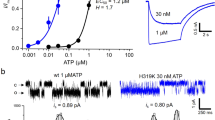
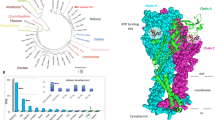
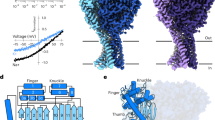
Abstract
THE adenosine-5′-triphosphate (ATP) molecule is an extracellular messenger in neural and non-neural tissues, where it activates several cell-surface-receptor subtypes, including G-protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels1. ATP-gated channels (termed P2X receptors) have been characterized on smooth muscle cells and autonomic and sensory neurons, where they mediate membrane depolarization and, in some cases, Ca2+ entry2. P2x receptors are functionally heterogeneous, but resemble acetylcholine-and serotonin-gated channels with respect to ion selectivity and kinetic parameters of channel gating. We report here that despite such close functional similarities, the deduced sequence of a cloned P2x receptor predicts an unusual subunit structure resembling voltage-insensitive cation channels. Thus, the P2x receptor provides a striking example of convergent evolution, whereby proteins have been fashioned with similar functional properties from subunits having very different structural characteristics. There is sequence similarity between the ATP receptor and RP-2, a gene activated in thymocytes undergoing programmed cell death3. RP-2 may encode a receptor for ATP or another metabolite released during apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock, G. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 603, 1–18 (1990).
Bean, B. P. Trends pharmac. Sci. 13, 87–90 (1992).
Owens, G. P., Hahn, W. E. & Cohen, J. J. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 4177–4188 (1991).
Nakazawa, K., Fujimori, K., Takanaka, A. & Inoue, K. J. Physiol. 428, 257–272 (1990).
Nakazawa, K., Inoue, K., Fujimori, K. & Takanaka, A. Neurosci. Lett. 119, 5–8 (1990).
Majid, M. A., Okajima, F. & Kondo, Y. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1136, 283–289 (1992).
Nakazawa, K. & Hess, P. J. gen. Physiol. 101, 377–392 (1993).
Fieber, L. A. & Adams, D. J. J. Physiol. 434, 239–256 (1991).
Cloues, R., Jones, S. & Brown, D. A. Pflug. Archiv. 424, 152–158 (1993).
Friel, D. D. J. Physiol. 401, 361–380 (1988).
Edwards, F. A., Gibb, A. J. & Colquhoun, D. Nature 359, 144–147 (1992).
Evans, R. J., Derkach, V. & Surprenant, A. Nature 357, 503–505 (1992).
Silinsky, E. M., Gerzanich, V. & Vanner, S. M. Br. J. Pharmac. 106, 762–763 (1993).
Benham, C. D. & Tsien, R. W. Nature 328, 275–278 (1987).
Nakazawa, K., Inoue, K., Fujimori, K. & Takanaka, A. Pflug. Archiv. 418, 214–219 (1991).
Li, C., Peoples, R. W., Li, Z. & Weight, F. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 8264–8267 (1993).
Canessa, C. M. et al. Nature 367, 463–467 (1994).
Ho, K. et al. Nature 362, 31–38 (1993).
Hong, K. & Driscoll, M. Nature 367, 470–473 (1994).
Huang, M. & Chalfie, M. Nature 367, 467–470 (1994).
Kubo, Y., Baldwin, T. J., Jan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Nature 362, 127–133 (1993).
Suzuki, M. et al. Nature 367, 642–645 (1994).
Unwin, N. Cell. 72, (suppl.) 31–41 (1993).
Saraste, M., Sibbald, P. R. & Wittinghofer, A. Trends biochem. Sci. 15, 430–434 (1990).
Li, M., Unwin, N., Staufer, K. A., Jan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Curr. Biol. 4, 110–115 (1994).
Thomas, S. A. & Hulme, R. I. J. gen. Physiol. 95, 569–590 (1990).
Friel, D. D. & Bean, B. P. Pflug. Archiv. 415, 651–657 (1990).
Maricq, A. V., Peterson, A. S., Brake, A. J., Myers, R. M. & Julius, D. Science 254, 432–437 (1991).
Tecott, L. H., Maricq, A. V. & Julius, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1430–1434 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brake, A., Wagenbach, M. & Julius, D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature 371, 519–523 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/371519a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/371519a0
This article is cited by
-
From purines to purinergic signalling: molecular functions and human diseases
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
ATP signaling in the integrative neural center of Aplysia californica
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Burnstock and the legacy of the inhibitory junction potential and P2Y1 receptors
Purinergic Signalling (2021)
-
Purinergic signalling in the cardiovascular system—a tribute to Geoffrey Burnstock
Purinergic Signalling (2021)
-
P2X3-Receptor Antagonists as Potential Antitussives: Summary of Current Clinical Trials in Chronic Cough
Lung (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.