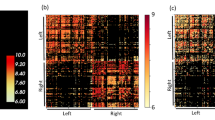
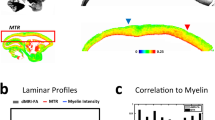
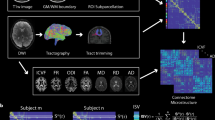
Abstract
The understanding of the relationship between structure and function has always characterized biology in general and neurobiology in particular. One such fundamental relationship is that between axon diameter and the axon’s conduction velocity (ACV). Measurement of these neuronal properties, however, requires invasive procedures that preclude direct elucidation of this relationship in vivo. Here we demonstrate that diffusion-based MRI is sensitive to the fine microstructural elements of brain wiring and can be used to quantify axon diameter in vivo. Moreover, we demonstrate the in vivo correlation between the diameter of an axon and its conduction velocity in the human brain. Using AxCaliber, a novel magnetic resonance imaging technique that enables us to estimate in vivo axon diameter distribution (ADD) and by measuring the interhemispheric transfer time (IHTT) by electroencephalography, we found significant linear correlation, across a cohort of subjects, between brain microstructure morphology (ADD) and its physiology (ACV) in the tactile and visual sensory domains. The ability to make a quantitative assessment of a fundamental physiological property in the human brain from in vivo measurements of ADD may shed new light on neurological processes occurring in neuroplasticity as well as in neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboitiz F, Scheibel a B, Fisher RS, Zaidel E (1992) Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res 598:143–53
Aboitiz F, López J, Montiel J (2003) Long distance communication in the human brain: timing constraints for inter-hemispheric synchrony and the origin of brain lateralization. Biol Res 36:89–99
Alexander DC, Hubbard PL, Hall MG et al (2010) Orientationally invariant indices of axon diameter and density from diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 52:1374–1389
Andreassi JL, Okamura H, Steam M (1975) Hemispheric asymmetries in the visual cortical evoked potential as a function of stimulus locations. Psychophysiology 12:541–546
Arbuthnott ER, Boyd IA, Kalu KU (1980) Ultrastructural dimensions of myelinated peripheral nerve fibres in the cat and their relation to conduction velocity. J Physiol 308:125–157
Assaf Y, Basser PJ (2005) Composite hindered and restricted model of diffusion (CHARMED) MR imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 27:48–58
Assaf Y, Pasternak O (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: a review. J Mol Neurosci 34:51–61. doi:10.1007/s12031-007-0029-0
Assaf Y, Freidlin RZ, Rohde GK, Basser PJ (2004) New modeling and experimental framework to characterize hindered and restricted water diffusion in brain white matter. Magn Reson Med 52:965–978
Assaf Y, Blumenfeld-Katzir T, Yovel Y, Basser PJ (2008) AxCaliber: a method for measuring axon diameter distribution from diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med 59:1347–1354. doi:10.1002/mrm.21577
Barazany D, Basser PJ, Assaf Y (2009) In vivo measurement of axon diameter distribution in the corpus callosum of rat brain. Brain 132:1210–1220. doi:10.1093/brain/awp042
Basser PJ, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C et al (2000) In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn Reson Med 44:625–632
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455. doi:10.1002/nbm.782
Ben-Amitay S, Jones DK, Assaf Y (2012) Motion correction and registration of high b-value diffusion weighted images. Magn Reson Med 67(6):s1694–1702
Braun CM (1992) Estimation of interhemispheric dynamics from simple unimanual reaction time to extrafoveal stimuli. Neuropsychol Rev 3:321–365
Brown WS, Jeeves MA (1993) Bilateral visual field processing and evoked potential interhemispheric transmission time. Neuropsychologia 31:1267–1281
Brown WS, Larson EB, Jeeves MA (1994) Directional asymmetries in interhemispheric transmission time: evidence from visual evoked potentials. Neuropsychologia 32:439–448. doi:10.1016/0028-3932(94)90089-2
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2009) Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:186–198. doi:10.1038/nrn2575
Coleman M (2005) Axon degeneration mechanisms: commonality amid diversity. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:889–898
Cornblath DR, Kuncl RW, Mellits ED et al (1992) Nerve conduction studies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 15:1111–1115
Cowan JM, Rothwell JC, Dick JP et al (1984) Central motor conduction in multiple sclerosis. Lance 2:304–307
Lifshits S, Horowitz A, Barazany D, Rosset S, Assaf Y (2013) Classification of axon diameter properties using machine learning. In: Proc 21st Annu Meets ISMRM
Dawson GD (1956) The relative excitability and conduction velocity of sensory and motor nerve fibres in man. J Physiol 131:436–45I
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–21
Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen J, Santhakumar V, Morgan RJ et al (2007) Topological determinants of epileptogenesis in large-scale structural and functional models of the dentate gyrus derived from experimental data. J Neurophysiol 97:1566–1587. doi:10.1152/jn.00950.2006
Fendrich R, Hutsler JJ, Gazzaniga MS (2004) Visual and tactile interhemispheric transfer compared with the method of Poffenberger. Exp Brain Res 158:67–74
Ferguson B, Matyszak MK, Esiri MM, Perry VH (1997) Axonal damage in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain A J Neurol 120s(Pt 3):393–399
Fields RD (2008) White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci 31:361–370
Frye RE, Hasan K, Malmberg B, et al. (2010) Superior longitudinal fasciculus and cognitive dysfunction in adolescents born preterm and at term. Dev Med Child Neurol 52:760–766. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03633.x
Gasser HS, Grundfest H (1939) Axon diameters in relation to the spike dimensions and the conduction velocity in mammalian a fibers. Am J Physiol 393
Goldman L, Albus JS (1968) Computation of impulse conduction in myelinated fibers; theoretical basis of the velocity-diameter relation. Biophys J 8:596–607
Harper AA, Lawson SN (1985) Electrical properties of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones with different peripheral nerve conduction velocities. J Physiol 359:47–63
Hursch J. (1939) Conduction velocity and diameter of nerve fibers. Am J Physiol
Ipata A, Girelli M, Miniussi C, Marzi CA (1997) Interhemispheric transfer of visual information in humans: the role of different callosal channels. Arch Ital Biol 135:169–182
Klingberg T, Hedehus M, Temple E, et al. (2000) Microstructure of temporo-parietal white matter as a basis for reading ability: evidence from diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Neuron 25:493–500
Lebel C, Rasmussen C, Wyper K, et al. (2010) Brain microstructure is related to math ability in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:354–363. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01097.x
Leemans A, Jeurissen B, Sijbers J, Jones D (2009) ExploreDTI: a graphical toolbox for processing, analyzing, and visualizing diffusion MR data. Proc 17th Sci Meet Int Soc Magn Reson Med 3537
Madden DJ, Whiting WL, Huettel SA, et al. (2004) Diffusion tensor imaging of adult age differences in cerebral white matter: relation to response time. Neuroimage 21:1174–1181. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.004
Marzi CA, Bisiacchi P, Nicoletti R (1991) Is interhemispheric transfer of visuomotor information asymmetric? Evidence from a meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia 29:1163–1177
McDonald WI (1974) Pathophysiology in multiple sclerosis. Brain 97:179–196
McNab J a, Edlow BL, Witzel T et al. (2013) The Human Connectome Project and beyond: initial applications of 300 mT/m gradients. Neuroimage 80:234–45. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.074
Moes PE, Brown WS, Minnema MT (2007) Individual differences in interhemispheric transfer time (IHTT) as measured by event related potentials. Neuropsychologia 45:2626–2630. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.03.017
Nowicka A, Grabowska A, Fersten E (1996) Interhemispheric transmission of information and functional asymmetry of the human brain. Neuropsychologia 34:147–151
Odde DJ, Cassimeris L, Buettner HM (1995) Kinetics of microtubule catastrophe assessed by probabilistic analysis. Biophys J 69:796–802
Patton HD (1982) Special properties of nerve trunks and tracts. Physiol Biophys 4
Reed TE, Jensen AR (1992) Conduction velocity in a brain nerve pathway of normal adults correlates with intelligence level. Intelligence 16:259–272
Reese TG, Heid O, Weisskoff RM, Wedeen VJ (2003) Reduction of eddy-current-induced distortion in diffusion MRI using a twice-refocused spin echo. Magn Reson Med 49:177–182
Ritchie JM (1982) On the relation between fibre diameter and conduction velocity in myelinated nerve fibres. Proc R Soc London Ser B Contain Pap a Biol character R Soc Gt Britain 217:29–35
Saron CD, Davidson RJ (1989) Visual evoked potential measures of interhemispheric transfer time in humans. Behav Neurosci 103:1115–1138
Satomi K, Horai T, Kinoshita Y, Wakazono A (1995) Hemispheric asymmetry of event-related potentials in a patient with callosal disconnection syndrome: a comparison of auditory, visual and somatosensory modalities. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94:440–449
Shu Y, Duque A, Yu Y et al (2007) Properties of action-potential initiation in neocortical pyramidal cells: evidence from whole cell axon recordings. J Neurophysiol 97:746–760
Snooks SJ, Swash M (1985) Motor conduction velocity in the human spinal cord: slowed conduction in multiple sclerosis and radiation myelopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:1135–1139
Song S-K, Yoshino J, Le TQ et al (2005) Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. Neuroimage 26:132–140. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.01.028
Tavor I, Yablonski M, Mezer A, et al. (2013) Separate parts of occipito-temporal white matter fibers are associated with recognition of faces and places. Neuroimage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.085
Terry RD, Gonatas NK, Weiss M (1964) Ultrastructural Studies in Alzheimer’s Presenile Dementia. Am J Pathol 44:269–297
Thiebaut de Schotten M, Cohen L, Amemiya E, et al. (2012) Learning to read improves the structure of the arcuate fasciculus. Cereb Cortex 3:1–7. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs383
Trapp BD, Peterson J, Ransohoff RM et al (1998) Axonal transection in the lesions of multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 338:278–285
Van Hecke W, Leemans A, Sijbers J et al (2008) A tracking-based diffusion tensor imaging segmentation method for the detection of diffusion-related changes of the cervical spinal cord with aging. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:978–991
Virtanen J, Uusitalo H, Palkama A, Kaufman H (1984) The effect of fixation on corneal endothelial cell dimensions and morphology in scanning electron microscopy. Acta Ophthalmol 62:577–585
Westerhausen R, Kreuder F, Woerner W et al (2006) Interhemispheric transfer time and structural properties of the corpus callosum. Neurosci Lett 409:140–145. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.09.028
Whitford TJ, Kubicki M, Ghorashi S et al (2011) Predicting inter-hemispheric transfer time from the diffusion properties of the corpus callosum in healthy individuals and schizophrenia patients: a combined ERP and DTI study. Neuroimage 54:2318–2329. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.048
Witelson SF (1989) Hand and sex differences in the isthmus and genu of the human corpus callosum. A postmortem morphological study. Brain A J Neurol 112(Pt 3):799–835
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horowitz, A., Barazany, D., Tavor, I. et al. In vivo correlation between axon diameter and conduction velocity in the human brain. Brain Struct Funct 220, 1777–1788 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0871-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0871-0