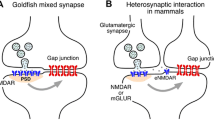
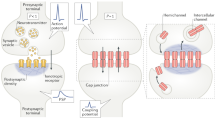
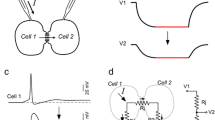
Abstract
Gap junctions are the morphological substrate of one class of electrical synapse. The history of the debate on electrical vs. chemical transmission is instructive. One lesson is that Occam’s razor sometimes cuts too deep; the nervous system does its operations in a number of different ways and a unitarian approach can lead one astray. Electrical synapses can do many things that chemical synapses can do, and do them just as slowly. More intriguing are the modulatory actions that chemical synapses can have on electrical synapses. Voltage dependence provides an important window on structure function relations of the connexins, even where the dependence may have no physiological role. The new molecular approaches will greatly advance our knowledge of where gap junctions occur and permit experimental manipulation with high specificity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auerbach, A. A. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1969a) Chemically mediated transmission at a giant fibre synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. Journal of General Physiology 53, 183–210.
Auerbach, A. A. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1969b) A rectifying electrotonic synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. Journal of General Physiology 53, 211–37.
Baker, R. & Llinas, R. (1971) Electronic coupling between neurons in the rat mesencephalic nucleus. Journal of Physiology 212, 45–63.
Barnes, T. M. (1994) OPUS: a growing family of gap junction proteins? Trends in Genetics 10, 303–5.
Barrio, L. C., Suchyna, T., Bargiello, T., Xu, L. X., Roginski, R. S., Bennett, M. V. L. & Nicholson, B. J. (1991) Gap junctions formed by connexins 26 and 32 alone and in combination are differently affected by applied voltage [published erratum appears in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 1992 May 1, 4220]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 88, 8410–14.
Bennett, M. V. L., Zheng, X. & Sogin, M. L. (1994) The connexins and their family tree. Society of General Physiologists Series 49, 223–33.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1966) Physiology of electronic junctions. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 137, 509–39.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1968) Neural control of electric organs. In The Central Nervous System and Fish Behavior (edited by Ingle, D.) pp. 147–69. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1971) Electric organs. In Fish Physiology (edited by Hoar, W. S. & Randall, D. J.) pp. 347–491. New York: Academic Press.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1977) Electrical transmission: a functional analysis and comparison to chemical transmission. In The Handbook of Physiology – The Nervous System I (edited by Kandel, E. R.) pp. 357–416. Washington: American Physiological Society.
Bennett, M. V. L. (1985) Nicked by Occam's razor: unitarianism in the investigation of synaptic transmission. Biological Bulletin 168, 159–67.
Bennett, M. V. L., Barrio, L. C., Bargiello, T. A., Spray, D. C., Hertzberg, E. & Saez, J. C. (1991) Gap junctions: new tools, new answers, new questions. Neuron 6, 305–20.
Bennett, M. V. L., Crain, S. M. & Grundfest, H. (1959a) Electrophysiology of supramedullary neurons in Spheroides maculatus. I. Orthodromic and antidromic responses. Journal of General Physiology 43, 159–88.
Bennett, M. V. L., Crain, S. M. & Grundfest, H. (1959b) Electrophysiology of supramedullary neurons in Spheroides maculatus. III. Organization of the supramedullary neurons. Journal of General Physiology 43, 221–50.
Bennett, M. V. L., Nakjima, Y. & Pappas, G. D. (1967a) Physiology and ultrastructure of electrotonic junctions. I. Supramedullary neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology 30, 161–79.
Bennett, M. V. L., Nakajima, Y. & Pappas, G. D. (1967b) Physiology and ultrastructure of electrotonic junctions. III. Giant electromotor neurons of Malapterurus electricus. Journal of Neurophysiology 30, 209–35.
Bennett, M. V. L. & Pappas, G. D. (1983) The electromotor system of the stargazer: a model for integrative actions at electrotonic synapses. Journal of Neuroscience 3, 748–61.
Bennett, M. V. L., Verselis, V., White, R. L. & Spray, D. C. (1988) Gap junctional conductance: Gating. In Gap Junctions (edited by Hertzberg, E. L. & Johnson, R. G.) pp. 287–304. New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.
Blackshaw, S. E. & Warner, A. E. (1976) Alterations in resting membrane properties during neural plate stages of development of the nervous system. Journal of Physiology 255, 231–47.
Bodian, D. (1938) The structure of the vertebrate synapse. A study of the axon endings on Mauthner's cell and neighboring centers in the goldfish. Journal of Comparative Neurology 68, 117–59.
Bukauskas, F. F., Elfgang, C., Willecke, K. & Weingart, R. (1995) Heterotypic gap junction channels (connexin26-connexin32) violate the paradigm of unitary conductance. Pflüger's Archiv 429, 870–2.
Burt, J. M. & Spray, D. C. (1989) Volatile anesthetics block intercellular communication between neonatal rat myocardial cells. Circulation Research 65, 829–37.
Calakos, N. & Scheller, R. H. (1996) Synaptic vesicle biogenesis, docking, and fusion: a molecular description. Physiological Reviews 76, 1–29.
Carr, C. E. & Boudreau, R. E. (1993) Organization of the nucleus magnocellularis and the nucleus laminaris in the barn owl: encoding and measuring interaural time differences. Journal of Comparative Neurology 334, 337–55.
Chang, M., Dahl, C. & Werner, R. (1994) Is the role of connexin 33 an inhibitory one? Biophysical Journal 66, A20.
Christensen, B. N. (1983) Distribution of electrotonic synapses on identified lamprey neurons: a comparison of a model prediction with an electron microscopic analysis. Journal of Neurophysiology 49, 705–16.
Dani, J. W. & Smith, S. J. (1995) The triggering of astrocytic calcium waves by NMDA-induced neuronal activation. Ciba Foundation Symposia 188, 195–205.
Dowling, J. E. (1991) Retinal neuromodulation: the role of dopamine. Visual Neuroscience 7, 87–97.
Dudek, F. E., Snow, R. W. & Taylor, C. P. (1986) Role of electrical interactions in synchronization of epileptiform bursts. Advances in Neurology 44, 593–617.
Eccles, J. C. (1964) The Physiology of Synapses. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Ek, J. F., Delmar, M., Perzova, R. & Taffet, S. M. (1994) Role of histidine 95 on pH gating of the cardiac gap junction protein connexin43. Circulation Research 74, 1058–64.
Elfgang, C., Eckert, R., Lichtenberg-Frate, H., Butterweck, A., Traub, O., Klein, R. A., Hulser, D. F. & Willecke, K. (1995) Specific permeability and selective formation of gap junction channels in connexin-transfected HeLa cells. Journal of Cell Biology 129, 805–17.
Faber, D. S. & Korn, H. (1989) Electrical field effects: their relevance in central neural networks. Physiological Reviews 69, 821–63.
Fatt, P. (1954) Biophysics of junctional transmission. Physiological Reviews 34, 674–710.
Furshpan, E. J. & Furukawa, T. (1962) Intracellular and extracellular responses of the several regions of the Mauthner cell of the goldfish. Journal of Neurophysiology 25, 732–71.
Furshpan, E. J. & Potter, D. D. (1959) Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. Journal of Physiology 145, 289–325.
Furukawa, T. & Furshpan, E. J. (1993) Two inhibitory mechanisms in the Mauthner neurons of goldfish. Journal of Neurophysiology 26, 140–76.
Goliger, J. A. & Paul, D. L. (1994) Expression of gap junction proteins Cx26, Cx31.1, Cx37, and Cx43 in developing and mature rat epidermis. Developmental Dynamics 200, 1–13.
Hall, D. H., Gilat, E. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1985) Ultrastructure of the rectifying electronic synapses between giant fibres and pectoral fin adductor motor neurons in the hatchetfish. Journal of Neurocytology 14, 825–34.
Hampson, E. C., Weiler, R. & Vaney, D. I. (1994) pH-gated dopaminergic modulation of horizontal cell gap junctions in mammalian retina. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series B 255, 67–72.
Harris, A. L., Spray, D. C. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1981) Kinetic properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. Journal of General Physiology 77, 95–117.
Harris, A. L., Spray, D. C. & Bennett, M. V. (1983) Control of intercellular communication by voltage dependence of gap junctional conductance. Journal of Neuroscience 3, 79–100.
Hassinger, T. D., Guthrie, P. B., Atkinson, P. B., Bennett, M. V. L. & Kater, S. B. (1996) An extracellular signalling component in propagation of astrocytic calcium waves. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 93, 13268–72.
Hatton, G. I. & Yang, Q. Z. (1994) Incidence of neuronal coupling in supraoptic nuclei of virgin and lactating rats: estimation by neurobiotin and lucifer yellow. Brain Research 650, 63–9.
Hinrichsen, C. F. L. & Larramendi, L. M. H. (1968) Synapses and cluster formation of the mouse memsecephalic fifth nucleus. Brain Research 7, 296–99.
Jefferys, J. G. R. (1995) Nonsynaptic modulation of neuronal activity in the brain: electric currents and extracellular ions. [Review]. Physiological Review 75, 689–723.
Johnston, M. F., Simon, S. A. & Ramon, F. (1980) Interaction of anaesthetics with electrical synapses. Nature 286, 498–500.
Knier, J., Verselis, V. K. & Spray, D. C. (1986) Gap junctions between tunicate blastomeres: gating similarities and differences compared to amphibia. Biophysical Journal 49, 203a.
Korn, H. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1975) Vestibular nystagmus and teleost oculomotor neurons: functions of electrotonic coupling and dendritic impulse initiation. Journal of Neurophysiology 38, 430–51.
Korn, H., Sotelo, C & Crepel, F. (1973) Electronic coupling between neurons in the rat lateral vestibular nucleus. Experimental Brain Research 16, 255–75.
Kriebel, M. E., Bennett, M. V. L., Waxman, S. G. & Pappas, G. D. (1969) Oculomotor neurons in fish: electrotonic coupling and multiple sites of impulse initiation. Science 166, 520–4.
Lin, J. W. & Faber, D. S. (1988) Synaptic transmission mediated by single club endings on the goldfish Mauthner cell. I. Characteristics of electrotonic and chemical postsynaptic potentials. Journal of Neuroscience 8, 1302–12.
Llinas, R., Baker, R. & Sotelo, C. (1974) Electrotonic coupling between neurons in cat inferior olive. Journal of Neurophysiology 37, 560–71.
Martin, A. R. & Pilar, G. (1963) Dual mode of synaptic transmission in the avian ciliary ganglion. Journal of Physiology 168, 443–63.
Meszler, R. M., Pappas, G. D. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1974) Morphology of the electromotor system in the spinal cord of the electric eel, Electrophorus electricus. Journal of Neurocytology 251–61.
Meyer, R. A., Laird, D. W., Revel, J. P. & Johnson, R. G. (1992) Inhibition of gap junction and adherens junction assembly by connexin and A-CAM antibodies. Journal of Cell Biology 119, 179–89.
Moore, L. K. & Burt, J. M. (1994) Selective block of gap junction channel expression with connexin-specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. American Journal of Physiology 267, C1371–80.
Moreno, A. P., Rook, M. B., Fishman, G. I. & Spray, D. C. (1994) Gap junction channels: distinct voltagesensitive and-insensitive conductance states. Biophysical Journal 67, 113–19.
Mushegian, A. R. & Koonin, E. V. (1993) The proposed plant connexin is a protein kinase-like protein [letter]. Plant Cell 5, 998–9.
Nelles, E., BÜtzler, C., Jung, D., Temme, A., Gabriel, H.-D., Dahl, U., Traub, O., StÜmpel, F., Jungermann, K., Zielasek, J., Toyka, K. V., Dermietzel, R. & Willecke, K. (1996) Defective propagation of signals generated by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the liver of connexin32-deficient mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 93, 9565–70.
Neyton, J. & Trautmann, A. (1985) Single-channel currents of an intercellular junction. Nature 317, 331–5.
Oliveira-Castro, G. M. & Loewenstein, W. R. (1971) Junctional membrane permeability. Effects of divalent cations. Journal of Membrane Biology 5, 51–77.
Osipchuk, Y. & Cahalan, M. (1992) Cell-to-cell spread of calcium signals mediated by ATP receptors in mast cells. Nature 359, 241–4.
Pappas, G. D. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1986) Specialized junctions involved in electrical transmission between neurons. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 137, 495–508.
Peinado, A., Yuste, R. & Katz, L. C. (1993) Extensive dye coupling between rat neocortical neurons during the period of circuit formation. Neuron 10, 103–14.
Pereda, A. E. & Faber, D. S. (1996) Activity-dependent short-term enhancement of intercellular coupling. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 983–92.
Perez-Armendariz, E. M., Romano, M. C., Luna, J., Miranda, C., Bennett, M. V. L & Moreno, A. P. (1994) Characterization of gap junctions between pairs of Leydig cells from mouse testis. American Journal of Physiology 267, C570–80.
Piccolino, M., Neyton, J. & Gerschenfeld, H. M. (1984) Decrease of gap junction permeability induced by dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in horizontal cells of turtle retina. Journal of Neuroscience 4, 2477–88.
Pinching, A. J. & Powell, T. P. S. (1971) The neuropil of the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Cell Science 9, 347–77.
Rash, J. E., Dillman, R. K., Bilhartz, B. L., Duffy, H. S., Whalen, L. R. & Yasumura, T. (1996) Mixed synapses discovered and mapped throughout mammalian spinal cord. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 93, 4235–9.
Reaume, A. G., de Sousa, P. A., Kulkarni, S., Langille, B. L., Zhu, D., Davies, T. C., Juneja, S. C., Kidder, G. M. & Rossant, J. (1995) Cardiac malformation in neonatal mice lacking connexin43. Science 267, 1831–4.
Reed, K. E., Westphale, E. M., Larson, D. M., Wang, H. Z., Veenstra, R. D. & Beyer, E. C. (1993) Molecular cloning and functional expression of human connexin37, an endothelial cell gap junction protein. Journal of Clinical Investigation 91, 997–1004.
Rorig, B., Klausa, G. & Sutor, B. (1995) Dye coupling between pyramidal neurons in developing rat prefrontal and frontal cortex is reduced by protein kinase A activation and dopamine. Journal of Neuroscience 15, 7386–400.
Saez, J. C., Connor, J. A., Spray, D. C. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1989) Hepatocyte gap junctions are permeable to the second messenger, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, and to calcium ions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 86, 2708–12.
Saez, J. C., Nairn, A. C., Czernik, A. J., Spray, D. C., Hertzberg, E. L., Greengard, P. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1990) Phosphorylation of connexin 32, a hepatocyte gap-junction protein, by cAMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulindependent protein kinase II. European Journal of Biochemistry 192, 263–73.
Sanderson, M. J. (1995) Intracellular calcium waves mediated by inositol trisphosphate. Ciba Foundation Symposia 188, 175–89.
Silva, A., Kumar, S., Pereda, A. & Faber, D. S. (1995) Regulation of synaptic strength at mixed synapses: effects of dopamine receptor blockade and protein kinase C activation. Neuropharmacology 34, 1559–65.
Sloper, J. J. (1972) Gap junctions between dendrites in the primate neocortex. Brain Research 44, 641–6.
Sotelo, C. & Llinas, R. (1972) Specialized membrane junctions between neurons in vertebrate cerebellar cortex. Journal of Cell Biology 53, 271–89.
Spira, M. E. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1972) Synaptic control of electrotonic coupling between neurons. Brain Research 37, 294–300.
Spira, M. E., Spray, D. C. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1980) Synaptic organization of expansion motoneurons of Navanax inermis. Brain Research 195, 241–69.
Spray, D. C., Harris, A. L. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1981a) Equilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. Journal of General Physiology 77, 77–93.
Spray, D. C., Harris, A. L. & Bennett, M. V. L. (1981b) Gap junctional conductance is a simple and sensitive function of intracellular pH. Science 211, 712–15.
Stauffer, K. A. (1995) The gap junction proteins beta 1-connexin (connexin-32) and beta 2-connexin (connexin-26) can form heteromeric hemichannels. Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 6768–72.
Teranishi, T., Negishi, K. & Kato, S. (1983) Dopamine modulates S-potential amplitude and dye-coupling between external horizontal cells in carp retina. Nature 301, 243–6.
Trexler, E. B., Bennett, M. V. L., Bargiello, T. A. & Verselis, V. K. (1996) Voltage gating and permeation in a gap junction hemichannel. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 93, 5836–41.
Turin, L. & Warner, A. E. (1977) Carbon dioxide reversibly abolishes ionic communication between cells of early amphibian embryo. Nature 270, 56–7.
Tuttle, R., Masuko, S. & Nakajima, Y. (1986) Freeze-fracture study of the large myelinated club ending synapse on the goldfish Mauthner cell: special reference to the quantitative analysis of gap junctions. Journal of Comparative Neurology 246, 202–11.
Valiante, T. A., Perez Velazquez, J. L., Jahromi, S. S. & Carlen, P. L. (1995) Coupling potentials in CA1 neurons during calcium-free-induced field burst activity. Journal of Neuroscience 15, 6946–56.
Vaney, D. I. (1991) Many diverse types of retinal neurons show tracer coupling when injected with biocytin or neurobiotin. Neuroscience Letters 125, 187–90.
Veenstra, R. D., Wang, H. Z., Beyer, E. C. & Brink, P. R. (1994) Selective dye and ionic permeability of gap junction channels formed by connexin45. Circulation Research 75, 483–90.
Veenstra, R. D., Wang, H. Z., Beblo, D. A., Chilton, M. G., Harris, A. L., Beyer, E. C. & Brink, P. R. (1995) Selectivity of connexin-specific gap junctions does not correlate with channel conductance. Circulation Research 77, 1156–65.
Verselis, V. K., Bennett, M. V. L. & Bargiello, T. A. (1991) A voltage-dependent gap junction in Drosophila melanogaster. Biophysical Journal 59, 114–26.
Verselis, V. K., Ginter, C. S. & Bargiello, T. A. (1994) Opposite voltage gating polarities of two closely related connexins. Nature 368, 348–51.
Watanabe, A. (1958) The interaction of electrical activity among neurons of lobster cardiac ganglion. Japanese Journal of Physiology 8, 305–18.
White, T. W., Bruzzone, R. & Paul, D. L. (1995a) The connexin family of intercellular channel forming proteins. Kidney International 48, 1148–57.
White, T. W., Paul, D. L., Goodenough, D. A. & Bruzzone, R. (1995b) Functional analysis of selective interactions among rodent connexins. Molecular Biology of the Cell 6, 459–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bennett, M.V.L. Gap junctions as electrical synapses. J Neurocytol 26, 349–366 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018560803261
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018560803261