Abstract
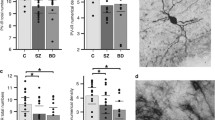
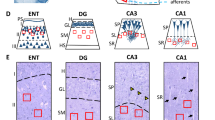
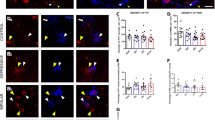
GABAergic interneurons synchronize network activities and monitor information flow. Post-mortem studies have reported decreased densities of cortical interneurons in schizophrenia (SZ) and bipolar disorder (BPD). The entorhinal cortex (EC) and the adjacent subicular regions are a hub for integration of hippocampal and cortical information, a process that is disrupted in SZ. Here we contrast and compare the density of interneuron populations in the caudal EC and subicular regions in BPD type I (BPD-I), SZ, and normal control (NC) subjects. Post-mortem human parahippocampal specimens of 13 BPD-I, 11 SZ and 17 NC subjects were used to examine the numerical density of parvalbumin-, somatostatin- or calbindin-positive interneurons. We observed a reduction in the numerical density of parvalbumin- and somatostatin-positive interneurons in the caudal EC and parasubiculum in BPD-I and SZ, but no change in the subiculum. Calbindin-positive interneuron densities were normal in all brain areas examined. The profile of decreased density was strikingly similar in BPD-I and SZ. Our results demonstrate a specific reduction of parvalbumin- and somatostatin-positive interneurons in the parahippocampal region in BPD-I and SZ, likely disrupting synchronization and integration of cortico-hippocampal circuits.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPD:
-
Bipolar disorder
- SZ:
-
Schizophrenia
- NC:
-
Normal control
- EC:
-
Entorhinal cortex
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- PV:
-
Parvalbumin
- SOM:
-
Somatostatin
- CB:
-
Calbindin
References
Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG et al (1995) Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:258–266
Apergis-Schoute J, Pinto A, Pare D (2006) Ultrastructural organization of medial prefrontal inputs to the rhinal cortices. Eur J Neurosci 24:135–144
Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR (1991) Some cytoarchitectural abnormalities of the entorhinal cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:625–632
Bartos M, Vida I, Jonas P (2007) Synaptic mechanisms of synchronized gamma oscillations in inhibitory interneuron networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:45–56
Beasley CL, Reynolds GP (1997) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons are reduced in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Schizophr Res 24:349–355
Beasley CL, Zhang ZJ, Patten I, Reynolds GP (2002) Selective deficits in prefrontal cortical GABAergic neurons in schizophrenia defined by the presence of calcium-binding proteins. Biol Psychiatry 52:708–715
Beierlein M, Gibson JR, Connors BW (2000) A network of electrically coupled interneurons drives synchronized inhibition in neocortex. Nat Neurosci 3:904–910
Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, SanGiovanni JP, Vincent SL (1991) Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal and cingulate cortices of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:996–1001
Berrettini W (2003) Evidence for shared susceptibility in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 123C:59–64
Bird ED, Spokes EG, Barnes J, MacKay AV, Iversen LL, Shepherd M (1977) Increased brain dopamine and reduced glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acetyl transferase activity in schizophrenia and related psychoses. Lancet 2:1157–1158
Buzsaki G, Chrobak JJ (1995) Temporal structure in spatially organized neuronal ensembles: a role for interneuronal networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:504–510
Carboni AA, Lavelle WG, Barnes CL, Cipolloni PB (1990) Neurons of the lateral entorhinal cortex of the rhesus monkey: a Golgi, histochemical, and immunocytochemical characterization. J Comp Neurol 291:583–608
Cotter D, Landau S, Beasley C et al (2002) The density and spatial distribution of GABAergic neurons, labelled using calcium binding proteins, in the anterior cingulate cortex in major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 51:377–386
Craddock N, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ (2005) The genetics of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: dissecting psychosis. J Med Genet 42:193–204
Daviss SR, Lewis DA (1995) Local circuit neurons of the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: selective increase in the density of calbindin-immunoreactive neurons. Psychiatry Res 59:81–96
De Lacalle S, Lim C, Sobreviela T, Mufson EJ, Hersh LB, Saper CB (1994) Cholinergic innervation in the human hippocampal formation including the entorhinal cortex. J Comp Neurol 345:321–344
DeFelipe J, Hendry SH, Jones EG (1989) Synapses of double bouquet cells in monkey cerebral cortex visualized by calbindin immunoreactivity. Brain Res 503:49–54
DeFelipe J, Hendry SH, Jones EG (1989) Visualization of chandelier cell axons by parvalbumin immunoreactivity in monkey cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2093–2097
Fung SJ, Webster MJ, Sivagnanasundaram S, Duncan C, Elashoff M, Weickert CS (2010) Expression of interneuron markers in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the developing human and in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 167:1479–1488
Fyhn M, Molden S, Witter MP, Moser EI, Moser MB (2004) Spatial representation in the entorhinal cortex. Science 305:1258–1264
Gabriel SM, Davidson M, Haroutunian V et al (1996) Neuropeptide deficits in schizophrenia vs. Alzheimer’s disease cerebral cortex. Biol Psychiatry 39:82–91
Galarreta M, Hestrin S (2002) Electrical and chemical synapses among parvalbumin fast-spiking GABAergic interneurons in adult mouse neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12438–12443
Goldman-Rakic PS, Selemon LD, Schwartz ML (1984) Dual pathways connecting the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex with the hippocampal formation and parahippocampal cortex in the rhesus monkey. Neuroscience 12:719–743
Hashimoto T, Arion D, Unger T et al (2008) Alterations in GABA-related transcriptome in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 13:147–161
Hashimoto T, Bazmi HH, Mirnics K, Wu Q, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2008) Conserved regional patterns of GABA-related transcript expression in the neocortex of subjects with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 165:479–489
Hashimoto T, Volk DW, Eggan SM et al (2003) Gene expression deficits in a subclass of GABA neurons in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. J Neurosci 23:6315–6326
Heckers S, Heinsen H, Geiger B, Beckmann H (1991) Hippocampal neuron number in schizophrenia. A stereological study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:1002–1008
Heckers S, Rauch SL, Goff D et al (1998) Impaired recruitment of the hippocampus during conscious recollection in schizophrenia. Nat Neurosci 1:318–323
Heckers S, Stone D, Walsh J, Shick J, Koul P, Benes FM (2002) Differential hippocampal expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 messenger RNA in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:521–529
Insausti R, Tunon T, Sobreviela T, Insausti AM, Gonzalo LM (1995) The human entorhinal cortex: a cytoarchitectonic analysis. J Comp Neurol 355:171–198
Jakob H, Beckmann H (1986) Prenatal developmental disturbances in the limbic allocortex in schizophrenics. J Neural Transm 65:303–326
Knable MB, Barci BM, Webster MJ, Meador-Woodruff J, Torrey EF (2004) Molecular abnormalities of the hippocampus in severe psychiatric illness: postmortem findings from the Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Mol Psychiatry 9:609–620 544
Konradi C, Eaton M, MacDonald ML, Walsh J, Benes FM, Heckers S (2004) Molecular evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:300–308
Konradi C, Yang CK, Zimmerman EI et al (2011) Hippocampal interneurons are abnormal in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 131:165–173
Konradi C, Zimmerman EI, Yang CK et al (2011) Hippocampal interneurons in bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:340–350
MacDonald ML, Eaton ME, Dudman JT, Konradi C (2005) Antipsychotic drugs elevate mRNA levels of presynaptic proteins in the frontal cortex of the rat. Biol Psychiatry 57:1041–1051
Markram H, Toledo-Rodriguez M, Wang Y, Gupta A, Silberberg G, Wu C (2004) Interneurons of the neocortical inhibitory system. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:793–807
Mikkonen M, Soininen H, Pitkanen A (1997) Distribution of parvalbumin-, calretinin-, and calbindin-D28k-immunoreactive neurons and fibers in the human entorhinal cortex. J Comp Neurol 388:64–88
Morris HM, Hashimoto T, Lewis DA (2008) Alterations in somatostatin mRNA expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Cereb Cortex 18:1575–1587
Nakatani N, Hattori E, Ohnishi T et al (2006) Genome-wide expression analysis detects eight genes with robust alterations specific to bipolar I disorder: relevance to neuronal network perturbation. Hum Mol Genet 15:1949–1962
O’Mara S (2006) Controlling hippocampal output: the central role of subiculum in hippocampal information processing. Behav Brain Res 174:304–312
Pantazopoulos H, Lange N, Baldessarini RJ, Berretta S (2007) Parvalbumin neurons in the entorhinal cortex of subjects diagnosed with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 61:640–652
Sakai T, Oshima A, Nozaki Y et al (2008) Changes in density of calcium-binding-protein-immunoreactive GABAergic neurons in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropathology 28:143–150
Schmidt S, Braak E, Braak H (1993) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive structures of the adult human entorhinal and transentorhinal region. Hippocampus 3:459–470
Thompson M, Weickert CS, Wyatt E, Webster MJ (2009) Decreased glutamic acid decarboxylase (67) mRNA expression in multiple brain areas of patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J Psychiatr Res 43:970–977
Tooney PA, Chahl LA (2004) Neurons expressing calcium-binding proteins in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:273–278
Torrey EF, Barci BM, Webster MJ, Bartko JJ, Meador-Woodruff JH, Knable MB (2005) Neurochemical markers for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression in postmortem brains. Biol Psychiatry 57:252–260
Tunon T, Insausti R, Ferrer I, Sobreviela T, Soriano E (1992) Parvalbumin and calbindin D-28K in the human entorhinal cortex. An immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 589:24–32
van Groen T, Wyss JM (1990) The connections of presubiculum and parasubiculum in the rat. Brain Res 518:227–243
Volk DW, Austin MC, Pierri JN, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2000) Decreased glutamic acid decarboxylase67 messenger RNA expression in a subset of prefrontal cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid neurons in subjects with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:237–245
Weiss AP, Goff D, Schacter DL et al (2006) Fronto-hippocampal function during temporal context monitoring in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 60:1268–1277
Witter MP, Groenewegen HJ, Lopes da Silva FH, Lohman AH (1989) Functional organization of the extrinsic and intrinsic circuitry of the parahippocampal region. Prog Neurobiol 33:161–253
Witter MP, Moser EI (2006) Spatial representation and the architecture of the entorhinal cortex. Trends Neurosci 29:671–678
Witter MP, Wouterlood FG, Naber PA, Van Haeften T (2000) Anatomical organization of the parahippocampal–hippocampal network. Ann N Y Acad Sci 911:1–24
Woo TU, Spencer K, McCarley RW (2010) Gamma oscillation deficits and the onset and early progression of schizophrenia. Harv Rev Psychiatry 18:173–189
Woo TU, Walsh JP, Benes FM (2004) Density of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 messenger RNA-containing neurons that express the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:649–657
Zaitsev AV, Gonzalez-Burgos G, Povysheva NV, Kroner S, Lewis DA, Krimer LS (2005) Localization of calcium-binding proteins in physiologically and morphologically characterized interneurons of monkey dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 15:1178–1186
Zhang ZJ, Reynolds GP (2002) A selective decrease in the relative density of parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the hippocampus in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 55:1–10
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health [MH67999 (SH) and MH068855 (Dr. Benes, HBTRC)]. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding institute or the National Institutes of Health. The authors are indebted to Dr. Gary Van Hoesen who advised on the layers of the parahippocampal regions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, A.Y., Lohmann, K.M., Yang, C.K. et al. Bipolar disorder type 1 and schizophrenia are accompanied by decreased density of parvalbumin- and somatostatin-positive interneurons in the parahippocampal region. Acta Neuropathol 122, 615–626 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0881-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0881-4