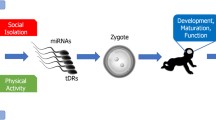
Abstract
Epigenetic modulation is found to get involved in multiple neurobehavioral processes. It is believed that different types of environmental stimuli could alter the epigenome of the whole brain or related neural circuits, subsequently contributing to the long-lasting neural plasticity of certain behavioral phenotypes. While the maternal influence on the health of offsprings has been long recognized, recent findings highlight an alternative way for neurobehavioral phenotypes to be passed on to the next generation, i.e., through the male germ line. In this review, we focus specifically on the transgenerational modulation induced by environmental stress, drugs of abuse, and other physical or mental changes (e.g., ageing, metabolism, fear) in fathers, and recapitulate the underlying mechanisms potentially mediating the alterations in epigenome or gene expression of offsprings. Together, these findings suggest that the inheritance of phenotypic traits through male germ-line epigenome may represent the unique manner of adaptation during evolution. Hence, more attention should be paid to the paternal health, given its equivalently important role in affecting neurobehaviors of descendants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bale TL (2015) Epigenetic and transgenerational reprogramming of brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(6):332–344. doi:10.1038/nrn3818
Klengel T, Binder EB (2015) Epigenetics of stress-related psychiatric disorders and gene x environment interactions. Neuron 86(6):1343–1357. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.05.036
Day JJ, Childs D, Guzman-Karlsson MC, Kibe M, Moulden J, Song E, Tahir A, Sweatt JD (2013) DNA methylation regulates associative reward learning. Nat Neurosci 16(10):1445–1452. doi:10.1038/nn.3504
Ma DK, Jang MH, Guo JU, Kitabatake Y, Chang ML, Pow-Anpongkul N, Flavell RA, Lu B et al (2009) Neuronal activity-induced Gadd45b promotes epigenetic DNA demethylation and adult neurogenesis. Science 323(5917):1074–1077. doi:10.1126/science.1166859
Guan JS, Haggarty SJ, Giacometti E, Dannenberg JH, Joseph N, Gao J, Nieland TJ, Zhou Y et al (2009) HDAC2 negatively regulates memory formation and synaptic plasticity. Nature 459(7243):55–60. doi:10.1038/nature07925
Monteggia LM, Kavalali ET (2009) Rett syndrome and the impact of MeCP2 associated transcriptional mechanisms on neurotransmission. Biol Psychiatry 65(3):204–210. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.036
Golden SA, Christoffel DJ, Heshmati M, Hodes GE, Magida J, Davis K, Cahill ME, Dias C et al (2013) Epigenetic regulation of RAC1 induces synaptic remodeling in stress disorders and depression. Nat Med 19(3):337–344. doi:10.1038/nm.3090
Marques SC, Oliveira CR, Pereira CM, Outeiro TF (2011) Epigenetics in neurodegeneration: a new layer of complexity. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(2):348–355. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.08.008
Kwok JB (2010) Role of epigenetics in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Epigenomics 2(5):671–682. doi:10.2217/epi.10.43
Bale TL (2014) Lifetime stress experience: transgenerational epigenetics and germ cell programming. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 16(3):297–305
Skinner MK (2014) Environmental stress and epigenetic transgenerational inheritance. BMC Med 12(1):153. doi:10.1186/s12916-014-0153-y
Dias BG, Ressler KJ (2014) Parental olfactory experience influences behavior and neural structure in subsequent generations. Nat Neurosci 17(1):89–96. doi:10.1038/nn.3594
Ng SF, Lin RC, Laybutt DR, Barres R, Owens JA, Morris MJ (2010) Chronic high-fat diet in fathers programs beta-cell dysfunction in female rat offspring. Nature 467(7318):963–966. doi:10.1038/nature09491
Sharma A (2013) Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: focus on soma to germline information transfer. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 113(3):439–446. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2012.12.003
Jablonka E, Raz G (2009) Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: prevalence, mechanisms, and implications for the study of heredity and evolution. Q Rev Biol 84(2):131–176
Jablonka E (2013) Epigenetic inheritance and plasticity: the responsive germline. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 111(2-3):99–107. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2012.08.014
Casas E, Vavouri T (2014) Sperm epigenomics: challenges and opportunities. Front Genet 5:330. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00330
Daxinger L, Whitelaw E (2012) Understanding transgenerational epigenetic inheritance via the gametes in mammals. Nat Rev Genet 13(3):153–162. doi:10.1038/nrg3188
Szyf M (2015) Nongenetic inheritance and transgenerational epigenetics. Trends Mol Med 21(2):134–144. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.12.004
Heard E, Martienssen RA (2014) Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: myths and mechanisms. Cell 157(1):95–109. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.045
Margueron R, Reinberg D (2010) Chromatin structure and the inheritance of epigenetic information. Nat Rev Genet 11(4):285–296. doi:10.1038/nrg2752
van der Heijden GW, Derijck AA, Ramos L, Giele M, van der Vlag J, de Boer P (2006) Transmission of modified nucleosomes from the mouse male germline to the zygote and subsequent remodeling of paternal chromatin. Dev Biol 298(2):458–469. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.051
Kim VN (2006) Small RNAs just got bigger: Piwiinteracting RNAs (piRNAs) in mammalian testes. Genes Dev 20(15):1993–1997
Yuan TF, Hou G (2015) The effects of stress on glutamatergic transmission in the brain. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):1139–1143. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8783-9
Nestler EJ (2014) Epigenetic mechanisms of depression. JAMA Psychiatry 71(4):454–456. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.4291
Vialou V, Feng J, Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2013) Epigenetic mechanisms of depression and antidepressant action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:59–87. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010611-134540
Murgatroyd C, Patchev AV, Wu Y, Micale V, Bockmuhl Y, Fischer D, Holsboer F, Wotjak CT et al (2009) Dynamic DNA methylation programs persistent adverse effects of early-life stress. Nat Neurosci 12(12):1559–1566. doi:10.1038/nn.2436
Elliott E, Ezra-Nevo G, Regev L, Neufeld-Cohen A, Chen A (2010) Resilience to social stress coincides with functional DNA methylation of the Crf gene in adult mice. Nat Neurosci 13(11):1351–1353. doi:10.1038/nn.2642
LaPlant Q, Vialou V, Covington HE 3rd, Dumitriu D, Feng J, Warren BL, Maze I, Dietz DM et al (2010) Dnmt3a regulates emotional behavior and spine plasticity in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 13(9):1137–1143. doi:10.1038/nn.2619
Lee JB, Wei J, Liu W, Cheng J, Feng J, Yan Z (2012) Histone deacetylase 6 gates the synaptic action of acute stress in prefrontal cortex. J Physiol 590(Pt 7):1535–1546. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224907
Tsankova NM, Berton O, Renthal W, Kumar A, Neve RL, Nestler EJ (2006) Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Nat Neurosci 9(4):519–525. doi:10.1038/nn1659
Covington HE 3rd, Maze I, LaPlant QC, Vialou VF, Ohnishi YN, Berton O, Fass DM, Renthal W et al (2009) Antidepressant actions of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Neurosci 29(37):11451–11460. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1758-09.2009
Issler O, Haramati S, Paul ED, Maeno H, Navon I, Zwang R, Gil S, Mayberg HS et al (2014) MicroRNA 135 is essential for chronic stress resiliency, antidepressant efficacy, and intact serotonergic activity. Neuron 83(2):344–360. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.042
Rodgers AB, Morgan CP, Bronson SL, Revello S, Bale TL (2013) Paternal stress exposure alters sperm microRNA content and reprograms offspring HPA stress axis regulation. J Neurosci 33(21):9003–9012. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0914-13.2013
Rodgers AB, Morgan CP, Leu NA, Bale TL (2015) Transgenerational epigenetic programming via sperm microRNA recapitulates effects of paternal stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. doi:10.1073/pnas.1508347112
Hou G, Xiong W, Wang M, Chen X, Yuan TF (2014) Chronic stress influences sexual motivation and causes damage to testicular cells in male rats. J Sex Med 11(3):653–663. doi:10.1111/jsm.12416
Gollenberg AL, Liu F, Brazil C, Drobnis EZ, Guzick D, Overstreet JW, Redmon JB, Sparks A et al (2010) Semen quality in fertile men in relation to psychosocial stress. Fertil Steril 93(4):1104–1111. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.12.018
Dietz DM, Laplant Q, Watts EL, Hodes GE, Russo SJ, Feng J, Oosting RS, Vialou V et al (2011) Paternal transmission of stress-induced pathologies. Biol Psychiatry 70(5):408–414. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.05.005
Franklin TB, Russig H, Weiss IC, Graff J, Linder N, Michalon A, Vizi S, Mansuy IM (2010) Epigenetic transmission of the impact of early stress across generations. Biol Psychiatry 68(5):408–415. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.05.036
Gapp K, Jawaid A, Sarkies P, Bohacek J, Pelczar P, Prados J, Farinelli L, Miska E et al (2014) Implication of sperm RNAs in transgenerational inheritance of the effects of early trauma in mice. Nat Neurosci 17(5):667–669. doi:10.1038/nn.3695
Sharma U, Rando OJ (2014) Father-son chats: inheriting stress through sperm RNA. Cell Metab 19(6):894–895. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.015
Bohacek J, Farinelli M, Mirante O, Steiner G, Gapp K, Coiret G, Ebeling M, Duran-Pacheco G et al (2015) Pathological brain plasticity and cognition in the offspring of males subjected to postnatal traumatic stress. Mol Psychiatry 20(5):621–631. doi:10.1038/mp.2014.80
Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (2011) Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(11):623–637. doi:10.1038/nrn3111
Nestler EJ (2014) Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt B:259-268. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.004
Feng J, Nestler EJ (2013) Epigenetic mechanisms of drug addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23(4):521–528. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.001
Anier K, Malinovskaja K, Aonurm-Helm A, Zharkovsky A, Kalda A (2010) DNA methylation regulates cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(12):2450–2461. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.128
Deng JV, Rodriguiz RM, Hutchinson AN, Kim IH, Wetsel WC, West AE (2010) MeCP2 in the nucleus accumbens contributes to neural and behavioral responses to psychostimulants. Nat Neurosci 13(9):1128–1136. doi:10.1038/nn.2614
Kumar A, Choi KH, Renthal W, Tsankova NM, Theobald DE, Truong HT, Russo SJ, Laplant Q et al (2005) Chromatin remodeling is a key mechanism underlying cocaine-induced plasticity in striatum. Neuron 48(2):303–314. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.023
Shen HY, Kalda A, Yu L, Ferrara J, Zhu J, Chen JF (2008) Additive effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors and amphetamine on histone H4 acetylation, cAMP responsive element binding protein phosphorylation and DeltaFosB expression in the striatum and locomotor sensitization in mice. Neuroscience 157(3):644–655. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.019
Schroeder FA, Penta KL, Matevossian A, Jones SR, Konradi C, Tapper AR, Akbarian S (2008) Drug-induced activation of dopamine D(1) receptor signaling and inhibition of class I/II histone deacetylase induce chromatin remodeling in reward circuitry and modulate cocaine-related behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(12):2981–2992. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.15
Sun H, Maze I, Dietz DM, Scobie KN, Kennedy PJ, Damez-Werno D, Neve RL, Zachariou V et al (2012) Morphine epigenomically regulates behavior through alterations in histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 32(48):17454–17464. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1357-12.2012
Wang L, Lv Z, Hu Z, Sheng J, Hui B, Sun J, Ma L (2010) Chronic cocaine-induced H3 acetylation and transcriptional activation of CaMKIIalpha in the nucleus accumbens is critical for motivation for drug reinforcement. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(4):913–928. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.193
Malvaez M, Mhillaj E, Matheos DP, Palmery M, Wood MA (2011) CBP in the nucleus accumbens regulates cocaine-induced histone acetylation and is critical for cocaine-associated behaviors. J Neurosci 31(47):16941–16948. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2747-11.2011
Malvaez M, McQuown SC, Rogge GA, Astarabadi M, Jacques V, Carreiro S, Rusche JR, Wood MA (2013) HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(7):2647–2652. doi:10.1073/pnas.1213364110
Renthal W, Maze I, Krishnan V, Covington HE 3rd, Xiao G, Kumar A, Russo SJ, Graham A et al (2007) Histone deacetylase 5 epigenetically controls behavioral adaptations to chronic emotional stimuli. Neuron 56(3):517–529. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.09.032
Kennedy PJ, Feng J, Robison AJ, Maze I, Badimon A, Mouzon E, Chaudhury D, Damez-Werno DM et al (2013) Class I HDAC inhibition blocks cocaine-induced plasticity by targeted changes in histone methylation. Nat Neurosci 16(4):434–440. doi:10.1038/nn.3354
Renthal W, Kumar A, Xiao G, Wilkinson M, Covington HE 3rd, Maze I, Sikder D, Robison AJ et al (2009) Genome-wide analysis of chromatin regulation by cocaine reveals a role for sirtuins. Neuron 62(3):335–348. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.026
Renthal W, Carle TL, Maze I, Covington HE 3rd, Truong HT, Alibhai I, Kumar A, Montgomery RL et al (2008) Delta FosB mediates epigenetic desensitization of the c-fos gene after chronic amphetamine exposure. J Neurosci 28(29):7344–7349. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1043-08.2008
Maze I, Covington HE 3rd, Dietz DM, LaPlant Q, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Mechanic M, Mouzon E et al (2010) Essential role of the histone methyltransferase G9a in cocaine-induced plasticity. Science 327(5962):213–216. doi:10.1126/science.1179438
Robison AJ, Vialou V, Mazei-Robison M, Feng J, Kourrich S, Collins M, Wee S, Koob G et al (2013) Behavioral and structural responses to chronic cocaine require a feedforward loop involving DeltaFosB and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the nucleus accumbens shell. J Neurosci 33(10):4295–4307. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5192-12.2013
Luscher C, Malenka RC (2011) Drug-evoked synaptic plasticity in addiction: from molecular changes to circuit remodeling. Neuron 69(4):650–663. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.017
Chandrasekar V, Dreyer JL (2009) microRNAs miR-124, let-7d and miR-181a regulate cocaine-induced plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci 42(4):350–362. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2009.08.009
Hollander JA, Im HI, Amelio AL, Kocerha J, Bali P, Lu Q, Willoughby D, Wahlestedt C et al (2010) Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signalling. Nature 466(7303):197–202. doi:10.1038/nature09202
Jonkman S, Kenny PJ (2013) Molecular, cellular, and structural mechanisms of cocaine addiction: a key role for microRNAs. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(1):198–211. doi:10.1038/npp.2012.120
Schaefer A, Im HI, Veno MT, Fowler CD, Min A, Intrator A, Kjems J, Kenny PJ et al (2010) Argonaute 2 in dopamine 2 receptor-expressing neurons regulates cocaine addiction. J Exp Med 207(9):1843–1851. doi:10.1084/jem.20100451
Saba R, Storchel PH, Aksoy-Aksel A, Kepura F, Lippi G, Plant TD, Schratt GM (2012) Dopamine-regulated microRNA MiR-181a controls GluA2 surface expression in hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Biol 32(3):619–632. doi:10.1128/MCB.05896-11
Vassoler FM, White SL, Schmidt HD, Sadri-Vakili G, Pierce RC (2013) Epigenetic inheritance of a cocaine-resistance phenotype. Nat Neurosci 16(1):42–47. doi:10.1038/nn.3280
Sasaki A, Constantinof A, Pan P, Kupferschmidt DA, McGowan PO, Erb S (2014) Cocaine exposure prior to pregnancy alters the psychomotor response to cocaine and transcriptional regulation of the dopamine D1 receptor in adult male offspring. Behav Brain Res 265:163–170. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.017
Abel EL (1993) Rat offspring sired by males treated with alcohol. Alcohol 10(3):237–242
Abel EL (1989) Paternal and maternal alcohol consumption: effects on offspring in two strains of rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 13(4):533–541
Finegersh A, Homanics GE (2014) Paternal alcohol exposure reduces alcohol drinking and increases behavioral sensitivity to alcohol selectively in male offspring. PLoS One 9(6):e99078. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099078
Lu H, Lim B, Poo MM (2009) Cocaine exposure in utero alters synaptic plasticity in the medial prefrontal cortex of postnatal rats. J Neurosci 29(40):12664–12674. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1984-09.2009
Buckingham-Howes S, Berger SS, Scaletti LA, Black MM (2013) Systematic review of prenatal cocaine exposure and adolescent development. Pediatrics 131(6):e1917–1936. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-0945
Lambert BL, Bauer CR (2012) Developmental and behavioral consequences of prenatal cocaine exposure: a review. J Perinatol 32(11):819–828. doi:10.1038/jp.2012.90
Bellone C, Mameli M, Luscher C (2011) In utero exposure to cocaine delays postnatal synaptic maturation of glutamatergic transmission in the VTA. Nat Neurosci 14(11):1439–1446. doi:10.1038/nn.2930
Kabir ZD, Katzman AC, Kosofsky BE (2013) Molecular mechanisms mediating a deficit in recall of fear extinction in adult mice exposed to cocaine in utero. PLoS One 8(12):e84165. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084165
Foldi CJ, Eyles DW, Flatscher-Bader T, McGrath JJ, Burne TH (2011) New perspectives on rodent models of advanced paternal age: relevance to autism. Front Behav Neurosci 5:32. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00032
Garcia-Palomares S, Pertusa JF, Minarro J, Garcia-Perez MA, Hermenegildo C, Rausell F, Cano A, Tarin JJ (2009) Long-term effects of delayed fatherhood in mice on postnatal development and behavioral traits of offspring. Biol Reprod 80(2):337–342. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.108.072066
Milekic MH, Xin Y, O'Donnell A, Kumar KK, Bradley-Moore M, Malaspina D, Moore H, Brunner D et al (2015) Age-related sperm DNA methylation changes are transmitted to offspring and associated with abnormal behavior and dysregulated gene expression. Mol Psychiatry 20(8):995–1001. doi:10.1038/mp.2014.84
Anway MD, Cupp AS, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK (2005) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 308(5727):1466–1469. doi:10.1126/science.1108190
Anway MD, Memon MA, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK (2006) Transgenerational effect of the endocrine disruptor vinclozolin on male spermatogenesis. J Androl 27(6):868–879. doi:10.2164/jandrol.106.000349
Crews D, Gore AC, Hsu TS, Dangleben NL, Spinetta M, Schallert T, Anway MD, Skinner MK (2007) Transgenerational epigenetic imprints on mate preference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(14):5942–5946. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610410104
Crews D, Gillette R, Scarpino SV, Manikkam M, Savenkova MI, Skinner MK (2012) Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of altered stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(23):9143–9148. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118514109
Skinner MK, Anway MD, Savenkova MI, Gore AC, Crews D (2008) Transgenerational epigenetic programming of the brain transcriptome and anxiety behavior. PLoS One 3(11):e3745. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003745
Skinner MK, Anway MD (2005) Seminiferous cord formation and germ-cell programming: epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1061:18–32. doi:10.1196/annals.1336.004
Skinner MK, Manikkam M, Haque MM, Zhang B, Savenkova MI (2012) Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of somatic transcriptomes and epigenetic control regions. Genome Biol 13(10):R91. doi:10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-r91
Guerrero-Bosagna CM, Skinner MK (2009) Epigenetic transgenerational effects of endocrine disruptors on male reproduction. Semin Reprod Med 27(5):403–408. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1237428
Guerrero-Bosagna C, Settles M, Lucker B, Skinner MK (2010) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of vinclozolin on promoter regions of the sperm epigenome. PLoS One 5(9):e13100. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013100
Gillette R, Miller-Crews I, Nilsson EE, Skinner MK, Gore AC, Crews D (2014) Sexually dimorphic effects of ancestral exposure to vinclozolin on stress reactivity in rats. Endocrinology 155(10):3853–3866. doi:10.1210/en.2014-1253
Walker DM, Gore AC (2011) Transgenerational neuroendocrine disruption of reproduction. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(4):197–207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2010.215
Anderson LM, Riffle L, Wilson R, Travlos GS, Lubomirski MS, Alvord WG (2006) Preconceptional fasting of fathers alters serum glucose in offspring of mice. Nutrition 22(3):327–331. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2005.09.006
Skinner MK (2010) Metabolic disorders: fathers’ nutritional legacy. Nature 467(7318):922–923. doi:10.1038/467922a
Wei Y, Yang CR, Wei YP, Zhao ZA, Hou Y, Schatten H, Sun QY (2014) Paternally induced transgenerational inheritance of susceptibility to diabetes in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(5):1873–1878. doi:10.1073/pnas.1321195111
Kaati G, Bygren LO, Edvinsson S (2002) Cardiovascular and diabetes mortality determined by nutrition during parents’ and grandparents’ slow growth period. Eur J Hum Genet 10(11):682–688. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200859
Pembrey ME, Bygren LO, Kaati G, Edvinsson S, Northstone K, Sjostrom M, Golding J, Team AS (2006) Sex-specific, male-line transgenerational responses in humans. Eur J Hum Genet 14(2):159–166. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201538
Carone BR, Fauquier L, Habib N, Shea JM, Hart CE, Li R, Bock C, Li C et al (2010) Paternally induced transgenerational environmental reprogramming of metabolic gene expression in mammals. Cell 143(7):1084–1096. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.008
Yamaguchi R, Nakagawa Y, Liu YJ, Fujisawa Y, Sai S, Nagata E, Sano S, Satake E et al (2010) Effects of maternal high-fat diet on serum lipid concentration and expression of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors in the early life of rat offspring. Horm Metab Res 42(11):821–825. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1261954
Radford EJ, Ito M, Shi H, Corish JA, Yamazawa K, Isganaitis E, Seisenberger S, Hore TA et al (2014) In utero effects. In utero undernourishment perturbs the adult sperm methylome and intergenerational metabolism. Science 345(6198):1255903. doi:10.1126/science.1255903
Hajkova P (2011) Epigenetic reprogramming in the germline: towards the ground state of the epigenome. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 366(1575):2266–2273. doi:10.1098/rstb.2011.0042
Stringer JM, Barrand S, Western P (2013) Fine-tuning evolution: germ-line epigenetics and inheritance. Reproduction 146(1):R37–48. doi:10.1530/REP-12-0526
Weaver JR, Susiarjo M, Bartolomei MS (2009) Imprinting and epigenetic changes in the early embryo. Mamm Genome 20(9-10):532–543. doi:10.1007/s00335-009-9225-2
Reik W, Dean W, Walter J (2001) Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science 293(5532):1089–1093. doi:10.1126/science.1063443
Seisenberger S, Andrews S, Krueger F, Arand J, Walter J, Santos F, Popp C, Thienpont B et al (2012) The dynamics of genome-wide DNA methylation reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mol Cell 48(6):849–862. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.001
Hajkova P, Jeffries SJ, Lee C, Miller N, Jackson SP, Surani MA (2010) Genome-wide reprogramming in the mouse germ line entails the base excision repair pathway. Science 329(5987):78–82. doi:10.1126/science.1187945
Hajkova P, Erhardt S, Lane N, Haaf T, El-Maarri O, Reik W, Walter J, Surani MA (2002) Epigenetic reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mech Dev 117(1-2):15–23
Ginsburg S, Jablonka E (2009) Epigenetic learning in non-neural organisms. J Biosci 34(4):633–646
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA, Beedle AS (2007) Non-genomic transgenerational inheritance of disease risk. Bioessays 29(2):145–154. doi:10.1002/bies.20522
Jablonka E, Lamb MJ (2005) Evolution in four dimensions: genetic, epigenetic, behavioral, and symbolic variation in the history of life. MIT Press, Cambridge
Funding
The work is supported by “Hundred Talents program”, “Qing Lan Project” of Nanjing Normal University, Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (#BK20140917), National Natural Science Foundation of China (#81501164, # 81501171), Hong Kong Health and Medical Research Fund, and by funds of Leading Talents of Guangdong (2013), and Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (B14036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Ti-Fei Yuan, Ang Li and Xin Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, TF., Li, A., Sun, X. et al. Transgenerational Inheritance of Paternal Neurobehavioral Phenotypes: Stress, Addiction, Ageing and Metabolism. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6367–6376 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9526-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9526-2