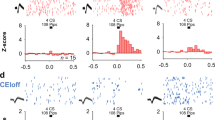
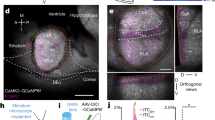
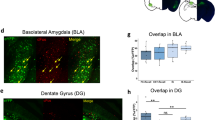
Abstract
Switching between exploratory and defensive behaviour is fundamental to survival of many animals, but how this transition is achieved by specific neuronal circuits is not known. Here, using the converse behavioural states of fear extinction and its context-dependent renewal as a model in mice, we show that bi-directional transitions between states of high and low fear are triggered by a rapid switch in the balance of activity between two distinct populations of basal amygdala neurons. These two populations are integrated into discrete neuronal circuits differentially connected with the hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex. Targeted and reversible neuronal inactivation of the basal amygdala prevents behavioural changes without affecting memory or expression of behaviour. Our findings indicate that switching between distinct behavioural states can be triggered by selective activation of specific neuronal circuits integrating sensory and contextual information. These observations provide a new framework for understanding context-dependent changes of fear behaviour.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quirk, G. J., Repa, C. & LeDoux, J. E. Fear conditioning enhances short-latency auditory responses of lateral amygdala neurons: parallel recordings in the freely behaving rat. Neuron 15, 1029–1039 (1995)
Collins, D. R. & Paré, D. Differential fear conditioning induces reciprocal changes in the sensory responses of lateral amygdala neurons to the CS(+) and CS(-). Learn. Mem. 7, 97–103 (2000)
Rosenkranz, J. A. & Grace, A. A. Dopamine-mediated modulation of odour-evoked amygdala potentials during Pavlovian conditioning. Nature 417, 282–287 (2002)
Goosens, K. A., Hobin, J. A. & Maren, S. Auditory-evoked spike firing in the lateral amygdala and Pavlovian fear conditioning: mnemonic code or fear bias? Neuron 40, 1013–1022 (2003)
LeDoux, J. E. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23, 155–184 (2000)
Maren, S. & Quirk, G. J. Neuronal signaling of fear memory. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 5, 844–852 (2004)
Quirk, G. J., Russo, G. K., Barron, J. L. & Lebron, K. The role of ventromedial prefrontal cortex in the recovery of extinguished fear. J. Neurosci. 20, 6225–6231 (2000)
Milad, M. R. & Quirk, G. J. Neurons in medial prefrontal cortex signal memory for fear extinction. Nature 420, 70–74 (2002)
Rosenkranz, J. A., Moore, H. & Grace, A. A. The prefrontal cortex regulates lateral amygdala neuronal plasticity and responses to previously conditioned stimuli. J. Neurosci. 23, 11054–11064 (2003)
Berretta, S., Pantazopoulos, H., Caldera, M., Pantazopoulos, P. & Paré, D. Infralimbic cortex activation increases c-Fos expression in intercalated neurons of the amygdala. Neuroscience 132, 943–953 (2005)
Paré, D., Quirk, G. J. & LeDoux, J. E. New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. J. Neurophysiol. 92, 1–9 (2004)
Falls, W. A., Miserendino, M. J. & Davis, M. Extinction of fear-potentiated startle: blockade by infusion of an NMDA antagonist into the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 12, 854–863 (1992)
Lu, K. T., Walker, D. L. & Davis, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in the basolateral nucleus of amygdala is involved in extinction of fear-potentiated startle. J. Neurosci. 21, RC162 (2001)
Herry, C., Trifilieff, P., Micheau, J., Lüthi, A. & Mons, N. Extinction of auditory fear conditioning requires MAPK/ERK activation in the basolateral amygdala. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 261–269 (2006)
Sotres-Bayon, F., Bush, D. E. & LeDoux, J. E. Acquisition of fear extinction requires activation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the lateral amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 32, 1929–1940 (2007)
Quirk, G. J., Garcia, R. & Gonzalez-Lima, F. Prefrontal mechanisms in extinction of conditioned fear. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 337–343 (2006)
Myers, K. M. & Davis, M. Mechanisms of fear extinction. Mol. Psychiatry 12, 120–150 (2007)
Bouton, M. E. Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: Sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol. Psychiatry 52, 976–986 (2002)
Bouton, M. E., Westbrook, R. F., Corcoran, K. A. & Maren, S. Contextual and temporal modulation of extinction: Behavioral and biological mechanisms. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 352–360 (2006)
Pitkänen, A., Pikkarainen, M., Nurminen, N. & Ylinen, A. Reciprocal connections between the amygdala and the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, and postrhinal cortex in rat. A review. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 911, 369–391 (2000)
Corcoran, K. A. & Maren, S. Hippocampal inactivation disrupts contextual retrieval of fear memory after extinction. J. Neurosci. 21, 1720–1726 (2001)
Corcoran, K. A., Desmond, T. J., Frey, K. A. & Maren, S. Hippocampal inactivation disrupts the acquisition and contextual encoding of fear extinction. J. Neurosci. 25, 8978–8987 (2005)
Hobin, J. A., Ji, J. & Maren, S. Ventral hippocampal muscimol disrupts context-specific fear memory retrieval after extinction in rats. Hippocampus 16, 174–182 (2006)
McDonald, A. J. Organization of amygdaloid projections to the prefrontal cortex and associated striatum in the rat. Neuroscience 44, 1–14 (1991)
McDonald, A. J., Mascagni, F. & Guo, L. Projections of the medial and lateral prefrontal cortices to the amygdala: a Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin study in the rat. Neuroscience 71, 55–75 (1996)
Herry, C. & Mons, N. Resistance to extinction is associated with impaired immediate early gene induction in medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 781–790 (2004)
Muramoto, K., Ono, T., Nishijo, H. & Fukuda, M. Rat amygdaloid neuron responses during auditory discrimination. Neuroscience 52, 621–636 (1993)
Maren, S., Poremba, A. & Gabriel, M. Basolateral amygdaloid multi-unit neuronal correlates of discriminative avoidance learning in rabbits. Brain Res. 549, 311–316 (1991)
Repa, J. C. et al. Two different lateral amygdala cell populations contribute to the initiation and storage of memory. Nature Neurosci. 4, 724–731 (2001)
Gallistel, C. R., Fairhurst, S. & Balsam, P. The learning curve: Implications of a quantitative analysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 13124–13131 (2004)
Herry, C. & Garcia, R. Prefrontal cortex long-term potentiation, but not long-term depression, is associated with the maintenance of extinction of learned fear in mice. J. Neurosci. 22, 577–583 (2002)
Likhtik, E., Pelletier, J. G., Popescu, A. T. & Paré, D. Identification of basolateral amygdala projection cells and interneurons using extracellular recordings. J. Neurophysiol. 96, 3257–3265 (2006)
Stalnaker, T. A., Franz, T. M., Singh, T. & Schoenbaum, G. Basolateral amygdala lesions abolish orbitofrontal-dependent reversal impairments. Neuron 54, 51–58 (2007)
Stalnaker, T. A. et al. Cocaine-induced decision-making deficits are mediated by miscoding in basolateral amygdala. Nature Neurosci. 10, 949–951 (2007)
Paré, D. Role of the basolateral amygdala in memory consolidation. Prog. Neurobiol. 70, 409–420 (2003)
McGaugh, J. L. The amygdala modulates the consolidation of memories of emotionally arousing experiences. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 1–28 (2004)
Paz, R., Pelletier, J. G., Bauer, E. P. & Paré, D. Emotional enhancement of memory via amygdala-driven facilitation of rhinal interactions. Nature Neurosci. 9, 1321–1329 (2006)
Amorapanth, P., LeDoux, J. E. & Nader, K. Different lateral amygdala outputs mediate reactions and actions elicited by a fear-arousing stimulus. Nature Neurosci. 3, 74–79 (2000)
Nader, K., Majidishad, P., Amorapanth, P. & LeDoux, J. E. Damage to the lateral and central, but not other, amygdaloid nuclei prevents the acquisition of auditory fear conditioning. Learn. Mem. 8, 156–163 (2001)
Sotres-Bayon, F., Bush, D. E. & LeDoux, J. E. Emotional perseveration: an update on prefrontal-amygdala interactions in fear extinction. Learn. Mem. 11, 525–535 (2004)
Anglada-Figueroa, D. & Quirk, G. J. Lesions of the basal amygdala block expression of conditioned fear but not extinction. J. Neurosci. 25, 9680–9685 (2005)
Goosens, K. A. & Maren, S. Contextual and auditory fear conditioning are mediated by the lateral, basal, and central amygdaloid nuclei in rats. Learn. Mem. 8, 148–155 (2001)
Jing, J. & Gillette, R. Escape swim network interneurons have diverse roles in behavioral switching and putative arousal in Pleurobranchanea . J. Neurophysiol. 83, 1346–1355 (2000)
Yapici, N., Kim, Y.-J., Ribeiro, C. & Dickson, B. J. A receptor that mediates the post-mating switch in Drosophila reproductive behavior. Nature 451, 33–37 (2007)
Milad, M. R., Orr, S. P., Pitman, R. K. & Rauch, S. L. Context modulation of memory for fear extinction in humans. Psychophysiology 42, 456–464 (2005)
Rodriguez, B. I., Craske, M. G., Mineka, S. & Hladek, D. Context-specificity of relapse: effects of therapist and environmental context on return of fear. Behav. Res. Ther. 37, 845–862 (1999)
Herry, C. et al. Processing of temporal unpredictability in human and animal amygdala. J. Neurosci. 27, 5958–5966 (2007)
Nicolelis, M. A. L. et al. Chronic, multisite, multielectrode recordings in macaque monkeys. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 11041–11046 (2003)
Jackson, A. & Fetz, E. E. Compact movable microwire array for long-term chronic unit recordings in cerebral cortex of primates. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 3109–3118 (2007)
Franklin, K. J. B. & Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic, 1997)
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Friedrich, A. Matus and all members of the Lüthi laboratory for discussions and critical comments on the manuscript and E. Oakeley and M. Stadler for advice on statistical analysis and programming. This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF), the Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research, and the Novartis Research Foundation.
Author Contributions C.H., S.C., V.S., L.D. and C.M. performed the experiments and analysed the data. C.H., S.C. and A.L. designed the experiments and wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information 1
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-9 with Legends. (PDF 1534 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herry, C., Ciocchi, S., Senn, V. et al. Switching on and off fear by distinct neuronal circuits. Nature 454, 600–606 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07166
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07166
This article is cited by
-
The amygdala NT3-TrkC pathway underlies inter-individual differences in fear extinction and related synaptic plasticity
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
-
Inhibition of fatty acid binding protein-5 in the basolateral amygdala induces anxiolytic effects and accelerates fear memory extinction
Psychopharmacology (2024)
-
Activity-dependent organization of prefrontal hub-networks for associative learning and signal transformation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Topographic representation of current and future threats in the mouse nociceptive amygdala
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Closed-loop brain stimulation augments fear extinction in male rats
Nature Communications (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.