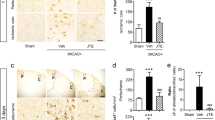
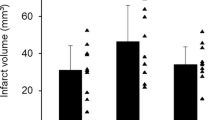
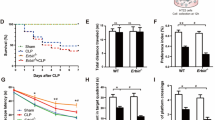
Abstract
The breakdown of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a key event in the development of sepsis-induced brain damage. BBB opening allows blood-born immune cells to enter the CNS to provoke a neuroinflammatory response. Abnormal expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) was shown to contribute to BBB opening. Using different mouse genotypes in a model of LPS-induced systemic inflammation, our present report reveals phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ (PI3Kγ) as a mediator of BBB deterioration and concomitant generation of MMP by microglia. Unexpectedly, microglia expressing lipid kinase-deficient mutant PI3Kγ exhibited similar MMP regulation as wild-type cells. Our data suggest kinase-independent control of cAMP phosphodiesterase activity by PI3Kγ as a crucial mediator of microglial cell activation, MMP expression and subsequent BBB deterioration. The results identify the suppressive effect of PI3Kγ on cAMP as a critical mediator of immune cell functions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks, W. A., & Erickson, M. A. (2010). The blood-brain barrier and immune function and dysfunction. Neurobiology of Diseases, 37(1), 26–32. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.031.
Candelario-Jalil, E., Yang, Y., & Rosenberg, G. A. (2009). Diverse roles of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation and cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience, 158(3), 983–994. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.025.
Comim, C. M., Vilela, M. C., Constantino, L. S., Petronilho, F., Vuolo, F., Lacerda-Queiroz, N., et al. (2011). Traffic of leukocytes and cytokine up-regulation in the central nervous system in sepsis. Intensive Care Medicine, 37(4), 711–718. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2151-2.
del Zoppo, G. J., Frankowski, H., Gu, Y. H., Osada, T., Kanazawa, M., Milner, R., et al. (2012). Microglial cell activation is a source of metalloproteinase generation during hemorrhagic transformation. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 32(5), 919–932. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.11.
Eidelman, L. A., Putterman, D., Putterman, C., & Sprung, C. L. (1996). The spectrum of septic encephalopathy. Definitions, etiologies, and mortalities. JAMA, 275(6), 470–473.
Gonnert, F. A., Recknagel, P., Seidel, M., Jbeily, N., Dahlke, K., Bockmeyer, C. L., et al. (2011). Characteristics of clinical sepsis reflected in a reliable and reproducible rodent sepsis model. Journal of Surgical Research, 170(1), e123–e134. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2011.05.019.
Guo, D., Kassiri, Z., Basu, R., Chow, F. L., Kandalam, V., Damilano, F., et al. (2010). Loss of PI3Kgamma enhances cAMP-dependent MMP remodeling of the myocardial N-cadherin adhesion complexes and extracellular matrix in response to early biomechanical stress. Circulation Research, 107(10), 1275–1289. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.229054.
Gurney, K. J., Estrada, E. Y., & Rosenberg, G. A. (2006). Blood-brain barrier disruption by stromelysin-1 facilitates neutrophil infiltration in neuroinflammation. Neurobiology of Diseases, 23(1), 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2006.02.006.
Hirsch, E., Katanaev, V. L., Garlanda, C., Azzolino, O., Pirola, L., Silengo, L., et al. (2000). Central role for G protein-coupled phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in inflammation. Science, 287(5455), 1049–1053.
Jacob, A., Brorson, J. R., & Alexander, J. J. (2011). Septic encephalopathy: Inflammation in man and mouse. Neurochemistry International, 58(4), 472–476. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.01.004.
Jin, R., Yu, S., Song, Z., Quillin, J. W., Deasis, D. P., Penninger, J. M., et al. (2010). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-gamma expression is upregulated in brain microglia and contributes to ischemia-induced microglial activation in acute experimental stroke. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 399(3), 458–464. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.116.
Kacimi, R., Giffard, R. G., & Yenari, M. A. (2011). Endotoxin-activated microglia injure brain derived endothelial cells via NF-kappaB, JAK-STAT and JNK stress kinase pathways. Journal of Inflammation (London), 8, 7. doi:10.1186/1476-9255-8-7.
Kerfant, B. G., Zhao, D., Lorenzen-Schmidt, I., Wilson, L. S., Cai, S., Chen, S. R., et al. (2007). PI3Kgamma is required for PDE4, not PDE3, activity in subcellular microdomains containing the sarcoplasmic reticular calcium ATPase in cardiomyocytes. Circulation Research, 101(4), 400–408. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.156422.
Kettenmann, H., Hanisch, U. K., Noda, M., & Verkhratsky, A. (2011). Physiology of microglia. Physiological Reviews, 91(2), 461–553. doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2010.
Langenfurth, A., Rinnenthal, J. L., Vinnakota, K., Prinz, V., Carlo, A. S., Stadelmann, C., et al. (2014). Membrane-type 1 metalloproteinase is upregulated in microglia/brain macrophages in neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 92(3), 275–286. doi:10.1002/jnr.23288.
Lee, D. K., Park, E. J., Kim, E. K., Jin, J., Kim, J. S., Shin, I. J., et al. (2012). Atorvastatin and simvastatin, but not pravastatin, up-regulate LPS-induced MMP-9 expression in macrophages by regulating phosphorylation of ERK and CREB. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 30(3), 499–511. doi:10.1159/000341433.
Lehnardt, S. (2010). Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: The role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia, 58(3), 253–263. doi:10.1002/glia.20928.
Murga, C., Laguinge, L., Wetzker, R., Cuadrado, A., & Gutkind, J. S. (1998). Activation of Akt/protein kinase B by G protein-coupled receptors. A role for alpha and beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins acting through phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinasegamma. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273(30), 19080–19085.
Nag, S., Kapadia, A., & Stewart, D. J. (2011). Review: molecular pathogenesis of blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute brain injury. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 37(1), 3–23. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01138.x.
Nagyoszi, P., Wilhelm, I., Farkas, A. E., Fazakas, C., Dung, N. T., Hasko, J., et al. (2010). Expression and regulation of toll-like receptors in cerebral endothelial cells. Neurochemistry International, 57(5), 556–564. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.07.002.
Nuttall, R. K., Silva, C., Hader, W., Bar-Or, A., Patel, K. D., Edwards, D. R., et al. (2007). Metalloproteinases are enriched in microglia compared with leukocytes and they regulate cytokine levels in activated microglia. Glia, 55(5), 516–526. doi:10.1002/glia.20478.
Passos, G. F., Figueiredo, C. P., Prediger, R. D., Silva, K. A., Siqueira, J. M., Duarte, F. S., et al. (2010). Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in the neuro-inflammatory response and cognitive impairments induced by beta-amyloid 1-40 peptide in mice. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 24(3), 493–501. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.12.003.
Patrucco, E., Notte, A., Barberis, L., Selvetella, G., Maffei, A., Brancaccio, M., et al. (2004). PI3Kgamma modulates the cardiac response to chronic pressure overload by distinct kinase-dependent and -independent effects. Cell, 118(3), 375–387. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.017.
Perino, A., Ghigo, A., Ferrero, E., Morello, F., Santulli, G., Baillie, G. S., et al. (2011). Integrating cardiac PIP3 and cAMP signaling through a PKA anchoring function of p110gamma. Molecular Cell, 42(1), 84–95. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.01.030.
Rosenberg, G. A., Cunningham, L. A., Wallace, J., Alexander, S., Estrada, E. Y., Grossetete, M., et al. (2001). Immunohistochemistry of matrix metalloproteinases in reperfusion injury to rat brain: Activation of MMP-9 linked to stromelysin-1 and microglia in cell cultures. Brain Research, 893(1–2), 104–112.
Schmidt, C., Schneble, N., Muller, J. P., Bauer, R., Perino, A., Marone, R., et al. (2013). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma mediates microglial phagocytosis via lipid kinase-independent control of cAMP. Neuroscience, 233, 44–53. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.036.
Setz, C., Brand, Y., Radojevic, V., Hanusek, C., Mullen, P. J., Levano, S., et al. (2011). Expression and activity after aminoglycoside exposition. Neuroscience, 181(28–39), 2011. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.02.043.
Stephens, L. R., Eguinoa, A., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Lui, M., Cooke, F., Coadwell, J., et al. (1997). The G beta gamma sensitivity of a PI3K is dependent upon a tightly associated adaptor, p101. Cell, 89(1), 105–114.
Stoyanov, B., Volinia, S., Hanck, T., Rubio, I., Loubtchenkov, M., Malek, D., et al. (1995). Cloning and characterization of a G protein-activated human phosphoinositide-3 kinase. Science, 269(5224), 690–693.
Wilson, J. X., & Young, G. B. (2003). Progress in clinical neurosciences: Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: evolving concepts. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences, 30(2), 98–105.
Woo, M. S., Park, J. S., Choi, I. Y., Kim, W. K., & Kim, H. S. (2008). Inhibition of MMP-3 or -9 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines and iNOS in microglia. Journal of Neurochemistry, 106(2), 770–780. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05430.x.
Yang, Y., & Rosenberg, G. A. (2011). Blood-brain barrier breakdown in acute and chronic cerebrovascular disease. Stroke, 42(11), 3323–3328. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.608257.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Mrs. R.-M., Zimmer for skillful technical assistance, and F. D. Bohmer, for his collegial review of the manuscript. The study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, Priority Program 1160 and Grant RTG 1715) and by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF; Grant FKZ 01EO1002; Center for Sepsis Control and Care). A.F. is a Ph.D. student of the Jena School for Microbial Communication, Priority Program 1160 of the DFG and supported in part by the Integrated Research and Treatment Center, Center for Sepsis Control and Care, Jena University Hospital, Jena, Germany. C.S and N.S. are PhD students of the Research Training Group 1715 “Adaptive Stress Responses” Grant RTG 1715 of the DFG.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Adrian Frister and Caroline Schmidt have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frister, A., Schmidt, C., Schneble, N. et al. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase γ Affects LPS-Induced Disturbance of Blood–Brain Barrier Via Lipid Kinase-Independent Control of cAMP in Microglial Cells. Neuromol Med 16, 704–713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8320-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8320-z