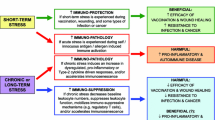
Abstract
The study examined the effects of a social stressor (Trier Social Stress Test) on 24 male and 32 female college students’ affective and physiological reactivity and their subsequent performance on a decision-making task (Iowa Gambling Task). The 56 participants were randomly assigned to a social stressor or a control condition. Compared to controls, participants in the stress condition responded with higher heart rates and skin conductance responses, reported more negative affect, and on the decision-making task made less advantageous choices. An exploratory regression analysis revealed that among men higher levels of heart rate were positively correlated with riskier choices on the Iowa Gambling Task, whereas for women this relationship was curvilinear. Exploratory correlational analyses showed that lower levels of skin conductance within the stress condition were associated with greater levels of substance use and gambling. The results suggest that the presence of a stressor may generally result in failure to attend to the full range of possible consequences of a decision. The relationship pattern between the degree of stress responding and successful decision making may be different for men and women.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechara, A., Damasio, A., Damasio, H., & Anderson, S. (1994). Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition, 50(1–3), 7–15. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(94)90018-3.
Bechara, A., Tranel, D., & Damasio, H. (2000). Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 123(11), 2189–2202. doi:10.1093/brain/123.11.2189.
Benedek, M., & Kaernbach, C. (2010). A continuous measure of phasic electrodermal activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 190, 80–91.
Burdick, J. D., Roy, A. L., & Raver, C. C. (2013). Evaluating the Iowa Gambling Task as a direct assessment of impulsivity with low-income children. Personality and individual differences, 55(7), 771–776.
Carlson, S. M., Zayas, V., & Guthormsen, A. (2009). Neural correlates of decision making on a gambling task. Child development, 80(4), 1076–1096.
Clark, L., & Robbins, T. (2002). Decision-making deficits in drug addiction. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6(9), 361. doi:10.1016/s1364-6613(02)01960-5.
CORE Institute (2004). National Reference Group: Cross- Tabulation. Carbondale, IL: Core Institute.
Critchley, H., Elliott, R., Mathias, C., & Dolan, R. (2000). Neural activity relating to generation and representation of galvanic skin conductance responses: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. The Journal of Neuroscience, 20(8), 3033–3040.
Damasio, A. R. (1994). Descartes’ error: Emotion, reason, and the human brain. New York: Putnam.
Dawson, M. E., Schell, A. M., & Filion, D. L. (2007). The Electrodermal System. In J. T. Cacioppo, L. G. Tassinary, & G. G. Bernston (Eds.), Handbook of psychophysiology (pp. 159–223), New York, NY: Cambridge University.
Dunn, B., Dalgleish, T., & Lawrence, A. (2006). The somatic marker hypothesis: A critical evaluation. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 30(2), 239–271. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.07.001.
Efron, B., & Tibshirani, R. (1993). An introduction to the bootstrap, London: Chapman and Hall.
Eysenck, M. W. (1975). Effects of noise, activation level, and response dominance on retrieval from semantic memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 1(2), 143.
Eysenck, M. W. (1975). Extraversion, arousal, and speed of retrieval from secondary storage1. Journal of Personality, 43(3), 390–401.
Gansler, D. A., Jerram, M. W., Vannorsdall, T. D., & Schretlen, D. J. (2011). Does the Iowa Gambling Task measure executive funciton? Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(8), 706–717.
Goudriaan, A., Oosterlaan, J., de Beurs, E., & van den Brink, W. (2005). Decision making in pathological gambling: A comparison between pathological gamblers, alcohol dependents, persons with Tourette syndrome, and normal controls. Cognitive Brain Research, 23(1), 137–151. doi:10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2005.01.017.
Goudriaan, A., Oosterlaan, J., de Beurs, E., & van den Brink, W. (2006). Psychophysiological determinants and concomitants of deficient decision making in pathological gamblers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 84(3), 231–239. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.02.007.
Gullo, M. J., & Stieger, A. A. (2011). Anticipatory stress restores decision-making deficits in heavy drinkers by increasing sensitivity to losses. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 117(2), 204–210.
Heaney, J., Ginty, A., Carroll, D., & Phillips, A. (2011). Preliminary evidence that exercise dependence is associated with blunted cardiac and cortisol reactions to acute psychological stress. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 79(2), 323–329. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2010.11.010.
Hooper, C. J., Luciana, M., Conklin, H. M., & Yarger, R. S. (2004). Adolescents’ performance on the Iowa Gambling Task: Implications for the development of decision making and ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Developmental Psychology, 40(6), 1148.
Kelly, M. M., Tyrka, A. R., Anderson, G. M., Price, L. H., & Carpenter, L. L. (2008). Sex differences in emotional and physiological responses to the Trier Social Stress Test. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 39(1), 87–98.
Kirschbaum, C., Pirke, K., & Hellhammer, D. (1993). The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’: A tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology, 28(1–2), 76–81.
Kudielka, B. M., Hellhammer, D. H., & Kirschbaum, C. (2007). Ten Years of Research with the Trier Social Stress Test–Revisited. In E. H.-J. P. Winkielman (Ed.), Social neuroscience: Integrating biological and psychological explanations of social behavior (pp. 56–83). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Lawrence, A., Luty, J., Bogdan, N., Sahakian, B., & Clark, L. (2009). Problem gamblers share deficits in impulsive decision-making with alcohol-dependent individuals. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 104(6), 1006–1015. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02533.x.
Mather, M., & Lighthall, N. (2012). Both risk and reward are processed differently in decisions made under stress. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21(2), 36–41. doi:10.1177/0963721411429452.
McEwen, B. (2008). Central effects of stress hormones in health and disease: Understanding the protective and damaging effects of stress and stress mediators. European Journal of Pharmacology, 583(2–3), 174–185. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.071.
Nagai, Y., Critchley, H. D., Featherstone, E., Trimble, M. R., & Dolan, R. J. (2004). Activity in ventromedial prefrontal cortex covaries with sympathetic skin conductance level: A physiological acount of a “default mode” of brain function. NeuroImage, 22, 243–251.
Pabst, S., Brand, M., & Wolf, O. T. (2013). Stress and decision making: A few minutes make all the difference. Behavioral Brain Research, 250, 39–45.
Paris, J., Franco, C., Sodano, R., Frye, C., & Wulfert, E. (2010). Gambling pathology is associated with dampened cortisol response among men and women. Physiology and Behavior, 99(2), 230–233. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2009.04.002.
Presley, C. A., Meilman, P. W., Cashin, J. R., & Lyerla, R. (1993). Alcohol and drugs on American college campuses: Use, consequences, and perceptions of the campus environment: Volume I: 1989–91. Carbondale, IL: Southern Illinois University.
Presley, C. A., Meilman, P. W., & Lyerla, R. (1994). Development of the Core Alcohol and Drug Survey: Initial findings and future directions. Core Institute, Southern Illinois University. Journal of American College Health, 42(6), 248–255.
Preston, S., Buchanan, T., Stansfield, R., & Bechara, A. (2007). Effects of anticipatory stress on decision making in a gambling task. Behavioral Neuroscience, 121(2), 257–263. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.121.2.257.
Shaffer, H. J., LaPlante, D. A., LaBrie, R. A., Kidman, R. C., Donato, A. N., & Stanton, M. V. (2004). Toward a syndrome model of addiction: Multiple expressions, common etiology. Harvard Review of Psychiatry, 12(6), 367–374.
Sherwood, L. (2004). The Peripheral Nervous System: Efferent Division. In Human physiology: From cells to systems (8th edn., pp. 239–256). Belmont, CA; Cengage Learning.
Shurman, B., Horan, W. P., & Nuechterlein, K. H. (2005). Schizophrenia patients demonstrate a distinctive pattern of decision-making impairment on the Iowa Gambling Task. Schizophrenia Research. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2004.03.020.
Sinha, R. (2008). Chronic stress, drug use, and vulnerability to addiction. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1141, 105–130. doi:10.1196/annals.1441.030.
Sinha, R. (2009). Stress and addiction: A dynamic interplay of genes, environment, and drug intake. Biological Psychiatry, 66(2), 100–101. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.05.003.
Sinha, R., Fox, H., Hong, K., Bergquist, K., Bhagwagar, Z., & Siedlarz, K. (2009). Enhanced negative emotion and alcohol craving, and altered physiological responses following stress and cue exposure in alcohol dependent individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 34(5), 1198–1208. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.78.
Sinha, R., Fox, H. C., Hong, K. I. A., Hansen, J., Tuit, K., & Kreek, M. J. (2011). Effects of adrenal sensitivity, stress-and cue-induced craving, and anxiety on subsequent alcohol relapse and treatment outcomes. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68(9), 942–952.
Starcke, K., & Brand, M. (2012). Decision making under stress: A selective review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(4), 1228–1248. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.02.003.
Steingroever, H., Wetzels, R., Horstmann, A., Neumann, J., & Wagenmakers, E. J. (2013). Performance of healthy participants on the Iowa Gambling Task. Psychological Assessment, 25(1), 180.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using Multivariate Statistics (6th edn.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Thayer, J., & Lane, R. (2009). Claude Bernard and the heart-brain connection: Further elaboration of a model of neurovisceral integration. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(2), 81–88. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.08.004.
Thomas, S., Bacon, A., Sinha, R., Uhart, M., & Adinoff, B. (2012). Clinical laboratory stressors used to study alcohol-stress relationships. Alcohol Research-Current Reviews, 34(4), 459–467.
Turpin, G., & Grandfield, T. (2009). Electrodermal Activity. In G. Fink (Ed.), Stress Science: Neuroendocrinology (1st edn., pp. 313–316), London: Academic Press.
van den Bos, R., Harteveld, M., & Stoop, H. (2009). Stress and decision-making in humans: Performance is related to cortisol reactivity, albeit differently in men and women. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 34(10), 1449–1458. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.04.016.
Verdejo-Garcia, A., Benbrook, A., Funderburk, F., David, P., Cadet, J.-L., & Bolla, K. (2007). The differential relationship between cocaine use and marijuana use on decision-making performance over repeat testing with the Iowa Gambling Task. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 90(1), 2–11. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.02.004.
Watson, D., Clark, L., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070.
Wemm, S., Fanean, A., Baker, A., Blough, E., Mewaldt, S., & Bardi, M. (2013). Problematic drinking and physiological responses among female college students. Alcohol (Fayetteville, N. Y.), 47(2), 149–157. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2012.12.006.
Yerkes, R. M., & Dodson, J. D. (1908). The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation. Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology, 18(5), 459–482.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wemm, S.E., Wulfert, E. Effects of Acute Stress on Decision Making. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 42, 1–12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-016-9347-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-016-9347-8