Abstract
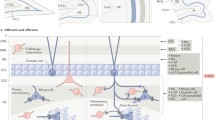
Hilar mossy cells (MCs) of the dentate gyrus (DG) distinguish the DG from other hippocampal subfields (CA1–3) because there are two glutamatergic cell types in the DG rather than one. Thus, in the DG, the main cell types include glutamatergic granule cells (GCs) and MCs, whereas in CA1–3, the only glutamatergic cell type is the pyramidal cell. In contrast to GCs, MCs are different in morphology, intrinsic electrophysiological properties, afferent input and axonal projections, so their function is likely to be very different from GCs. Why are MCs necessary to the DG? In past studies, the answer has been unclear because MCs not only excite GCs directly but also inhibit them disynaptically, by exciting GABAergic neurons that project to GCs. Results of new studies are discussed that shed light on this issue. These studies take advantage of recently available transgenic mice with Cre recombinase expression mostly in MCs and techniques such as optogenetics and DREADDs (designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs). The recent studies also address in vivo behavioral functions of MCs. Some of the results support past hypotheses whereas others suggest new conceptualizations of how the MCs contribute to DG circuitry and function. While substantial progess has been made, additional research is still needed to clarify the characteristics and functions of these unique cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral D (1978) A golgi study of cell types in the hilar region of the hippocampus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 15:851–914
Assaf SY, Miller JJ (1981) Commissural potentiation of perforant path evoked responses in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:1117–1121
Bekenstein JW, Lothman EW (1993) Dormancy of inhibitory interneurons in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Science 259:97–100
Berger TW, Semple-Rowland S, Basset JL (1981) Hippocampal polymorph neurons are the cells of origin for ipsilateral association and commissural afferents to the dentate gyrus. Brain Res 215:329–336
Bernard C, Esclapez M, Hirsch JC, Ben-Ari Y (1998) Interneurones are not so dormant in temporal lobe epilepsy: a critical reappraisal of the dormant basket cell hypothesis. Epilepsy Res 32:93–103
Bilkey DK, Goddard GV (1987) Septohippocampal and commissural pathways antagonistically control inhibitory interneurons in the dentate gyrus. Brain Res 405:320–325
Blackstad JB, Osen KK, Scharfman HE, Storm-Mathisen J, Blackstad TW, Leergaard TB (2015) Observations on hippocampal mossy cells in mink (Neovison vison) with special reference to dendrites ascending to the granular and molecular layers. Hippocampus 26:229–245
Blackstad JS, Osen KK, Scharfman HE, Storm-Mathisen J, Blackstad TW, Leergaard TB (2016) Observations on hippocampal mossy cells in mink (neovison vison) with special reference to dendrites ascending to the granular and molecular layers. Hippocampus 26:229–245
Buckmaster PS, Jongen-Relo AL (1999) Highly specific neuron loss preserves lateral inhibitory circuits in the dentate gyrus of kainate-induced epileptic rats. J Neurosci 19:9519–9529
Buckmaster PS, Strowbridge BW, Kunkel DD, Schmiege DL, Schwartzkroin PA (1992) Mossy cell axonal projections to the dentate gyrus molecular layer in the rat hippocampal slice. Hippocampus 2:349–362
Buckmaster PS, Wenzel HJ, Kunkel DD, Schwartzkroin PA (1996) Axon arbors and synaptic connections of hippocampal mossy cells in the rat in vivo. J Comp Neurol 366:271–292
Buzsaki G, Czeh G (1981) Commissural and perforant path interactions in the rat hippocampus. Field potentials and unitary activity. Exp Brain Res 43:429–438
Buzsaki G, Eidelberg E (1981) Commissural projection to the dentate gyrus of the rat: evidence for feed-forward inhibition. Brain Res 230:346–350
Chancey JH, Poulsen DJ, Wadiche JI, Overstreet-Wadiche L (2014) Hilar mossy cells provide the first glutamatergic synapses to adult-born dentate granule cells. J Neurosci 34:2349–2354
Danielson NB, Turi GF, Ladow M, Chavlis S, Petrantonakis PC, Poirazi P, Losonczy A (2017) In vivo imaging of dentate gyrus mossy cells in behaving mice. Neuron 93:552–559 e554
Deadwyler SA, West JR, Cotman CW, Lynch GS (1975) A neurophysiological analysis of commissural projections to dentate gyrus of the rat. J Neurophysiol 38:167–184
Deller T, Nitsch R, Frotscher M (1995) Phaseolus Vulgaris-leucoagglutinin tracing of commissural fibers to the rat dentate gyrus: evidence for a previously unknown commissural projection to the outer molecular layer. J Comp Neurol 352:55–68
Deller T, Martinez A, Nitsch R, Frotscher M (1996) A novel entorhinal projection to the rat dentate gyrus: direct innervation of proximal dendrites and cell bodies of granule cells and GABAergic neurons. J Neurosci 16:3322–3333
Deller T, Katona I, Cozzari C, Frotscher M, Freund TF (1999) Cholinergic innervation of mossy cells in the rat fascia dentata. Hippocampus 9:314–320
Douglas RM, McNaughton BL, Goddard GV (1983) Commissural inhibition and facilitation of granule cell discharge in fascia dentata. J Comp Neurol 219:285–294
Duffy AM, Schaner MJ, Chin J, Scharfman HE (2013) Expression of c-fos in hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus in vivo. Hippocampus 23:649–655
Etter G, Krezel W (2014) Dopamine D2 receptor controls hilar mossy cells excitability. Hippocampus 24:725–732
Freund TF, Buzsaki G (1996) Interneurons of the hippocampus. Hippocampus 6:347–470
Fricke R, Cowan WM (1978) An autoradiographic study of the commissural and ipsilateral hippocampo-dentate projections in the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 181:253–269
Fujise N, Kosaka T (1999) Mossy cells in the mouse dentate gyrus: identification in the dorsal hilus and their distribution along the dorsoventral axis. Brain Res 816:500–511
Fujise N, Liu Y, Hori N, Kosaka T (1998) Distribution of calretinin immunoreactivity in the mouse dentate gyrus: II. Mossy cells, with special reference to their dorsoventral difference in calretinin immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 82:181–200
Gangarossa G, Longueville S, De Bundel D, Perroy J, Herve D, Girault JA, Valjent E (2012) Characterization of dopamine d1 and D2 receptor-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus 22:2199–2207
Goodman JH, Sloviter RS (1992) Evidence for commissurally projecting parvalbumin-immunoreactive basket cells in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Hippocampus 2:13–21
GoodSmith D, Chen X, Wang C, Kim SH, Song H, Burgalossi A, Christian KM, Knierim JJ (2017) Spatial representations of granule cells and mossy cells of the dentate gyrus. Neuron 93:677–690 e675
Gottlieb DI, Cowan WM (1973) Autoradiographic studies of the commissural and ipsilateral association connection of the hippocampus and detentate gyrus of the rat. I. The commissural connections. J Comp Neurol 149:393–422
Halasy K, Somogyi P (1993) Subdivisions in the multiple GABAergic innervation of granule cells in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 5:411–429
Han ZS, Buhl EH, Lorinczi Z, Somogyi P (1993) A high degree of spatial selectivity in the axonal and dendritic domains of physiologically identified local-circuit neurons in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 5:395–410
Henze DA, Buzsaki G (2007) Hilar mossy cells: functional identification and activity in vivo. Prog Brain Res 163:199–216
Hjorth-Simonsen A, Laurberg S (1977) Commissural connections of the dentate area in the rat. J Comp Neurol 174:591–606
Hosp JA, Struber M, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Vida I, Jonas P, Bartos M (2013) Morpho-physiological criteria divide dentate gyrus interneurons into classes. Hippocampus 24:189–203
Houser CR (2007) Interneurons of the dentate gyrus: an overview of cell types, terminal fields and neurochemical identity. Prog Brain Res 163:217–232
Hsu TT, Lee CT, Tai MH, Lien CC (2016) Differential recruitment of dentate gyrus interneuron types by commissural versus perforant pathways. Cereb Cortex 26:2715–2727
Hyde RA, Strowbridge BW (2012) Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro. Nat Neurosci 15:1430–1438
Jackson MB, Scharfman HE (1996) Positive feedback from hilar mossy cells to granule cells in the dentate gyrus revealed by voltage-sensitive dye and microelectrode recording. J Neurophysiol 76:601–616
Jiao Y, Nadler JV (2007) Stereological analysis of glur2-immunoreactive hilar neurons in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy: correlation of cell loss with mossy fiber sprouting. Exp Neurol 205:569–582
Jinde S, Zsiros V, Jiang Z, Nakao K, Pickel J, Kohno K, Belforte JE, Nakazawa K (2012) Hilar mossy cell degeneration causes transient dentate granule cell hyperexcitability and impaired pattern separation. Neuron 76:1189–1200
Jinde S, Zsiros V, Nakazawa K (2013) Hilar mossy cell circuitry controlling dentate granule cell excitability. Front Neural Circ 7:14
Jinno S, Ishizuka S, Kosaka T (2003) Ionic currents underlying rhythmic bursting of ventral mossy cells in the developing mouse dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 17:1338–1354
Kesner RP (2007) A behavioral analysis of dentate gyrus function. Prog Brain Res 163:567–576
Kesner RP (2017) An analysis of dentate gyrus function (an update). Behav Brain Res 235:73–76
Larimer P, Strowbridge BW (2008) Nonrandom local circuits in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 28:12212–12223
Larimer P, Strowbridge BW (2010) Representing information in cell assemblies: persistent activity mediated by semilunar granule cells. Nat Neurosci 13:213–222
Laurberg S, Sorensen KE (1981) Associational and commissural collaterals of neurons in the hippocampal formation (hilus fasciae dentatae and subfield CA3). Brain Res 212:287–300
Leranth C, Szeidemann Z, Hsu M, Buzsáki G (1996) AMPA receptors in the rat and primate hippocampus: a possible absence of GluR2/3 subunits in most interneurons. Neuroscience 70:631–652
Leutgeb JK, Leutgeb S, Moser M-B, Moser EI (2007) Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus. Science 315:961–966
Li XG, Somogyi P, Ylinen A, Buzsaki G (1994) The hippocampal CA3 network: an in vivo intracellular labeling study. J Comp Neurol 339:181–208
Livsey CT, Vicini S (1992) Slower spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents in spiny versus aspiny hilar neurons. Neuron 8:745–755
Lowenstein DH, Thomas MJ, Smith DH, McIntosh TK (1992) Selective vulnerability of dentate hilar neurons following traumatic brain injury: a potential mechanistic link between head trauma and disorders of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 12:4846–4853
Moretto JN, Duffy AM, Scharfman HE (2017) Acute restraint stress decreases c-fos immunoreactivity in hilar mossy cells of the adult dentate gyrus. Brain Struct Funct 222:2405–2419
Morgan RJ, Santhakumar V, Soltesz I (2007) Modeling the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:639–658
Myers CE, Scharfman HE (2009) A role for hilar cells in pattern separation in the dentate gyrus: a computational approach. Hippocampus 19:321–337
Myers CE, Scharfman HE (2011) Pattern separation in the dentate gyrus: a role for the CA3 backprojection. Hippocampus 21:1190–1215
Nakazawa K (2017) Dentate mossy cell and pattern separation. Neuron 93:1236
Ratzliff AH, Howard AL, Santhakumar V, Osapay I, Soltesz I (2004) Rapid deletion of mossy cells does not result in a hyperexcitable dentate gyrus: implications for epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 24:2259–2269
Ribak CE, Seress L, Peterson GM, Seroogy KB, Fallon JH, Schmued LC (1986) A GABAergic inhibitory component within the hippocampal commissural pathway. J Neurosci 6:3492–3498
Santhakumar V, Bender R, Frotscher M, Ross ST, Hollrigel GS, Toth Z, Soltesz I (2000) Granule cell hyperexcitability in the early post-traumatic rat dentate gyrus: the ‘irritable mossy cell’ hypothesis. J Physiol 524:117–134
Scharfman HE (1991) Dentate hilar cells with dendrites in the molecular layer have lower thresholds for synaptic activation by perforant path than granule cells. J Neurosci 11:1660–1673
Scharfman HE (1992) Differentiation of rat dentate neurons by morphology and electrophysiology in hippocampal slices: granule cells, spiny hilar cells and aspiny ‘fast-spiking’ cells. Epilepsy Res Suppl 7:93–109
Scharfman HE (1993) Characteristics of spontaneous and evoked epsps recorded from dentate spiny hilar cells in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 70:742–757
Scharfman HE (1994a) Evidence from simultaneous intracellular recordings in rat hippocampal slices that area CA3 pyramidal cells innervate dentate hilar mossy cells. J Neurophysiol 72:2167–2180
Scharfman HE (1994b) Epsps of dentate gyrus granule cells during epileptiform bursts of dentate hilar “mossy” cells and area CA3 pyramidal cells in disinhibited rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 14:6041–6057
Scharfman HE (1995a) Electrophysiological diversity of pyramidal-shaped neurons at the granule cell layer/hilus border of the rat dentate gyrus recorded in vitro. Hippocampus 5:287–305
Scharfman HE (1995b) Electrophysiological evidence that dentate hilar mossy cells are excitatory and innervate both granule cells and interneurons. J Neurophysiol 74:179–194
Scharfman HE (1999) The role of nonprincipal cells in dentate gyrus excitability and its relevance to animal models of epilepsy and temporal lobe epilepsy. Adv Neurol 79:805–820
Scharfman HE (2007) The CA3 “backprojection” to the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:627–637
Scharfman HE (2016) The enigmatic mossy cell of the dentate gyrus. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:562–575
Scharfman HE, Myers CE (2013) Hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus: a historical perspective. Front Neural Circ 6:106
Scharfman H, Schwartzkroin P (1988) Electrophysiology of morphologically identified mossy cells of the dentate hilus recorded in guinea pig hippocampal slices. J Neurosci 8:3819–3821
Scharfman HE, Kunkel DD, Schwartzkroin PA (1990) Synaptic connections of dentate granule cells and hilar neurons: results of paired intracellular recordings and intracellular horseradish peroxidase injections. Neuroscience 37:693–707
Senzai Y, Buzsaki G (2017) Physiological properties and behavioral correlates of hippocampal granule cells and mossy cells. Neuron 93:691–704 e695
Seress L, Ribak CE (1983) GABAergic cells in the dentate gyrus appear to be local circuit and projection neurons. Exp Brain Res 50:173–182
Sloviter R (1983) “Epileptic” brain damage in rats induced by sustained electrical stimulation of the perforant path. I. Acute electrophysiological and light microscopical studies. Brain Res Bull 10:675–697
Sloviter R (1987) Decreased hippocampal inhibition and a selective loss of intemeurons in experimental epilepsy. Science 235:73–76
Sloviter RS (1989) Calcium-binding protein (calbindin-d28k) and parvalbumin immunocytochemistry: localization in the rat hippocampus with specific reference to the selective vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to seizure activity. J Comp Neurol 280:183–196
Sloviter RS (1991) Permanently altered hippocampal structure, excitability, and inhibition after experimental status epilepticus in the rat: the “dormant basket cell” hypothesis and its possible relevance to temporal lobe epilepsy. Hippocampus 1:41–66
Sloviter RS (1994) The functional organization of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and its relevance to the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 35:640–654
Sloviter RS, Bumanglag AV, Schwarcz R, Frotscher M (2012) Abnormal dentate gyrus network circuitry in temporal lobe epilepsy. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV (eds) Jasper’s basic mechanisms of the epilepsies [Internet]. 4th edition. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US), Bethesda, p 454–469
Soriano E, Frotscher M (1994) Mossy cells of the rat fascia dentata are glutamate-immunoreactive. Hippocampus 4:65–69
Steward O, White WF, Cotman CW (1977) Potentiation of the excitatory synaptic action of commissural, associational and entorhinal afferents to dentate granule cells. Brain Res 134:551–560
Sun Y, Grieco SF, Holmes TC, Xu X (2017) Local and long-range circuit connections to hilar mossy cells in the dentate gyrus. ENEURO. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0097-17.2017
Weeden CS, Hu NJ, Ho LU, Kesner RP (2014) The role of the ventral dentate gyrus in olfactory pattern separation. Hippocampus 24:553–559
Willaims PA, Larimer P, Gao X, Strowbridge BW (2007) Semilunar granule cells: glutamatergic neurons in the rat dentate gyrus with axon collaterals in the inner molecular layer. J Neurosci 27:13756–13761
Zappone CA, Sloviter RS (2004) Translamellar disinhibition in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus after seizure-induced degeneration of vulnerable hilar neurons. J Neurosci 24:853–864
Zimmer J (1971) Ipsilateral afferents to the commissural zone of the fascia dentata, demonstrated in decommissurated rats by silver impregnation. J Comp Neurol 142:393–416
Acknowledgements
NIH R01 MH-09305, NS-081203, NS-093991 and the New York State Office of Mental Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scharfman, H.E. Advances in understanding hilar mossy cells of the dentate gyrus. Cell Tissue Res 373, 643–652 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2750-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2750-5