Abstract
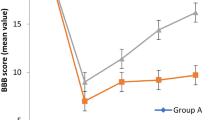
We assessed the effect of treatment with the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein (IRAP) on morphological and functional recovery in a rat model of SCI. All sections were processed for immunohistochemistry, hematoxylin–eosin, and Nissl staining. Rats were assessed for hind limb motor function using the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan (BBB) hind limb locomotor rating scale and the inclined plane test. At 1, 48, and 72 h after operation, there was a significant increase in neurofilament proteins and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the IRAP group I when compared with the saline group I and the sham-operated group I (P < 0.05). The mean inclined plane scores and BBB scores for the IRAP group II were higher than the saline group II at 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks post-injury (P < 0.05). In conclusion, treatment with IRAP enhanced neuronal survival after SCI.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sud, S., S.Y. Yang, C.H. Evans, P.D. Robbins, and P.H. Wooley. 2001. Effects of cytokine gene therapy on particulate-induced inflammation in the murine air pouch. Inflammation 25: 361–372.
Bravo, G., R. Rojas-Martínez, F. Larios, E. Hong, G. Castañeda-Hernández, G. Rojas, and G. Guízar-Sahagún. 2001. Mechanisms involved in the cardiovascular alterations immediately after spinal cord injury. Life Sciences 68: 1527–1534.
Huang, H., S. Fan, X. Ji, Y. Zhang, F. Bao, and G. Zhang. 2009. Recombinant human erythropoietin protects against experimental spinal cord trauma injury by regulating expression of the proteins MKP-1 and p-ERK. The Journal of International Medical Research 37: 511–519.
Tzeng, S.F., H. Cheng, Y.S. Lee, J.P. Wu, B.J. Hoffer, and J.S. Kuo. 2001. Expression of neural cell adhesion molecule in spinal cords following a complete transection. Life Sciences 68(9): 1005–1012.
Johnson, R.W., S. Arkins, R. Dantzer, and K.W. Kelley. 1997. Hormones, lymphohemopoietic cytokines and the neuroimmune axis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part A, Physiology 116: 183–201.
Xu, Z., B.R. Wang, X. Wang, F. Kuang, X.L. Duan, X.Y. Jiao, and G. Ju. 2006. ERK1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediate iNOS-induced spinal neuron degeneration after acute traumatic spinal cord injury. Life Sciences 79: 1895–1905.
Rothwell, N.J., and G.N. Luheshi. 2000. Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target. Trends in Neurosciences 23: 618–625.
Wang, X.F., L.D. Huang, P.P. Yu, J.G. Hu, L. Yin, L. Wang, X.M. Xu, and P.H. Lu. 2006. Upregulation of type I interleukin-1 receptor after traumatic spinal cord injury in adult rats. Acta Neuropatho 111: 220–228.
Baamonde, A., V. Curto-Reyes, L. Juárez, A. Meana, A. Hidalgo, and L. Menéndez. 2007. Antihyperalgesic effects induced by the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra and increased IL-1beta levels in inflamed and osteosarcoma-bearing mice. Life Sciences 81: 673–682.
Rohleder, N., J.M. Wolf, I. Herpfer, B.L. Fiebich, C. Kirschbaum, and K. Lieb. 2006. No response of plasma substance P, but delayed increase of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist to acute psychosocial stress. Life Sciences 78: 3082–3089.
Wu, J., H. Yang, Z. Qiu, Q. Zhang, T. Ding, and D. Geng. 2010. Effect of combined treatment with methylprednisolone and Nogo-A monoclonal antibody after rat spinal cord injury. The Journal of International Medical Research 38: 570–582.
Khan, T., R.M. Havey, S.T. Sayers, A. Patwardhan, and W.W. King. 1999. Animal models of spinal cord contusion injuries. Laboratory Animal Science 49: 161–172.
Maharajh, G.S., E.A. Pascoe, W.C. Halliday, H.P. Grocott, D.B. Thiessen, L.G. Girling, M.S. Cheang, and W.A. Mutch. 1996. Neurological outcome in a porcine model of descending thoracic aortic surgery. Left atrial-femoral artery bypass versus clamp/repair. Stroke 27: 2095–2100.
Panico, A.M., P. Vicini, G. Massimo, V. Cardile, B. Gentile, S. Avondo, F. Vittorio, and G. Ronsisvalle. 2004. Protective effects of benzisothiazolylamidines on IL-1 beta induced alterations in human articular chondrocyte metabolism. Inflammation 28: 231–235.
Sanchez, C.P., and Y.Z. He. 2002. Alterations in the growth plate cartilage of rats with renal failure receiving corticosteroid therapy. Bone 30: 692–698.
Yao, H.W., J. Li, J.Q. Chen, and S.Y. Xu. 2004. A 771726, the active metabolite of leflunomide, inhibits TNF-alpha and IL-1 from Kupffer cells. Inflammation 28: 97–103.
Theodorou, V., J. Fioramonti, and L. Bueno. 1993. Recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein prevents sensitization and intestinal anaphylaxis in guinea pigs. Life Sciences 53: 733–738.
Fitch, M.T., C. Doller, C.K. Combs, G.E. Landreth, and J. Silver. 1999. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of glial scarring and progressive cavitation: In vivo and in vitro analysis of inflammation-induced secondary injury after CNS trauma. Journal of Neuroscience 19: 8182–8198.
Rapalino, O., O. Lazarov-Spiegler, E. Agranov, G.J. Velan, E. Yoles, M. Fraidakis, A. Solomon, R. Gepstein, A. Katz, M. Belkin, M. Hadani, and M. Schwartz. 1998. Implantation of stimulated homologous macrophages results in partial recovery of paraplegic rats. Nat Med 4: 814–821.
Kamei, N., N. Tanaka, Y. Oishi, T. Hamasaki, K. Nakanishi, N. Sakai, and M. Ochi. 2007. BDNF, NT-3, and NGF released from transplanted neural progenitor cells promote corticospinal axon growth in organotypic cocultures. Spine 32: 1272–1278.
Sasaki, M., C. Radtke, A.M. Tan, P. Zhao, H. Hamada, K. Houkin, O. Honmou, and J.D. Kocsis. 2009. BDNF-hypersecreting human mesenchymal stem cells promote functional recovery, axonal sprouting, and protection of corticospinal neurons after spinal cord injury. The Journal of Neuroscience 29: 14932–14941.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by Dr. Start Fund of Guangxi Medical University (308010) and Research Foundation of Guangxi Education Department (Gui Education200710LX063).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gaofeng Zeng contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, S., Zeng, G., Wei, B. et al. Beneficial Effect of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Protein on Spinal Cord Injury Recovery in the Rat. Inflammation 35, 520–526 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9341-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9341-5