Abstract
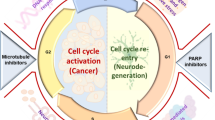
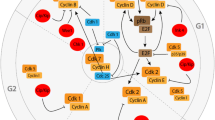
Currently, there is no effective treatment for neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Thus, a major focus of neuroscience research is to examine the mechanisms involved in neuronal loss in order to identify potential drug targets. Recent results indicate that DNA damage and re-entry into the cell cycle may constitute a common pathway in apoptosis in neurological diseases. The role of the cell cycle in such disorders is supported by data on the brain of patients who showed an increase in cell-cycle protein expression. Indeed, studies performed in neuronal cell preparations indicate that oxidative stress could be the main mechanism responsible for cell cycle re-entry. DNA damage and repair after oxidative stress may activate the enzyme ataxia telangiectasia mutated, which is a cell-cycle regulator. Once the cell cycle is activated, the increase in the expression of transcription factor E2F-1 could induce neuronal apoptosis. Furthermore, the potential routes involved in E2F-1 induced apoptosis could be p53-dependent or p53-independent. Under this E2F-1 hypothesis of cell death, multiple mitochondria-dependent pathways may be activated, including caspase and caspase-independent signaling cascades. Finally, given that cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory drugs have neuroprotective and anti-apoptotic effects in experimental models, their potential application for the treatment of neurological disorders should be taken into account.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashiba H, Matsuki N, Nishiyama N (2006) p27 small interfering RNA induces cell death through elevating cell cycle activity in cultured cortical neurons: a proof-of-concept study. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2397–2404
Akashiba H, Ikegaya Y, Nishiyama N, Matsuki N (2008) Differential involvement of cell cycle reactivation between striatal and cortical neurons in cell death induced by 3-nitropropionic acid. J Biol Chem 283:6594–6606
Alvira D, Tajes M, Verdaguer E, de Arriba SG, Allgaier C, Matute C, Trullas R, Jiménez A, Pallàs M, Camins A (2007) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases is neuroprotective in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis in neurons. Neuroscience 146:350–365
Alvira D, Ferrer I, Gutierrez-Cuesta J, Garcia-Castro B, Pallàs M, Camins A (2008) Activation of the calpain/cdk5/p25 pathway in the girus cinguli in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:309–313
Appert-Collin A, Hugel B, Levy R, Niederhoffer N, Coupin G, Lombard Y, André P, Poindron P, Gies JP (2006) Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors prevent apoptosis of postmitotic mouse motoneurons. Life Sci 79:484–490
Arendt T (2009) Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:167–179
Arendt T, Rödel L, Gärtner U, Holzer M (1996) Expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 7:3047–3049
Arendt T, Holzer M, Gärtner U (1998) Neuronal expression of cycline dependent kinase inhibitors of the INK4 family in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 105:949–960
Atabay KD, Karabay A. Pin1 inhibition activates cyclin D and produces neurodegenerative pathology. J Neurochem. 2011 Mar 28. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07259.x. [Epub ahead of print]
Barbato C, Corbi N, Canu N, Fanciulli M, Serafino A, Ciotti M, Libri V, Bruno T, Amadoro G, De Angelis R, Calissano P, Passananti C (2003) Rb binding protein Che-1 interacts with Tau in cerebellar granule neurons. Modulation during neuronal apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:1038–1050
Bashari D, Hacohen D, Ginsberg D (2011) JNK activation is regulated by E2F and promotes E2F1-induced apoptosis. Cell Signal 23:65–70
Baumann K, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Piwnica-Worms H, Mandelkow E (1993) Abnormal Alzheimer-like phosphorylation of tau-protein by cyclin-dependent kinases cdk2 and cdk5. FEBS Lett 336:417–424
Becker EB, Bonni A (2004) Cell cycle regulation of neuronal apoptosis in development and disease. Prog Neurobiol 72:1–25
Biswas SC, Liu DX, Greene LA (2005) Bim is a direct target of a neuronal E2F-dependent apoptotic pathway. J Neurosci 25:8349–8358
Biton S, Barzilai A, Shiloh Y (2008) The neurological phenotype of ataxia-telangiectasia: solving a persistent puzzle. DNA Repair 7:1028–1038
Bonda DJ, Evans TA, Santocanale C, Llosá JC, Viña J, Bajic VP, Castellani RJ, Siedlak SL, Perry G, Smith MA, Lee HG (2009) Evidence for the progression through S-phase in the ectopic cell cycle re-entry of neurons in Alzheimer disease. Aging (Albany NY) 1:382–388
Bonda DJ, Bajić VP, Spremo-Potparevic B, Casadesus G, Zhu X, Smith MA, Lee HG (2010) Cell cycle aberrations and neurodegeneration. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:157–163
Brouillet E, Condé F, Beal MF, Hantraye P (1999) Replicating Huntington’s disease phenotype in experimental animals. Prog Neurobiol 59:427–468
Brouillet E, Jacquard C, Bizat N, Blum D (2005) 3-Nitropropionic acid: a mitochondrial toxin to uncover physiopathological mechanisms underlying striatal degeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurochem 95:1521–1540
Camins A, Verdaguer E, Folch J, Beas-Zarate C, Canudas AM, Pallàs M (2007) Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia-p53–E2F-1 pathway in neurons as a target for the prevention of neuronal apoptosis. Curr Drug Metab 8:709–715
Camins A, Pizarro JG, Alvira D, Gutierrez-Cuesta J, de la Torre AV, Folch J, Sureda FX, Verdaguer E, Junyent F, Jordán J, Ferrer I, Pallàs M (2010) Activation of ataxia telangiectasia muted under experimental models and human Parkinson’s disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:3865–3882
Cernak I, Stoica B, Byrnes KR, Di Giovanni S, Faden AI (2005) Role of the cell cycle in the pathobiology of central nervous system trauma. Cell Cycle 4:1286–1293
Chang KH, de Pablo Y, Lee HP, Lee HG, Smith MA, Shah K (2010) Cdk5 is a major regulator of p38 cascade: relevance to neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 113:1221–1229
Chong ZZ, Li F, Maiese K (2005) Employing new cellular therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease: a change for the better? Curr Neurovasc Res 2:55–72
Copani A, Condorelli F, Caruso A, Vancheri C, Sala A, Giuffrida Stella AM, Canonico PL, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA (1999) Mitotic signaling by beta-amyloid causes neuronal death. FASEB J 13:2225–2234
Copani A, Uberti D, Sortino MA, Bruno V, Nicoletti F, Memo M (2001) Activation of cell-cycle-associated proteins in neuronal death: a mandatory or dispensable path? Trends Neurosci 24:25–31
Copani A, Sortino MA, Caricasole A, Chiechio S, Chisari M, Battaglia G, Giuffrida-Stella AM, Vancheri C, Nicoletti F (2002) Erratic expression of DNA polymerases by beta-amyloid causes neuronal death. FASEB J 16:2006–2008
Copani A, Caraci F, Hoozemans JJ, Calafiore M, Sortino MA, Nicoletti F (2007) The nature of the cell cycle in neurons: focus on a “non-canonical” pathway of DNA replication causally related to death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:409–412
Copani A, Guccione S, Giurato L, Caraci F, Calafiore M, Sortino MA, Nicoletti F (2008) The cell cycle molecules behind neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease: perspectives for drug development. Curr Med Chem 15:2420–2432
Cregan SP, Arbour NA, Maclaurin JG, Callaghan SM, Fortin A, Cheung EC, Guberman DS, Park DS, Slack RS (2004) p53 activation domain 1 is essential for PUMA upregulation and p53-mediated neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 24:10003–10012
Croxton R, Ma Y, Cress WD (2002) Differences in DNA binding properties between E2F1 and E2F4 specify repression of the Mcl-1 promoter. Oncogene 21:1563–1570
Cruz JC, Tsai LH (2004) Cdk5 deregulation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 10:452–458
Cruz JC, Tseng HC, Goldman JA, Shih H, Tsai LH (2003) Aberrant Cdk5 activation by p25 triggers pathological events leading to neurodegeneration and neurofibrillary tangles. Neuron 40:471–483
Damiano M, Galvan L, Déglon N, Brouillet E (2010) Mitochondria in Huntington’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:52–61
Di Giovanni S, Movsesyan V, Ahmed F, Cernak I, Schinelli S, Stoica B, Faden AI (2005) Cell cycle inhibition provides neuroprotection and reduces glial proliferation and scar formation after traumatic brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8333–8338
Dimova DK, Dyson NJ (2005) The E2F transcriptional network: old acquaintances with new faces. Oncogene 24:2810–2826
Eischen CM, Packham G, Nip J, Fee BE, Hiebert SW, Zambetti GP, Cleveland JL (2001) Bcl-2 is an apoptotic target suppressed by both c-Myc and E2F–1. Oncogene 20:6983–6993
Fernandez–Fernandez MR, Ferrer I, Lucas JJ (2011) Impaired ATF6α processing, decreased Rheb and neuronal cell cycle re-entry in Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 41:23–32
Furukawa Y, Nishimura N, Furukawa Y, Satoh M, Endo H, Iwase S, Yamada H, Matsuda M, Kano Y, Nakamura M (2002) Apaf-1 is a mediator of E2F-1-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:39760–39768
Giovanni A, Keramaris E, Morris EJ, Hou ST, O’Hare M, Dyson N, Robertson GS, Slack RS, Park DS (2000) E2F1 mediates death of B-amyloid-treated cortical neurons in a manner independent of p53 and dependent on Bax and caspase 3. J Biol Chem 275:11553–11560
Herrup K, Neve R, Ackerman SL, Copani A (2004) Divide and die: cell cycle events as triggers of nerve cell death. J Neurosci 24:9232–9239
Hershko T, Ginsberg D (2004) Up-regulation of Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3)-only proteins by E2F1 mediates apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:8627–8634
Höglinger GU, Breunig JJ, Depboylu C, Rouaux C, Michel PP, Alvarez-Fischer D, Boutillier AL, Degregori J, Oertel WH, Rakic P, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2007) The pRb/E2F cell-cycle pathway mediates cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3585–3590
Hou ST, Callaghan D, Fournier MC, Hill I, Kang L, Massie B, Morley P, Murray C, Rasquinha I, Slack R, MacManus JP (2000) The transcription factor E2F1 modulates apoptosis of neurons. J Neurochem 75:91–100
Hou ST, Cowan E, Walker T, Ohan N, Dove M, Rasqinha I, MacManus JP (2001) The transcription factor E2F1 promotes dopamine-evoked neuronal apoptosis by a mechanism independent of transcriptional activation. J Neurochem 78:287–297
Huang E, Qu D, Park DS (2010a) Cdk5: links to DNA damage. Cell Cycle 9:3142–3143
Huang E, Qu D, Zhang Y, Venderova K, Haque ME, Rousseaux MW, Slack RS, Woulfe JM, Park DS (2010b) The role of Cdk5-mediated apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 phosphorylation in neuronal death. Nat Cell Biol 12:563–571
Irwin M, Marin MC, Phillips AC, Seelan RS, Smith DI, Liu W, Flores ER, Tsai KY, Jacks T, Vousden KH, Kaelin WG (2000) Role for the p53 homologue p73 in E2F-1-induced apoptosis. Nature 407:645–648
Jacobsen E, Beach T, Shen Y, Li R, Chang Y (2004) Deficiency of the Mre11 DNA repair complex in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 128:1–7
Jiang H, Martin V, Gomez-Manzano C, Johnson DG, Alonso M, White E, Xu J, McDonnell TJ, Shinojima N, Fueyo J (2010) The RB-E2F1 pathway regulates autophagy. Cancer Res 70:7882–7893
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Morgan K, Bowser R (1999) Increased cyclin G1 immunoreactivity during Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 1:409–417
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Wang G, Murphy-Corb M, Wiley CA (2000) Induction of cell-cycle regulators in simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. Am J Pathol 2000(157):497–507
Jordan-Sciutto K, Rhodes J, Bowser R (2001) Altered subcellular distribution of transcriptional regulators in response to Abeta peptide and during Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 123:11–20
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Malaiyandi LM, Bowser R (2002a) Altered distribution of cell cycle transcriptional regulators during Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neuro 2002(61):358–367
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Wang G, Murphey-Corb M, Wiley CA (2002b) Cell cycle proteins exhibit altered expression patterns in lentiviral-associated encephalitis. J Neurosci 22:2185–2195
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Dorsey R, Chalovich EM, Hammond RR, Achim CL (2003) Expression patterns of retinoblastoma protein in Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:68–74
Katchanov J, Harms C, Gertz K, Hauck L, Waeber C, Hirt L, Priller J, von Harsdorf R, Bruck W, Hortnagl H, Dirnagl U, Bhide PG, Endres M (2000) Mild cerebral ischemia induces loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and activation of cell cycle machinery before delayed neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 2001(21):5045–5053
Kim D, Frank CL, Dobbin MM, Tsunemoto RK, Tu W, Peng PL, Guan JS, Lee BH, Moy LY, Giusti P, Broodie N, Mazitschek R, Delalle I, Haggarty SJ, Neve RL, Lu Y, Tsai LH (2008) Deregulation of HDAC1 by p25/Cdk5 in neurotoxicity. Neuron 60:803–817
Kim MK, Kim SC, Kang JI, Hyun JH, Boo HJ, Eun SY, Park DB, Yoo ES, Kang HK, Kang JH (2011) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced PC12 cell death is mediated by MEF2D down-regulation. Neurochem Res 36:223–231
Klein JA, Ackerman SL (2003) Oxidative stress, cell cycle, and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 111:785–793
Klein JA, Longo-Guess CM, Rossmann MP, Seburn KL, Hurd RE, Frankel WN, Bronson RT, Ackerman SL (2002) The harlequin mouse mutation downregulates apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 419:367–374
Konishi Y, Bonni A (2003) The E2F-Cdc2 cell-cycle pathway specifically mediates activity deprivation-induced apoptosis of postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci 23:1649–1658
Koulich E, Nguyen T, Johnson K, Giardina C, D’mello S (2001) NF-kappaB is involved in the survival of cerebellar granule neurons: association of Ikappa β phosphorylation with cell survival. J Neurochem 76:1188–1198
Kruman II (2004) Why do neurons enter the cell cycle? Cell Cycle 3:769–773
Kruman II, Wersto RP, Cardozo-Pelaez F, Smilenov L, Chan SL, Chrest FJ, Emokpae R Jr, Gorospe M, Mattson MP (2004) Cell cycle activation linked to neuronal cell death initiated by DNA damage. Neuron 41:549–561
Lee HG, Casadesus G, Zhu X, Castellani RJ, McShea A, Perry G, Petersen RB, Bajic V, Smith MA (2009) Cell cycle re-entry mediated neurodegeneration and its treatment role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 54:84–88
Lee CH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Park OK, Hwang IK, Choi SY, Kim DH, Won MH (2011) Cyclin D1 immunoreactivity changes in CA1 pyramidal neurons and dentate granule cells in the gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia. Neurol Res 33:93–100
Lim AC, Qi RZ (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinases in neural development and degeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 5:329–335
Liu DX, Greene LA (2001) Regulation of neuronal survival and death by E2F-dependent gene repression and derepression. Neuron 32:425–438
Liu DX, Biswas SC, Greene LA (2004) B-myb and C-myb play required roles in neuronal apoptosis evoked by nerve growth factor deprivation and DNA damage. J Neurosci 24:8720–8725
Lockshin RA, Zakari Z (2004) Apoptosis, autophagy and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2405–2419
Lopes JP, Agostinho P (2011) Cdk5: multitasking between physiological and pathological conditions. Prog Neurobiol 94:49–63
Lopes JP, Oliveira CR, Agostinho P (2009) Cdk5 acts as a mediator of neuronal cell cycle re-entry triggered by amyloid-beta and prion peptides. Cell Cycle 8:97–104
Lopes JP, Oliveira CR, Agostinho P (2010) Neurodegeneration in an Abeta-induced model of Alzheimer’s disease: the role of Cdk5. Aging Cell 9:64–77
Love S (2003) Neuronal expression of cell cycle-related proteins after brain ischaemia in man. Neurosci Lett 353:29–32
Luo Y, Hattori A, Munoz J, Qin ZH, Roth GS (1999) Intrastriatal dopamine injection induces apoptosis through oxidation-involved activation of transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB in rats. Mol Pharmacol 56:254–264
Maccioni RB, Munoz JP, Barbeito L (2001) The molecular bases of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Arch Med Res 32:367–381
MacManus JP, Koch CJ, Jian M, Walker T, Zurakowski B (1999) Decreased brain infarct following focal ischemia in mice lacking the transcription factor E2F1. Neuroreport 10:2711–2714
MacManus JP, Jian M, Preston E, Rasquinha I, Webster J, Zurakowski B (2003) Absence of the transcription factor E2F1 attenuates brain injury and improves behavior after focal ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1020–1028
Martin-Romero FJ, Santiago-Josefat B, Correa-Bordes J, Gutierrez-Merino C, Fernandez-Salguero P (2000) Potassium-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells involves cell-cycle blockade at the G1/S transition. J Mol Neurosci 15:155–165
Massagué J (2004) G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature 432:298–306
McMurray CT (2005) To die or not to die: DNA repair in neurons. Mutat Res 2005(577):260–274
Morris LG, Veeriah S, Chan TA (2010) Genetic determinants at the interface of cancer and neurodegenerative disease. Oncogene 29:3453–34564
Motonaga K, Itoh M, Hirayama A, Hirano S, Becker LE, Goto Y, Takashima S (2001) Up-regulation of E2F1 in Down’s syndrome brain exhibiting neuropathological features of Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Res 905:250–253
Nagy Z, Esiri MM, Smith AD (1998) The cell division cycle and the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 87:731–739
Nahle Z, Polakoff J, Davuluri RV, McCurrach ME, Jacobson MD, Narita M, Zhang MQ, Lazebnik Y, Bar-Sagi D, Lowe SW (2002) Direct coupling of the cell cycle and cell death machinery by E2F. Nat Cell Biol 4:859–864
Nair VD (2006) Activation of p53 signaling initiates apoptotic death in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Apoptosis 11:955–966
Neve RL, McPhie DL (2006) The cell cycle as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Ther 111:99–113
Nunomura A, Moreira PI, Lee HG, Zhu X, Castellani RJ, Smith MA, Perry G (2007) Neuronal death and survival under oxidative stress in Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6:411–423
O’Hare MJ, Hou ST, Morris EJ, Cregan SP, Xu Q, Slack RS, Park DS (2000) Induction and modulation of cerebellar granule neuron death by E2F1. J Biol Chem 275:25264–25358
Osuga H, Osuga S, Wang F, Fetni R, Hogan MJ, Slack RS, Hakim AM, Ikeda JE, Park DS (2000) Cyclin-dependent kinases as a therapeutic target for stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10254–10259
Ozaki T, Okoshi R, Sang M, Kubo N, Nakagawara A (2009) Acetylation status of E2F–1 has an important role in the regulation of E2F-1-mediated transactivation of tumor suppressor p73. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:207–211
Padmanabhan J, Park DS, Greene LA, Shelanski ML (1999) Role of cell cycle regulatory proteins in cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis. J Neurosci 19:8747–8756
Paik JC, Wang B, Liu K, Lue JK, Lin WC (2010) Regulation of E2F1-induced apoptosis by the nucleolar protein RRP1B. J Biol Chem 285:6348–6363
Pallas M, Verdaguer E, Jorda EG, Jimenez A, Canudas AM, Camins A (2005) Flavopiridol: an antitumor drug with potential application in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Med Hypotheses 64:120–123
Park DS, Morris EJ, Greene LA, Geller HM (1997) G1/S cell cycle blockers and inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases suppress camptothecin-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 17:1256–1270
Park DS, Morris EJ, Stefanis L, Troy CM, Shelanski ML, Geller HM, Greene LA (1998) Multiple pathways of neuronal death induced by DNA-damaging agents, NGF deprivation, and oxidative stress. J Neurosci 18:830–840
Park DS, Obeidat A, Giovanni A, Greene LA (2000) Cell cycle regulators in neuronal death evoked by excitotoxic stress: implications for neurodegeneration and its treatment. Neurobiol Aging 21:771–871
Patrick GN, Zukerberg L, Nikolic M, de la Monte S, Dikkes P, Tsai LH (1999) Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402:615–622
Patzke H, Tsai LH (2002) Calpain-mediated cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase-5 activator p39 to p29. J Biol Chem 277:8054–8060
Pelegrí C, Duran-Vilaregut J, del Valle J, Crespo-Biel N, Ferrer I, Pallàs M, Camins A, Vilaplana J (2008) Cell cycle activation in striatal neurons from Huntington’s disease patients and rats treated with 3-nitropropionic acid. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:665–671
Phillips AC, Ernst MK, Bates S, Rice NR, Vousden KH (1999) E2F1 potentiates cell death by blocking antiapoptotic signaling pathways. Mol Cell 4:771–781
Pizarro JG, Junyent F, Verdaguer E, Jordan J, Beas-Zarate C, Pallàs M, Camins A, Folch J (2010) Effects of MPP+ on the molecular pathways involved in cell cycle control in B65 neuroblastoma cells. Pharmacol Res 61:391–399
Polager S, Ginsberg D (2008) E2F - at the crossroads of life and death. Trends Cell Biol 18:528–535
Polager S, Ginsberg D (2009) p53 and E2f: partners in life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 9:738–748
Polager S, Ofir M, Ginsberg D (2008) E2F1 regulates autophagy and the transcription of autophagy genes. Oncogene 27:4860–4864
Putzer BM, Tuve S, Tannapfel A, Stiewe T (2003) Increased DeltaN-p73 expression in tumors by upregulation of the E2F1-regulated, TA-promoter-derived DeltaN’-p73 transcript. Cell Death Differ 10:612–624
Ranganathan S, Bowser R (2003) Alterations in G(1) to S phase cell-cycle regulators during amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Pathol 162:823–835
Ranganathan S, Bowser R (2010) p53 and cell cycle proteins participate in spinal motor neuron cell death in ALS. Open Pathol J 4:11–22
Rashidian J, Iyirhiaro G, Aleyasin H, Rios M, Vincent I, Callaghan S, Bland RJ, Slack RS, During MJ, Park DS (2005) Multiple cyclin-dependent kinases signals are critical mediators of ischemia/hypoxic neuronal death in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14080–14085
Rashidian J, Iyirhiaro GO, Park DS (2007) Cell cycle machinery and stroke. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:484–493
Sakai K, Kitagawa Y, Saiki S, Saiki M, Hirose G (2004) Effect of a paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration-associated neural protein on B-myb promoter activity. Neurobiol Dis 15:529–533
Salon C, Eymin B, Micheau O, Chaperot L, Plumas J, Brambilla C, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S (2006) E2F1 induces apoptosis and sensitizes human lung adenocarcinoma cells to death-receptor-mediated apoptosis through specific downregulation of c-FLIP(short). Cell Death Differ 13:260–272
Schmetsdorf S, Gärtner U, Arendt T (2007) Constitutive expression of functionally active cyclin-dependent kinases and their binding partners suggests noncanonical functions of cell cycle regulators in differentiated neurons. Cereb Cortex 17:1821–1829
Schmetsdorf S, Arnold E, Holzer M, Arendt T, Gärtner U (2009) A putative role for cell cycle-related proteins in microtubule-based neuroplasticity. Eur J Neurosci 29:1096–1107
Schwartz EI, Smilenov LB, Price MA, Osredkar T, Baker RA, Ghosh S, Shi FD, Vollmer TL, Lencinas A, Stearns DM, Gorospe M, Kruman II (2007) Cell cycle activation in postmitotic neurons is essential for DNA repair. Cell Cycle 6:318–329
Smith PD, Crocker SJ, Jackson-Lewis V, Jordan-Sciutto KL, Hayley S, Mount MP, O’Hare MJ, Callaghan S, Slack RS, Przedborski S, Anisman H, Park DS (2003a) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a mediator of dopaminergic neuron loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13650–13655
Smith RA, Walker T, Xie X, Hou ST (2003b) Involvement of the transcription factor E2F1/Rb in kainic acid-induced death of murine cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 116:70–79
Smith PD, O’Hare MJ, Park DS (2004) Emerging pathogenic role for cyclin dependent kinases in neurodegeneration. Cell Cycle 3:289–291
Stanelle J, Putzer BM (2006) E2F1-induced apoptosis: turning killers into therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 12:177–185
Stanelle J, Tu-Rapp H, Putzer BM (2005) A novel mitochondrial protein DIP mediates E2F1-induced apoptosis independently of p53. Cell Death Differ 12:347–357
Strachan GD, Koike MA, Siman R, Hall DJ, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2005) E2F1 induces cell death, calpain activation, and MDMX degradation in a transcription independent manner implicating a novel role for E2F1 in neuronal loss in SIV encephalitis. J Cell Biochem 96:728–740
Sun KH, de Pablo Y, Vincent F, Shah K (2008) Deregulated Cdk5 promotes oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurochem 107:265–278
Sun KH, Lee HG, Smith MA, Shah K (2009) Direct and indirect roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 as an upstream regulator in the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase cascade: relevance to neurotoxic insults in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Biol Cell 2021:4611–4619
Tracy K, Dibling BC, Spike BT, Knabb JR, Schumacker P, Macleod KF (2007) BNIP3 is an RB/E2F target gene required for hypoxia-induced autophagy. Mol Cell Biol 27:6229–6242
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness VS Jr, Chae T, Harlow E (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371(6496):419–423
Tsai LH, Lee MS, Cruz J (2004) Cdk5, a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease? Biochim Biophys Acta 1697:137–142
Ueberham U, Arendt T (2005) The expression of cell cycle proteins in neurons and its relevance for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4:293–306
Veeriah S, Morris L, Solit D, Chan TA (2010) The familial Parkinson disease gene PARK2 is a multisite tumor suppressor on chromosome 6q25.2–27 that regulates cyclin E. Cell Cycle 9:1451–1452
Verdaguer E, Garcia-Jorda E, Canudas AM, Dominguez E, Jimenez A, Pubill D, Escubedo E, Camarasa J, Pallas M, Camins A (2002) Kainic acid-induced apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons: an attempt at cell cycle re-entry. Neuroreport 13:413–416
Verdaguer E, Jimenez A, Canudas AM, Jorda EG, Sureda FX, Pallas M, Camins A (2004) Inhibition of cell cycle pathway by flavopiridol promotes survival of cerebellar granule cells after an excitotoxic treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:609–616
Verdaguer E, Jorda EG, Alvira D, Jimenez A, Canudas AM, Folch J, Rimbau V, Pallas M, Camins A (2005) Inhibition of multiple pathways accounts for the antiapoptotic effects of flavopiridol on potassium withdrawal-induced apoptosis in neurons. J Mol Neurosci 26:71–84
Vincent I, Rosado M, Davies P (1996) Mitotic mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease? J Cell Biol 132:413–425
Wallace DM, Cotter TG (2009) Histone deacetylase activity in conjunction with E2F-1 and p53 regulates Apaf-1 expression in 661 W cells and the retina. J Neurosci Res 87:887–905
Wang F, Corbett D, Osuga H, Osuga S, Ikeda JE, Slack RS, Hogan MJ, Hakim AM, Park DS (2002) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases improves CA1 neuronal survival and behavioral performance after global ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:171–182
Wang B, Liu K, Lin FT, Lin WC (2004) A role for 14–3-3 tau in E2F1 stabilization and DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:54140–54152
Webber KM, Raina AK, Marlatt MW, Zhu X, Prat MI, Morelli L, Casadesus G, Perry G, Smith MA (2005) The cell cycle in Alzheimer disease: a unique target for neuropharmacology. Mech Ageing Dev 126:1019–1025
Wen Y, Yang S, Liu R, Simpkins JW (2005) Cell-cycle regulators are involved in transient cerebral ischemia induced neuronal apoptosis in female rats. FEBS Lett 579:4591–4599
Wu Chen R, Zhang Y, Rose ME, Graham SH (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 activity contributes to neuronal expression of cyclin D1 after anoxia/ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 132:31–37
Xie W, Jiang P, Miao L, Zhao Y, Zhimin Z, Qing L, Zhu WG, Wu M (2006) Novel link between E2F1 and Smac/DIABLO: proapoptotic Smac/DIABLO is transcriptionally upregulated by E2F1. Nucleic Acids Res 34:2046–2255
Yang Y, Geldmacher DS, Herrup K (2001) DNA replication precedes neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 21:2661–2668
Yang Y, Mufson EJ, Herrup K (2003) Neuronal cell death is preceded by cell cycle events at all stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 23:2557–2563
Yu X, Caltagarone J, Smith MA, Bowser R (2005) DNA damage induces cdk2 protein levels and histone H2B phosphorylation in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J Alzheimers Dis 8:7–21
Zhang M, Li J, Chakrabarty P, Bu B, Vincent I (2004) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors attenuate protein hyperphosphorylation, cytoskeletal lesion formation, and motor defects in Niemann-Pick Type C mice. Am J Pathol 165:843–853
Zhu X, Castellani RJ, Takeda A, Nunomura A, Atwood CS, Perry G, Smith MA (2001) Differential activation of neuronal ERK, JNK/SAPK and p38 in Alzheimer disease: the ‘two hit’ hypothesis. Mech Ageing Dev 123:39–46
Zhu X, Raina AK, Perry G, Smith MA (2004) Alzheimer’s disease: the two-hit hypothesis. Lancet Neurol 3:219–226
Zhu X, Lee HG, Perry G, Smith MA (2007) Alzheimer disease, the two-hit hypothesis: an update. Biochim Biophys Acta 1772:494–502
Zhu J, Li W, Mao Z. (2011) Cdk5: Mediator of neuronal development, death and the response to DNA damage. Mech Ageing Dev. May 11. [Epub ahead of print]
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Spain’s “Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia” SAF2009-13093, SAF2011-23631, BFU2010-19119 and BFU2010-22149 the “Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria”, and the “Instituto de Salud Carlos III” PI080400 and PS09/01789 (FEDER FOUNDS). 610RT0405 from Programa Iberoamericano de Ciencia y Tecnologia para el Desarrollo (CYTED). The authors would like to thank the “Generalitat de Catalunya” for supporting the research groups (2009/SGR00853) and the “Fundació la Marató TV3” (063230). The authors wish to thank the Language Assessment Service of the University of Barcelona for revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Folch, J., Junyent, F., Verdaguer, E. et al. Role of Cell Cycle Re-Entry in Neurons: A Common Apoptotic Mechanism of Neuronal Cell Death. Neurotox Res 22, 195–207 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9277-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9277-4