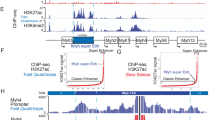
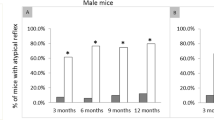
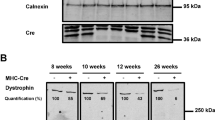
Abstract
HUNDREDS of murine dilute mutations have been identified and analysed, making dilute one of the best genetically characterized of all mammalian loci. The recessive dilute (d) coat colour mutation carried by many inbred strains of mice produces a lightening of coat colour, caused by an abnormal adendritic melanocyte morphology that results in an uneven release of pigment granules into the developing hair shaft1,2. Most dilute alleles (dilute-lethal) also produce a neurological defect, characterized by convulsions and opisthotonus, apparent at 8–10 days of age and continuing until the death of the animal at 2–3 weeks of age3. The discovery that the original dilute allele (now termed dilute-viral or dv) is the result of the integration of an ecotropic murine leukaemia provirus4 has allowed the cloning of genomic DNA5,6 and in this study complementary DNA, from the dilute locus. The predicted dilute amino-acid sequence indicates that dilute encodes a novel type of myosin heavy chain, with a tail, or C-terminal, region that has elements of both type II (α-helical coiled-coil) and type I (non-coiled-coil) myosin heavy chains. Dilute transcipts are differentially expressed in both embryonic and adult tissues and are very abundant in neurons of the central nervous system, cephalicganglia, and spinal ganglia. These results suggest an important role for the dilute gene product in the elaboration, maintenance, or function of cellular processes of melanocytes and neurons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell, E. S. Genetics 34, 146–166 (1949).
Markert, C. L. & Silvers, W. K. Genetics 41, 429–450 (1956).
Searle, A. G. Heredity 6, 395–401 (1952).
Jenkins, N. A., Copeland, N. G., Taylor, B. A. & Lee, B. K. Nature 293, 370–374 (1981).
Copeland, N. G., Hutchison, K. W. & Jenkins, N. A. Cell 33, 379–387 (1983).
Strobel, M. C., Seperack, P. K., Copeland, N. G. & Jenkins, N. A. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 501–509 (1990).
Kiehart, D. P. Cell 60, 347–350 (1990).
Fukui, Y., Lynch, T. J., Brzeska, H. & Korn, E. D. Nature 341, 328–331 (1989).
Korn, E. D. & Hammer, J. A. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2, 57–61 (1990).
Garcia, A. et al. J. Cell Biol. 109, 2895–2903 (1989).
Hoshimaru, M. & Nakanishi, S. J. biol. Chem. 262, 14625–14632 (1987).
Coluccio, L. M. & Bretscher, A. J. Cell Biol. 105, 325–333 (1987).
Conzelman, K. A. & Mooseker, M. S. J. Cell Biol. 105, 313–324 (1987).
Hoshimaru, M., Fujio, Y., Sobue, K., Sugimoto, T. & Nakanishi, S. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 106, 455–459 (1989).
Hayden, S. M., Wolenski, J. S. & Mooseker, M. S. J. Cell Biol. 111, 443–451 (1990).
Mitchell, E. J. et al. J. molec. Biol. 208, 199–205 (1989).
Cohen, C. & Parry, D. A. Proteins 7, 1–15 (1990).
Mitchison, T. & Kirschner, M. Neuron 1, 761–772 (1988).
Smith, S. J. Science 242, 708–715 (1988).
Sheetz, M. P., Baumrind, N. L., Wayne, D. B. & Pearlman, A. L. Cell 61, 231–241 (1990).
Bray, D. & Vasiliev, J. Nature 338, 203–204 (1989).
Jung, G. & Hammer, J. A. J. Cell Biol. 110, 1955–1964 (1990).
Moore, K. J. et al. Genetics 119, 933–941 (1988).
Moore, K. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 8131–8135 (1988).
Gyllensten, U. B. & Erlich, H. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 7652–7656 (1988).
Shohet, R. V. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 7726–7730 (1989).
Strehler, E. E., Strehler, P. M., Perriard, J. C., Periasamy, M. & Nadal-Ginard, B. J. molec. Biol. 190, 291–317 (1986).
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P. & Smithies, O. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 387–395 (1984).
Warrick, H. M., DeLozanne, A., Leinwand, L. A. & Spudich, J. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 9433–9437 (1986).
Takahashi, N., Roach, A., Teplow, D. B., Prusiner, S. B. & Hood, L. Cell 42, 139–148 (1985).
Haase, A. T. et al. Virology 119, 399–410 (1982).
Martin-Zanca, D., Barbacid, M. & Parada, L. F. Genes Dev. 4, 683–694 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercer, J., Seperack, P., Strobel, M. et al. Novel myosin heavy chain encoded by murine dilute coat colour locus. Nature 349, 709–713 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/349709a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/349709a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.