Abstract
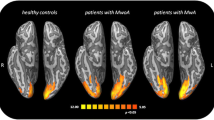
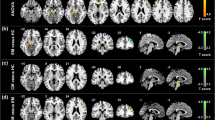
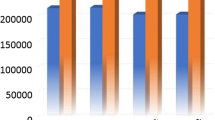
The hippocampus is classically involved in memory consolidation, spatial navigation and is involved in the stress response. Migraine is an episodic disorder characterized by intermittent attacks with a number of physiological and emotional stressors associated with or provoking each attack. Given that migraine attacks can be viewed as repeated stressors, alterations in hippocampal function and structure may play an important role in migraine pathophysiology. Using high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging, hippocampal morphometric and functional differences (in response to noxious heat stimulation) were compared in age and gender-matched acute episodic migraineurs with high (HF) versus low (LF) frequency of migraine attacks. Morphometric results were compared with age and gender-matched healthy control (HC) cohort. Significant larger bilateral hippocampal volume was found in LF group relative to the HF and HC groups suggestive of an initial adaptive plasticity that may then become dysfunctional with increased frequency. Functional correlates of greater deactivation (LF > HF) in the same hippocampal regions in response to noxious stimulation was also accompanied by overall reduction in functional connectivity of the hippocampus with other brain regions involved in pain processing in the HF group. The results implicate involvement of hippocampus in the pathophysiology of the migraine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becerra L, Breiter HC, Wise R, Gonzalez RG, Borsook D (2001) Reward circuitry activation by noxious thermal stimuli. Neuron 32(5):927–946. doi:S0896-6273(01)00533-5
Bigal ME, Serrano D, Buse D, Scher A, Stewart WF, Lipton RB (2008) Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: a longitudinal population-based study. Headache 48(8):1157–1168. doi:HED121710.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01217.x
Bingel U, Wanigasekera V, Wiech K, Ni Mhuircheartaigh R, Lee MC, Ploner M, Tracey I (2011) The effect of treatment expectation on drug efficacy: imaging the analgesic benefit of the opioid remifentanil. Sci Transl Med 3(70):70ra14. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001244
Boshuisen ML, den Boer JA (2000) Zolmitriptan (a 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist with central action) does not increase symptoms in obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152(1):74–79
Bourne JN, Harris KM (2008) Balancing structure and function at hippocampal dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:47–67. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125646
Buckner RL, Head D, Parker J, Fotenos AF, Marcus D, Morris JC, Snyder AZ (2004) A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas-based head size normalization: reliability and validation against manual measurement of total intracranial volume. Neuroimage 23(2):724–738. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.018
Cho K (2001) Chronic ‘jet lag’ produces temporal lobe atrophy and spatial cognitive deficits. Nat Neurosci 4:567–568
Craft RM, Mogil JS, Aloisi AM (2004) Sex differences in pain and analgesia: the role of gonadal hormones. Eur J Pain 8(5):397–411. doi:10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.01.003S1090380104000175
Cupini LM, Calabresi P (2005) Medication-overuse headache: pathophysiological insights. J Headache Pain 6(4):199–202. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0184-z
DaSilva AF, Becerra L, Pendse G, Chizh B, Tully S, Borsook D (2008) Colocalized structural and functional changes in the cortex of patients with trigeminal neuropathic pain. PLoS One 3(10):e3396. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003396
Devanand DP, Pradhaban G, Liu X, Khandji A, De Santi S, Segal S, Rusinek H, Pelton GH, Honig LS, Mayeux R, Stern Y, Tabert MH, de Leon MJ (2007) Hippocampal and entorhinal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: prediction of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 68(11):828–836. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000256697.20968.d7
Dodick DW, Martin V (2004) Triptans and CNS side-effects: pharmacokinetic and metabolic mechanisms. Cephalalgia 24(6):417–424. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00694.xCHA694
Dreier JP (2011) The role of spreading depression, spreading depolarization and spreading ischemia in neurological disease. Nat Med 17(4):439–447. doi:10.1038/nm.2333
Drevets WC, Price JL, Simpson JR Jr, Todd RD, Reich T, Vannier M, Raichle ME (1997) Subgenual prefrontal cortex abnormalities in mood disorders. Nature 386(6627):824–827. doi:10.1038/386824a0
Eichenbaum H, Dudchenko P, Wood E, Shapiro M, Tanila H (1999) The hippocampus, memory, and place cells: is it spatial memory or a memory space? Neuron 23(2):209–226. doi:S0896-6273(00)80773-4
Eikermann-Haerter K, Ayata C (2010) Cortical spreading depression and migraine. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 10(3):167–173. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0099-1
Erickson KI, Voss MW, Prakash RS, Basak C, Szabo A, Chaddock L, Kim JS, Heo S, Alves H, White SM, Wojcicki TR, Mailey E, Vieira VJ, Martin SA, Pence BD, Woods JA, McAuley E, Kramer AF (2011) Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(7):3017–3022. doi:101595010810.1073/pnas.1015950108
Fields HL (1999) Pain: an unpleasant topic. Pain Suppl 6:S61–S69
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, van der Kouwe A, Killiany R, Kennedy D, Klaveness S, Montillo A, Makris N, Rosen B, Dale AM (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33(3):341–355. doi:S089662730200569X
Fischl B, Salat DH, van der Kouwe AJ, Makris N, Segonne F, Quinn BT, Dale AM (2004) Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S69–S84. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.016
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(27):9673–9678. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504136102
Gianaros PJ, Jennings JR, Sheu LK, Greer PJ, Kuller LH, Matthews KA (2007) Prospective reports of chronic life stress predict decreased grey matter volume in the hippocampus. Neuroimage 35:795–803
Gilbertson MW, Shenton ME, Ciszewski A, Kasai K, Lasko NB, Orr SP, Pitman RK (2002) Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma. Nat Neurosci 5(11):1242–1247. doi:10.1038/nn958nn958
Glasper ER, Schoenfeld TJ, Gould E (2011) Adult neurogenesis: optimizing hippocampal function to suit the environment. Behav Brain Res. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.05.013
Golub G, Cv Loan (1996) Matrix computations, 3rd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, London
Hufner K, Binetti C, Hamilton DA, Stephan T, Flanagin VL, Linn J, Labudda K, Markowitsch H, Glasauer S, Jahn K, Strupp M, Brandt T (2010) Structural and functional plasticity of the hippocampal formation in professional dancers and slackliners. Hippocampus. doi:10.1002/hipo.20801
Ising H, Braun C (2000) Acute and chronic endocrine effects of noise: review of the research conducted at the institute for water, soil and air hygiene. Noise Health 2(7):7–24
Khanna S, Sinclair JG (1989) Noxious stimuli produce prolonged changes in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus. Pain 39(3):337–343
Klausberger T (2009) GABAergic interneurons targeting dendrites of pyramidal cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 30(6):947–957. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06913.x
Koolschijn PC, van Haren NE, Cahn W, Schnack HG, Janssen J, Klumpers F, Hulshoff Pol HE, Kahn RS (2010) Hippocampal volume change in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 71(6):737–744. doi:10.4088/JCP.08m04574yel
Kunkler PE, Kraig RP (2003) Hippocampal spreading depression bilaterally activates the caudal trigeminal nucleus in rodents. Hippocampus 13(7):835–844. doi:10.1002/hipo.10139
Leuner B, Gould E (2010) Structural plasticity and hippocampal function. Annu Rev Psychol 61(111–140):C111–C113. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.093008.100359
Liu J, Qin W, Nan J, Li J, Yuan K, Zhao L, Zeng F, Sun J, Yu D, Dong M, Liu P, von Deneen KM, Gong Q, Liang F, Tian J (2011) Gender-related differences in the dysfunctional resting networks of migraine suffers. PLoS One 6(11):e27049. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027049PONE-D-11-10682
Liu MG, Chen J (2009) Roles of the hippocampal formation in pain information processing. Neurosci Bull 25(5):237–266
Maleki N, Linnman C, Brawn J, Burstein R, Becerra L, Borsook D (2012) Her vs. his migraine: multiple sex differences in brain function and structure brain (in press)
Marsland AL, Gianaros PJ, Abramowitch SM, Manuck SB, Hariri AR (2008) Interleukin-6 covaries inversely with hippocampal grey matter volume in middle-aged adults. Biol Psychiatry 64:484–490
McEwen BS (1998) Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators. New Engl J Med 338:171–179
McEwen BS (1999) Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:105–122
McEwen BS (2001) Plasticity of the hippocampus: adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 933:265–277
McEwen BS (2008) Central effects of stress hormones in health and disease: understanding the protective and damaging effects of stress and stress mediators. Eur J Pharmacol 583(2–3):174–185. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.071
McEwen BS (2010) Stress, sex, and neural adaptation to a changing environment: mechanisms of neuronal remodeling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1204 Suppl:E38–E59. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05568.x
McEwen BS, Gianaros P (2010a) Stress- and allostasis-induced brain plasticity. Annu Rev Med. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-052209-100430
McEwen BS, Gianaros PJ (2010b) Central role of the brain in stress and adaptation: links to socioeconomic status, health, and disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 1186:190–222
McKenna JE, Melzack R (1992) Analgesia produced by lidocaine microinjection into the dentate gyrus. Pain 49(1):105–112
Metz AE, Yau HJ, Centeno MV, Apkarian AV, Martina M (2009) Morphological and functional reorganization of rat medial prefrontal cortex in neuropathic pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(7):2423–2428. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809897106
Milde-Busch A, Blaschek A, Heinen F, Borggrafe I, Koerte I, Straube A, Schankin C, von Kries R (2011) Associations between stress and migraine and tension-type headache: results from a school-based study in adolescents from grammar schools in Germany. Cephalalgia 31(7):774–785. doi:10.1177/0333102410390397
Morey RA, Petty CM, Xu Y, Hayes JP, Wagner HR 2nd, Lewis DV, LaBar KS, Styner M, McCarthy G (2009) A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. Neuroimage 45(3):855–866. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.12.033
Moulton EA, Becerra L, Maleki N, Pendse G, Tully S, Hargreaves R, Burstein R, Borsook D (2010) Painful heat reveals hyperexcitability of the temporal pole in interictal and ictal migraine states. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq109
Nason MW Jr, Adhikari A, Bozinoski M, Gordon JA, Role LW (2011) Disrupted activity in the hippocampal-accumbens circuit of type III neuregulin 1 mutant mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(2):488–496. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.180
Niddam DM, Tsai SY, Lu CL, Ko CW, Hsieh JC (2011) Reduced Hippocampal glutamate–glutamine levels in irritable bowel syndrome: preliminary findings using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.120
Nordanskog P, Dahlstrand U, Larsson MR, Larsson EM, Knutsson L, Johanson A (2010) Increase in hippocampal volume after electroconvulsive therapy in patients with depression: a volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study. J ECT 26(1):62–67. doi:10.1097/YCT.0b013e3181a95da800124509-201003000-00017
Pendse G, Borsook D, Becerra L (2009) Enhanced false discovery rate using Gaussian mixture models for thresholding fMRI statistical maps. Neuroimage 47(1):231–261. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.035
Peterlin BL, Katsnelson MJ, Calhoun AH (2009) The associations between migraine, unipolar psychiatric comorbidities, and stress-related disorders and the role of estrogen. Curr Pain Headache Rep 13(5):404–412
Piche M, Arsenault M, Rainville P (2010) Dissection of perceptual, motor and autonomic components of brain activity evoked by noxious stimulation. Pain 149(3):453–462. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.01.005
Ploghaus A, Becerra L, Borras C, Borsook D (2003) Neural circuitry underlying pain modulation: expectation, hypnosis, placebo. Trends Cogn Sci 7(5):197–200.
Ploghaus A, Narain C, Beckmann CF, Clare S, Bantick S, Wise R, Matthews PM, Rawlins JN, Tracey I (2001) Exacerbation of pain by anxiety is associated with activity in a hippocampal network. J Neurosci 21(24):9896–9903.
Prado WA, Roberts MH (1985) An assessment of the antinociceptive and aversive effects of stimulating identified sites in the rat brain. Brain Res 340(2):219–228.
Rains JC (2009) Epidemiology and neurobiology of stress and migraine. Headache 49(9):1391–1394. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01477.x
Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE, Sapolsky RM (2009) The influence of stress hormones on fear circuitry. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:289–313. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135620
Rothman SM, Mattson MP (2010) Adverse stress, hippocampal networks, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med 12(1):56–70. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8107-9
Sapolsky RM (2000) Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57(10):925–935.
Sauro KM, Becker WJ (2009) The stress and migraine interaction. Headache 49(9):1378–1386. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2009.01486.x
Schwartzkroin PA (1994) Role of the hippocampus in epilepsy. Hippocampus 4(3):239–242. doi:10.1002/hipo.450040302
Schwedt TJ, Krauss MJ, Frey K, Gereau RWT (2011) Episodic and chronic migraineurs are hypersensitive to thermal stimuli between migraine attacks. Cephalalgia 31(1):6–12. doi:10.1177/0333102410365108
Segonne F, Dale AM, Busa E, Glessner M, Salat D, Hahn HK, Fischl B (2004) A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI. Neuroimage 22(3):1060–1075. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.032S1053811904001880
Sheline YI (2003) Neuroimaging studies of mood disorder effects on the brain. Biol Psychiat 54:338–352
Starkman MN, Giordani B, Gebrski SS, Berent S, Schork MA, Schteingart DE (1999) Decrease in cortisol reverses human hippocampal atrophy following treatment of Cushing’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 46:1595–1602
Tfelt-Hansen PC (2010) Does sumatriptan cross the blood–brain barrier in animals and man? J Headache Pain 11(1):5–12. doi:10.1007/s10194-009-0170-y
van der Flier WM, Scheltens P (2009) Alzheimer disease: hippocampal volume loss and Alzheimer disease progression. Nat Rev Neurol 5(7):361–362. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2009.94
Woon FL, Sood S, Hedges DW (2010) Hippocampal volume deficits associated with exposure to psychological trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder in adults: a meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34(7):1181–1188. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.06.016
Yeung JC, Yaksh TL, Rudy TA (1977) Concurrent mapping of brain sites for sensitivity to the direct application of morphine and focal electrical stimulation in the production of antinociception in the rat. Pain 4(1):23–40
Zhang D, Snyder AZ, Fox MD, Sansbury MW, Shimony JS, Raichle ME (2008) Intrinsic functional relations between human cerebral cortex and thalamus. J Neurophysiol 100(4):1740–1748. doi:10.1152/jn.90463.2008
Zimmerman ME, Pan JW, Hetherington HP, Lipton ML, Baigi K, Lipton RB (2009) Hippocampal correlates of pain in healthy elderly adults: a pilot study. Neurology 73(19):1567–1570. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c0d454
Acknowledgments
The work was supported in by grants from NIH (K24 NS064050 (NINDS) and R01 NS056195 (NINDS) and R01-NS073997 (NINDS) to DB) and an Investigator Initiated Grant from Merck and Co.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1 – Correlation Between Attacks and the Hippocampus Volume. Significant correlation between the total number of migraine attacks for left hippocampus r = -0.55 (P < 0.009) and for right hippocampus r = -0.468 (P < 0.032) in a separate control cohort of 22 episodic migraineurs (11 male, 11 female).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleki, N., Becerra, L., Brawn, J. et al. Common hippocampal structural and functional changes in migraine. Brain Struct Funct 218, 903–912 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0437-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0437-y