Abstract
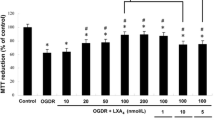
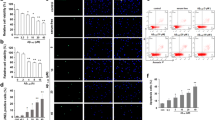
Astrocyte inflammation plays important roles both in physiological and pathological processes in the central nervous system (CNS). Ischemic injury in the CNS causes damage to astrocytes and the release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6. This current study investigates whether mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) inhibits oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell damage and inflammatory cytokine secretion by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat primary astrocytes. We found that MANF alleviated OGD-induced astrocyte damage and rescued the cell viability, and the upregulation of GRP78 (endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress marker) and NF-κB p65 (one of the central mediators of proinflammatory pathways) induced by OGD were significantly reduced by preincubation of MANF. In addition, the increases of secretion and mRNA expression levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in astrocytes induced by OGD were significantly suppressed by MANF. These findings demonstrate that MANF shows the potential to alleviate cell damage and inflammation in rat primary astrocytes by suppressing ER stress, indicating that MANF plays an important role in astrocyte inflammation and functioning and may suggest a promising strategy for neuroprotection in the CNS.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolou A, Shen Y et al (2008) Armet, a UPR-upregulated protein, inhibits cell proliferation and ER stress-induced cell death. Exp Cell Res 314(13):2454–2467
Aronica E, Ravizza T et al (2012) Astrocyte immune responses in epilepsy. Glia 60(8):1258–1268
Baumann O, Walz B (2001) Endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells and its organization into structural and functional domains. Int Rev Cytol 205:149–214
Begum G, Kintner D et al (2012) DHA inhibits ER Ca2+ release and ER stress in astrocytes following in vitro ischemia. J Neurochem 120(4):622–630
Benarroch EE (2005) Neuron-astrocyte interactions: partnership for normal function and disease in the central nervous system. Mayo Clin Proc 80(10):1326–1338
Cray C, Zaias J et al (2009) Acute phase response in animals: a review. Comp Med 59(6):517–526
Dong Y, Benveniste EN (2001) Immune function of astrocytes. Glia 36(2):180–190
Emsley JG, Arlotta P et al (2004) Star-cross’d neurons: astroglial effects on neural repair in the adult mammalian CNS. Trends Neurosci 27(5):238–240
Hosoi T, Ozawa K (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Clin Sci (Lond) 118(1):19–29
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6):900–917
Hotamisligil GS, Erbay E (2008) Nutrient sensing and inflammation in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 8(12):923–934
Kintner DB, Luo J et al (2007) Role of Na+-K+-Cl– cotransport and Na+/Ca2+ exchange in mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocytes following in vitro ischemia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(3):C1113–C1122
Korbelik M, Cecic I et al (2008) Acute phase response induction by cancer treatment with photodynamic therapy. Int J Cancer 122(6):1411–1417
Lau LT, Yu AC (2001) Astrocytes produce and release interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon-gamma following traumatic and metabolic injury. J Neurotrauma 18(3):351–359
Lee KS, Kim SR et al (2006) Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma modulates reactive oxygen species generation and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in allergic airway disease of mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(1):120–127
Li J, Wang JJ et al (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is implicated in retinal inflammation and diabetic retinopathy. FEBS Lett 583(9):1521–1527
Lindholm P, Saarma M (2010) Novel CDNF/MANF family of neurotrophic factors. Dev Neurobiol 70(5):360–371
Lindholm P, Voutilainen MH et al (2007) Novel neurotrophic factor CDNF protects and rescues midbrain dopamine neurons in vivo. Nature 448(7149):73–77
Ridet JL, Malhotra SK et al (1997) Reactive astrocytes: cellular and molecular cues to biological function. Trends Neurosci 20(12):570–577
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529
Song H, Stevens CF et al (2002) Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature 417(6884):39–44
Verfaillie T, Garg AD et al (2013) Targeting ER stress induced apoptosis and inflammation in cancer. Cancer Lett 332(2):249–264
Wang J, Li G et al (2012) High glucose-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 202:58–68
Zhang K, Kaufman RJ (2008) From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 454(7203):455–462
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Chen ZY (Department of Neurobiology, Shandong University) and Prof. Tang DQ, Wang XL, Cui TX, Cui ZQ (Research Center for Cell Therapy, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University), for their kind advice and help with this research. The study was supported by a grant from Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (20110131120079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Liu, Y., Cheng, L. et al. Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Inhibits Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Cell Damage and Inflammation by Suppressing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Rat Primary Astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 51, 671–678 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0042-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0042-4