Kempermann, G., Kuhn, H.G. & Gage, F.H. Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10409–10414 (1997).
Capani, F., Martone, M.E., Deerinck, T.J. & Ellisman, M.H. Selective localization of high concentrations of F-actin in subpopulations of dendritic spines in rat central nervous system: a three-dimensional electron microscopic study. J. Comp. Neurol. 435, 156–170 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Harris and J. Fiala for 3D reconstruction software (http://www.synapses.bu.edu), R. Tsien (University of California, San Diego) for the gift of mRFP1, Y. Jones and J. Jepsen for technical assistance, J. Simon for artwork, and T. Shikorski and M.L. Gage for comments on the manuscript. N.T. is supported by the Human Science Frontier Program Organization and the Swiss National Science Foundation, F.H.G. is supported by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) NS050217-02, and a research grant from the Picower and the Lookout Foundations. Some of this work was conducted at the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research supported by NIH RRP41-04050 to M.H.E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.T. conceived the study, performed the experiments, analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript. E.M.T. helped with confocal microscopy and electron tomography data collection and analyses. E.A.B. provided technical expertise for intracellular injections. J.B.A. provided help with the filopodia study. C.Z. performed the live imaging experiment. A.C. provided the lentivirus. H.v.P. provided the Moloney virus construct and technical expertise. M.E.M. contributed to the analyses of the tomography data. M.H.E. contributed to the tomography experiment and provided support for all the electron microscopy experiments. F.H.G. discussed the experiments and the data, revised the manuscript and provided financial support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Dendritic spines from new neurons are apposed to perforant path axonal boutons. (PDF 19885 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toni, N., Teng, E., Bushong, E. et al. Synapse formation on neurons born in the adult hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 10, 727–734 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1908
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1908
This article is cited by
-
Bioinspired nanofluidic iontronics for brain-like computing
Nano Research (2024)
-
Prolonged fixation and post-mortem delay impede the study of adult neurogenesis in mice
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Engram neurons: Encoding, consolidation, retrieval, and forgetting of memory
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Effect of adult-born immature granule cells on pattern separation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus
Cognitive Neurodynamics (2023)
-
GSK-3β orchestrates the inhibitory innervation of adult-born dentate granule cells in vivo
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)