Abstract
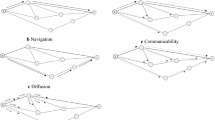
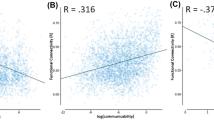
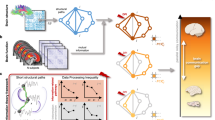
Computational analysis of communication efficiency of brain networks often relies on graph-theoretic measures based on the shortest paths between network nodes. Here, we explore a communication scheme that relaxes the assumption that information travels exclusively through optimally short paths. The scheme assumes that communication between a pair of brain regions may take place through a path ensemble comprising the k-shortest paths between those regions. To explore this approach, we map path ensembles in a set of anatomical brain networks derived from diffusion imaging and tractography. We show that while considering optimally short paths excludes a significant fraction of network connections from participating in communication, considering k-shortest path ensembles allows all connections in the network to contribute. Path ensembles enable us to assess the resilience of communication pathways between brain regions, by measuring the number of alternative, disjoint paths within the ensemble, and to compare generalized measures of path length and betweenness centrality to those that result when considering only the single shortest path between node pairs. Furthermore, we find a significant correlation, indicative of a trade-off, between communication efficiency and resilience of communication pathways in structural brain networks. Finally, we use k-shortest path ensembles to demonstrate hemispherical lateralization of efficiency and resilience.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelnour F, Voss HU, Raj A (2014) Network diffusion accurately models the relationship between structural and functional brain connectivity networks. Neuroimage 90:335–347
Achard S, Bullmore E (2007) Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Comput Biol 3(2):e17–e17
Achard S, Salvador R, Whitcher B, Suckling J, Bullmore ED (2006) A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J Neurosci 26(1):63–72
Avena-Koenigsberger A, Goñi J, Betzel RF, van den Heuvel MP, Griffa A, Hagmann P, Sporns O (2014) Using Pareto optimality to explore the topology and dynamics of the human connectome. Philos Trans Royal Soc B Biol Sci 369(1653):20130530
Barthélemy M (2011) Spatial networks. Phys Rep 499(1):1–101
Bassett DS, Bullmore ED (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12(6):512–523
Bassett DS, Greenfield DL, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Moore SW, Bullmore ET (2010) Efficient physical embedding of topologically complex information processing networks in brains and computer circuits. PLoS Comput Biol 6(4):e1000748
Betzel RF, Byrge L, He Y, Goñi J, Zuo XN, Sporns O (2014) Changes in structural and functional connectivity among resting-state networks across the human lifespan. NeuroImage 102:345–357
Betzel RF, Avena-Koenigsberger A, Goñi J, He Y, de Reus MA, Griffa A, van den Heuvel M (2016) Generative models of the human connectome. Neuroimage 124:1054–1064
Biggs N, Lloyd EK, Wilson RJ (1976) Graph theory 1736–1936. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Boguña M, Krioukov D, Claffy KC (2009) Navigability of complex networks. Nat Phys 5(1):74–80
Borgatti SP (2005) Centrality and network flow. Soc Netw 27(1):55–71
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2012) The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(5):336–349
Buzsáki G, Mizuseki K (2014) The log-dynamic brain: how skewed distributions affect network operations. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(4):264–278
Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meskaldji D, Thiran JP, Sporns O, Do KQ, Maeder P, Meuli R, Hagmann P (2012) Mapping the human connectome at multiple scales with diffusion spectrum MRI. J Neurosci Methods 203:386–397
Chung FR (1997) Spectral graph theory, vol 92. American Mathematical Society
Collin G, Sporns O, Mandl RC, van den Heuvel MP (2014) Structural and functional aspects relating to cost and benefit of rich club organization in the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 24(9):2258–2267
Cormen TH, Leiserson CE, Rivest RL, Stein C (2001) Introduction to algorithms, vol 6. MIT press, Cambridge
da Fontoura Costa L, Travieso G (2007) Exploring complex networks through random walks. Phys Rev E 75(1):016102
Daducci A, Gerhard S, Griffa A, Lemkaddem A, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meuli R, Hagmann P, Thiran JP (2012) The connectome mapper: an open-source processing pipeline to map connectomes with MRI. PLoS One 7:e48121
Desikan RS, Ségonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Albert MS (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31(3):968–980
Estrada E, Hatano N (2008) Communicability in complex networks. Phys Rev E 77(3):036111
Ford LR Jr, Fulkerson DR (1987) Maximal flow through a network. Classic papers in combinatorics. Birkhäuser, Boston, pp 243–248
Friston KJ (2011) Functional and effective connectivity: a review. Brain Connect 1(1):13–36
Galán RF (2008) On how network architecture determines the dominant patterns of spontaneous neural activity. PLoS One 3(5):e2148
Gallos LK, Makse HA, Sigman M (2012) A small world of weak ties provides optimal global integration of self-similar modules in functional brain networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(8):2825–2830
Gong G, Rosa-Neto P, Carbonell F, Chen ZJ, He Y, Evans AC (2009) Age-and gender-related differences in the cortical anatomical network. J Neurosci 29(50):15684–15693
Goñi J, Avena-Koenigsberger A, de Mendizabal NV, van den Heuvel M, Betzel R, Sporns O (2013) Exploring the morphospace of communication efficiency in complex networks. PLoS One 8(3):e58070
Goñi J, van den Heuvel MP, Avena-Koenigsberger A, de Mendizabal NV, Betzel RF, Griffa A, Sporns O (2014) Resting-brain functional connectivity predicted by analytic measures of network communication. Proc Nat Acad Sci 111(2):833–838
Gotts SJ, Jo HJ, Wallace GL, Saad ZS, Cox RW, Martin A (2013) Two distinct forms of functional lateralization in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(36):E3435–E3444
Grinstead CM, Snell JL (2012) Introduction to probability. American Mathematical Society
Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Meuli R, Honey CJ, Wedeen VJ, Sporns O (2008) Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol 6:e159
Hermundstad AM, Bassett DS, Brown KS, Aminoff EM, Clewett D, Freeman S, Frithsen A, Johnson A, Tipper CM, Miller MB, Grafton ST, Carlson JM (2013) Structural foundations of resting-state and task-based functional connectivity in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(15):6169–6174
Honey CJ, Sporns O, Cammoun L, Gigandet X, Thiran JP, Meuli R, Hagmann P (2009) Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(6):2035–2040
Iturria-Medina Y, Fernández AP, Morris DM, Canales-Rodríguez EJ, Haroon HA, Pentón LG, Melie-García L (2011) Brain hemispheric structural efficiency and interconnectivity rightward asymmetry in human and nonhuman primates. Cereb Cortex 21(1):56–67
Jones DK, Knösche TR, Turner R (2013) White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: the do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 73:239–254
Joyce KE, Laurienti PJ, Burdette JH, Hayasaka S (2010) A new measure of centrality for brain networks. PLoS One 5(8):e12200
Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2006) Nonoptimal component placement, but short processing paths, due to long-distance projections in neural systems. PLoS Comput Biol 2(7):e95–e95
Kaiser M, Martin R, Andras P, Young MP (2007) Simulation of robustness against lesions of cortical networks. Eur J Neurosci 25(10):3185–3192
Latora V, Marchiori M (2001) Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 87(19):198701
Liu H, Stufflebeam SM, Sepulcre J, Hedden T, Buckner RL (2009) Evidence from intrinsic activity that asymmetry of the human brain is controlled by multiple factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(48):20499–20503
Lynall ME, Bassett DS, Kerwin R, McKenna PJ, Kitzbichler M, Muller U, Bullmore E (2010) Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 30(28):9477–9487
Markov NT, Ercsey-Ravasz MM, Gomes AR, Lamy C, Magrou L, Vezoli J, Sallet J (2012) A weighted and directed interareal connectivity matrix for macaque cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. bhs270
Masel J, Trotter MV (2010) Robustness and evolvability. Trends Genet 26(9):406–414
McGhee GR (2006) The geometry of evolution: adaptive landscapes and theoretical morphospaces. Cambridge University Press, England
Mišić B, Sporns O, McIntosh AR (2014) Communication efficiency and congestion of signal traffic in large-scale brain networks. PLoS Comput Biol 10(1):e1003427
Mišić B, Betzel RF, Nematzadeh A, Goñi J, Griffa A, Hagmann P, Sporns O (2015) Cooperative and competitive spreading dynamics on the human connectome. Neuron 86(6):1518–1529
Newman ME (2005) A measure of betweenness centrality based on random walks. Soc Netw 27(1):39–54
Park HJ, Friston K (2013) Structural and functional brain networks: from connections to cognition. Science 342(6158):1238411
Passingham RE, Stephan KE, Kötter R (2002) The anatomical basis of functional localization in the cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(8):606–616
Powell JL, Kemp GJ, García-Finaña M (2012) Association between language and spatial laterality and cognitive ability: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 59(2):1818–1829
Rosvall M, Grönlund A, Minnhagen P, Sneppen K (2005) Searchability of networks. Phys Rev E 72(4):046117
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52(3):1059–1069
Seghier ML, Josse G, Leff AP, Price CJ (2011) Lateralization is predicted by reduced coupling from the left to right prefrontal cortex during semantic decisions on written words. Cereb Cortex 21(7):1519–1531
Shoval O, Sheftel H, Shinar G, Hart Y, Ramote O, Mayo A, Alon U (2012) Evolutionary trade-offs, Pareto optimality, and the geometry of phenotype space. Science 336(6085):1157–1160
Simas T, Rocha LM (2015) Distance closures on complex networks. Netw Sci 3(02):227–268
Smith SM, Fox PT, Miller KL, Glahn DC, Fox PM, Mackay CE, Filippini N, Watkins KE, Toro R, Laird AR, Beckmann CF (2009) Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(31):13040–13045
Sporns O (2013) Network attributes for segregation and integration in the human brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol 23(2):162–171
Sporns O, Tononi G, Kötter R (2005) The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput Biol 1(4):e42
Sporns O, Honey CJ, Kötter R (2007) Identification and classification of hubs in brain networks. PLoS One 2(10):e1049–e1049
Stern Y, Habeck C, Moeller J, Scarmeas N, Anderson KE, Hilton HJ, van Heertum R (2005) Brain networks associated with cognitive reserve in healthy young and old adults. Cereb Cortex 15(4):394–402
Thomas C, Frank QY, Irfanoglu MO, Modi P, Saleem KS, Leopold DA, Pierpaoli C (2014) Anatomical accuracy of brain connections derived from diffusion MRI tractography is inherently limited. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(46):16574–16579
Tombu MN, Asplund CL, Dux PE, Godwin D, Martin JW, Marois R (2011) A unified attentional bottleneck in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(33):13426–13431
Tononi G, Sporns O, Edelman GM (1994) A measure for brain complexity: relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91(11):5033–5037
van den Heuvel MP, Sporns O (2011) Rich-club organization of the human connectome. J Neurosci 31(44):15775–15786
van den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Pol HEH (2009) Efficiency of functional brain networks and intellectual performance. J Neurosci 29(23):7619–7624
van den Heuvel MP, Kahn RS, Goñi J, Sporns O (2012) High-cost, high-capacity backbone for global brain communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(28):11372–11377
Van Essen DC, Glasser MF, Dierker DL, Harwell J, Coalson T (2012) Parcellations and hemispheric asymmetries of human cerebral cortex analyzed on surface-based atlases. Cereb Cortex 22(10):2241–2262
Vértes PE, Alexander-Bloch AF, Gogtay N, Giedd JN, Rapoport JL, Bullmore ET (2012) Simple models of human brain functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(15):5868–5873
Wedeen VJ, Wang RP, Schmahmann JD, Benner T, Tseng WYI, Dai G, Pandya DN, Hagmann P, D’Arceuil H, de Crespigny AJ (2008) Diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI) tractography of crossing fibers. Neuroimage 41:1267–1277
Yan C, Gong G, Wang J, Wang D, Liu D, Zhu C, He Y (2011) Sex-and brain size–related small-world structural cortical networks in young adults: a DTI tractography study. Cereb Cortex 21(2):449–458
Yen JY (1971) Finding the k shortest loopless paths in a network. Manage Sci 17(11):712–716
Yeo BT, Krienen FM, Sepulcre J, Sabuncu MR, Lashkari D, Hollinshead M, Roffman JL, Smoller JW, Zöllei L, Polimeni JR, Fischl B, Liu H, Buckner RL (2011) The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol 106(3):1125–1165
Yoo SW, Han CE, Shin JS, Seo SW, Na DL, Kaiser M, Seong JK (2015) A network flow-based analysis of cognitive reserve in normal ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Scientific reports 5:10057
Zuo XN, Ehmke R, Mennes M, Imperati D, Castellanos FX, Sporns O, Milham MP (2012) Network centrality in the human functional connectome. Cereb Cortex 22(8):1862–1875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments of comparable ethical standards.
Funding statement
B.M. was supported by a Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada postdoctoral fellowship. A.G. and P.H. were supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (#310030-156874, NCCR-Synapsy 51AU40_125759), the Center for Biomedical Imaging (CIBM) of the Geneva-Lausanne Universities and EPFL, Leenaards Foundation, and Louis-Jeantet Foundation. J.G. was supported by the National Institute of Health (1R01 MH108467-01). O.S. was supported by the J.S. McDonnell Foundation (220020387), the National Science Foundation (1212778), and the National Institutes of Health (R01 AT009036-01).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avena-Koenigsberger, A., Mišić, B., Hawkins, R.X.D. et al. Path ensembles and a tradeoff between communication efficiency and resilience in the human connectome. Brain Struct Funct 222, 603–618 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1238-5