Abstract
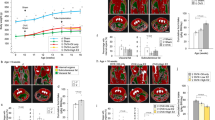
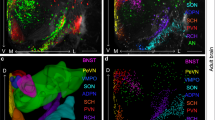
Oxytocin (OT) is a nonapeptide essential for maternal care. The development of the OT neuroendocrine system is a multi-step process dependent on the action of many transcription factors, but upstream signaling molecules regulating this process are still poorly understood. In this study, we examined if fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8), a signaling molecule critical for forebrain development, is essential for the proper formation of the OT system. Using immunohistochemistry, we showed a significant reduction in the number of neurons immunoreactive for the mature OT peptide in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supraoptic nucleus (SON) in the hypothalamus of homozygous (HOMO) FGF8 hypomorphic mice compared to wild-type mice. The number of neurons positive for oxyphysin prohormone in the SON but not the PVN was also significantly reduced in FGF8 HOMO hypomorphs. However, steady-state mRNA levels of the oxyphysin prohormone were not significantly different between FGF8 hypomorphs and WT mice. These data suggest that a global reduction in FGF8 signaling leads to an overall reduction of mature OT and oxyphysin prohormone levels that may have resulted from defects in multiple stages of the hormone-synthesis pathway. Since proper hormone synthesis is a hallmark of mature OT neurons, this study suggests that FGF8 signaling may contribute to the phenotypic maturation of a neuroendocrine system that originates within the diencephalon.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Nishimori, L.J. Young, Q. Guo, Z. Wang, T.R. Insel, M.M. Matzuk, Oxytocin is required for nursing but is not essential for parturition or reproductive behavior. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11699–11704 (1996)
H. Shoji, K. Kato, Maternal behavior of primiparous females in inbred strains of mice: a detailed descriptive analysis. Physiol. Behav. 89, 320–328 (2006)
J. Altman, S.A. Bayer, Development of the diencephalon in the rat. II. Correlation of the embryonic development of the hypothalamus with the time of origin of its neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 182, 973–993 (1978)
M.A. Karim, J.C. Sloper, Histogenesis of the supraoptic and paraventricular neurosecretory cells of the mouse hypothalamus. J. Anat. 130, 341–347 (1980)
S. Nakai, H. Kawano, T. Yudate, M. Nishi, J. Kuno, A. Nagata, K. Jishage, H. Hamada, H. Fujii, K. Kawamura et al., The POU domain transcription factor Brn-2 is required for the determination of specific neuronal lineages in the hypothalamus of the mouse. Genes Dev. 9, 3109–3121 (1995)
A. Simeone, M.R. D’Apice, V. Nigro, J. Casanova, F. Graziani, D. Acampora, V. Avantaggiato, Orthopedia, a novel homeobox-containing gene expressed in the developing CNS of both mouse and Drosophila. Neuron 13, 83–101 (1994)
D. Acampora, M.P. Postiglione, V. Avantaggiato, M. Di Bonito, A. Simeone, The role of Otx and Otp genes in brain development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44, 669–677 (2000)
Y.H. Jo, S. Chua Jr., Transcription factors in the development of medial hypothalamic structures. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 297, E563–E567 (2009)
R. Dono, Fibroblast growth factors as regulators of central nervous system development and function. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 284, R867–R881 (2003)
P.H. Crossley, S. Martinez, G.R. Martin, Midbrain development induced by FGF8 in the chick embryo. Nature 380, 66–68 (1996)
W. Ye, K. Shimamura, J.L. Rubenstein, M.A. Hynes, A. Rosenthal, FGF and Shh signals control dopaminergic and serotonergic cell fate in the anterior neural plate. Cell 93, 755–766 (1998)
E.E. Storm, S. Garel, U. Borello, J.M. Hebert, S. Martinez, S.K. McConnell, G.R. Martin, J.L. Rubenstein, Dose-dependent functions of Fgf8 in regulating telencephalic patterning centers. Development 133, 1831–1844 (2006)
S. Kawauchi, J. Shou, R. Santos, J.M. Hebert, S.K. McConnell, I. Mason, A.L. Calof, Fgf8 expression defines a morphogenetic center required for olfactory neurogenesis and nasal cavity development in the mouse. Development 132, 5211–5223 (2005)
M. Ford-Perriss, H. Abud, M. Murphy, Fibroblast growth factors in the developing central nervous system. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 28, 493–503 (2001)
P.H. Crossley, G.R. Martin, The mouse Fgf8 gene encodes a family of polypeptides and is expressed in regions that direct outgrowth and patterning in the developing embryo. Development 121, 439–451 (1995)
J.P. Burbach, Genetic pathways in the developmental specification of hypothalamic neuropeptide and midbrain catecholamine systems. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 405, 55–62 (2000)
A.M. Gonzalez, A. Logan, W. Ying, D.A. Lappi, M. Berry, A. Baird, Fibroblast growth factor in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis: differential expression of fibroblast growth factor-2 and a high affinity receptor. Endocrinology 134, 2289–2297 (1994)
S. Norlin, U. Nordstrom, T. Edlund, Fibroblast growth factor signaling is required for the proliferation and patterning of progenitor cells in the developing anterior pituitary. Mech. Dev. 96, 175–182 (2000)
J. Ericson, S. Norlin, T.M. Jessell, T. Edlund, Integrated FGF and BMP signaling controls the progression of progenitor cell differentiation and the emergence of pattern in the embryonic anterior pituitary. Development 125, 1005–1015 (1998)
W. Herzog, C. Sonntag, S. von der Hardt, H.H. Roehl, Z.M. Varga, M. Hammerschmidt, FGF3 signaling from the ventral diencephalon is required for early specification and subsequent survival of the zebrafish adenohypophysis. Development 131, 3681–3692 (2004)
J.P. Burbach, S.M. Luckman, D. Murphy, H. Gainer, Gene regulation in the magnocellular hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Physiol. Rev. 81, 1197–1267 (2001)
M. Altstein, H. Gainer, Differential biosynthesis and posttranslational processing of vasopressin and oxytocin in rat brain during embryonic and postnatal development. J. Neurosci. 8, 3967–3977 (1988)
M.H. Whitnall, S. Key, Y. Ben-Barak, K. Ozato, H. Gainer, Neurophysin in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. II. Immunocytochemical studies of the ontogeny of oxytocinergic and vasopressinergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 5, 98–109 (1985)
H. Gainer, M. Altstein, M.H. Whitnall, The cell biology and development of vasopressinergic and oxytocinergic neurons. Prog. Brain Res. 72, 153–161 (1987)
M. Morris, M. Castro, J.C. Rose, Alterations in oxytocin prohormone processing during early development in the fetal sheep. Am. J. Physiol. 263, R738–R740 (1992)
J.P. Burbach, J.L. Lebouille, Proteolytic conversion of arginine-vasopressin and oxytocin by brain synaptic membranes. Characterization of formed peptides and mechanisms of proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 1487–1494 (1983)
W.C. Wetsel, D.F. Hill, S.R. Ojeda, Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates the conversion of pro-luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (Pro-LHRH) to LHRH in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 137, 2606–2616 (1996)
W.C. Chung, S.S. Moyle, P.S. Tsai, Fibroblast growth factor 8 signaling through fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is required for the emergence of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Endocrinology 149, 4997–5003 (2008)
E.N. Meyers, M. Lewandoski, G.R. Martin, An FGF8 mutant allelic series generated by Cre- and Flp-mediated recombination. Nat. Genet. 18, 136–141 (1998)
T.R. de Jong, M. Chauke, B.N. Harris, W. Saltzman, From here to paternity: neural correlates of the onset of paternal behavior in California mice (Peromyscus californicus). Horm. Behav. 56, 220–231 (2009)
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by NIH R01 HD042634 to PST and Endocrine Society Summer Fellowship to L.R.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brooks, L.R., Chung, W.C.J. & Tsai, PS. Abnormal hypothalamic oxytocin system in fibroblast growth factor 8-deficient mice. Endocr 38, 174–180 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9366-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-010-9366-9