Abstract
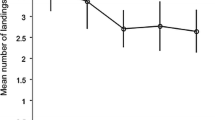
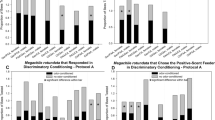
Olfactory learning and memory processes in Drosophila have been well investigated with aversive conditioning, but appetitive conditioning has rarely been documented. Here, we report for the first time individual olfactory conditioning of proboscis activity in restrained Drosophila melanogaster. The protocol was adapted from those developed for proboscis extension conditioning in the honeybee Apis mellifera. After establishing a scale of small proboscis movements necessary to characterize responses to olfactory stimulation, we applied Pavlovian conditioning, with five trials consisting of paired presentation of a banana odour and a sucrose reward. Drosophila showed conditioned proboscis activity to the odour, with a twofold increase of percentage of responses after the first trial. No change occurred in flies experiencing unpaired presentations of the stimuli, confirming an associative basis for this form of olfactory learning. The adenylyl cyclase mutant rutabaga did not exhibit learning in this paradigm. This protocol generated at least a short-term memory of 15 min, but no significant associative memory was detected at 1 h. We also showed that learning performance was dependent on food motivation, by comparing flies subjected to different starvation regimes.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CS:
-
Conditioned stimulus
- US:
-
Unconditioned stimulus
- CR:
-
Conditioned response
- UR:
-
Unconditioned response
- WT:
-
Wild-type
- SOG:
-
Suboesophageal ganglion
- N:
-
No movement
- T:
-
Labellum trembling
- PL:
-
Palp trembling and/or slight extension of the labellum
- E1:
-
Extension of the labellum
- E2:
-
Extension of the labellum and the haustellum
- E3:
-
Complete extension
- Ns:
-
Samples size
References
Ackerman SL, Siegel RW (1986) Chemically reinforced conditioned courtship in Drosophila: responses to wild-type and the dunce, amnesiac and don giovanni mutants. J Neurogenet 3:111–123
Bitterman ME, Menzel R, Fietz A, Schäfer S (1983) Classical conditioning of proboscis extension in honeybees (Apis mellifera). J Comp Psychol 97:107–119
Campan R, Scapini F (2002) Ethologie, approche systématique du comportement. De Boeck Université, Bruxelles, pp 134–136
Dahanukar A, Foster K, van der Goes van Naters WM, Carlson JR (2001) A Gr receptor is required for response to the sugar trehalose in taste neurons of Drosophila. Nat Neurosci 4:1182–1186
Davis RL (2005) Olfactory memory formation in Drosophila: from molecular to systems neuroscience. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:275–302
de Belle SJ, Heisenberg M (1994) Associative odor learning in Drosophila abolished by chemical ablation of mushroom bodies. Science 263(5147):692–695
de Bruyne M, Clyne PJ, Carlson JR (1999) Odor coding in a model olfactory organ: the Drosophila maxillary palp. J Neurosci 19(11):4520–4532
DeJianne D, McGuire TR, Pruzan-Hotchkiss A (1985) Conditioned suppression of proboscis extension in Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Psychol 99(1):74–80
Dethier VG, Solomon RL, Turner LH (1965) Sensory input and central excitation and inhibition in the blowfly. J Comp Physiol Psychol 60(3):303–313
Devaud JM, Acebes A, Ramaswami M, Ferrùs A (2003) Structural and functional changes in the olfactory pathways of adult Drosophila take place at a critical age. J Neurobiol 56(1):13–23
Dudai Y, Corfas G, Hazvi S (1988) What is the possible contribution of Ca2+-stimulated adenylate cyclase to acquisition, consolidation and retention of an associative olfactory memory in Drosophila. J Comp Physiol A 162(1):101–109
Duerr JS, Quinn WG (1982) Three Drosophila mutations that block associative learning also affect habituation and sensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79(11):3646–3650
Edgecomb RS, Murdock LL (1991) Central projections of axons from taste hairs on the labellum and tarsi of the blowfly, Phormia regina Meigen. J Comp Biol 315(3):431–444
Edgecomb RS, Harth CE, Schneiderman AM (1994) Regulation of feeding in adult Drosophila melanogaster varies with feeding regime and nutritional state. J Exp Biol 197:215–235
Ejima A, Smith BPC, Lucas C, Levine JD, Griffith LC (2005) Sequential learning of pheromonal cues modulates memory consolidation in trainer-specific associative courtship conditioning. Curr Biol 15:194–2
Faber T, Joerges J, Menzel R (1999) Associative learning modifies neural representations of odors in the insect brain. Nat Neurosci 2(1):74–78
Fan RJ, Anderson P, Hansson BS (1997) Behavioural analysis of olfactory conditioning in the moth Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Exp Biol 200:2969–2976
Fresquet N, Fournier D, Gauthier M (1998) A new attempt to assess the effect of learning processes on the cholinergic system: studies on fruitflies and honeybees. Comp Biochem Physiol B 119(2):349–353
Fresquet N (1999) Effects of aging on the acquisition and extinction of excitatory conditioning in Drosophila melanogaster. Physiol Behav 67(2):205–211
Frye MA, Tarsinato M, Dickinson MH (2003) Odor localization requires feedback during free flight in Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol 206:843–855
Hallem EA, Ho MG, Carlson JR (2004) The molecular basis of odor coding in the Drosophila antenna. Cell 117:965–979
Hammer M (1993) An identified neuron mediates the unconditioned stimulus in associative olfactory learning in honeybees. Nature 366:59–63
Hartlieb E (1996) Olfactory conditioning in the moth Heliothis virescens. Naturwissenschaften 83:87–88
Heisenberg M, Borst A, Wagner S, Byers D (1985) Drosophila mushroom body mutants are deficient in olfactory learning. J Neurogenet 2:1–30
Holliday M, Hirsch J (1986) Excitatory conditioning of individual Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Psychol: Anim Behav Process 12(2):131–142
Ishimoto H, Tanimura T (2004) Molecular neurophysiology of taste in Drosophila. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(1):10–18
Isabel G, Pascual A, Preat T (2004) Exclusive consolidated memory phases in Drosophila. Science 304:1024–1027
Laloi D, Sandoz JC, Picard-Nizou AL, Marchesi A, Pouvreau A, Taséi JN, Poppy G, Pham-Delègue MH (1998) Olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension in bumble bees. Entomol Exp Appl 90:123–1
Laloi D (1999) Reconnaissance d’odeurs complexes par l’abeille domestique (Apis mellifera L.) et le bourdon (Bombus terrestris L.): facteurs épigénétiques et génétiques de la plasticité comportementale. PhD Thesis, Paris XI University, Orsay, France
Lambin M, Déglise P, Gauthier M (2005) Antennal movements as indicators of odor detection by worker honeybees. Apidologie 36:119–126
Lent DD, Kwon HW (2004) Antennal movements reveal associative learning in the American cockroach Periplaneta americana. J Exp Biol 207:369–375
Marella S, Fischler W, Kong P, Asgarian S, Rueckert E, Scott K (2006) Imaging taste responses in the fly brain reveals a functional map of taste category and behaviour. Neuron 49:285–295
Medioni J, Cadieu N, Vaysse G (1978) Divergent selection for the rapid acquisition of conditioning in Drosophila (Drosophila melanogaster). C R Soc Biol 172(5):961–967
Menzel R, Bitterman ME (1983) Learning by honeybees in an unnatural situation. In: Huber F, Markl H (eds) Neuroethology and behavioral physiology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 206–215
Menzel R (2001) Searching for memory trace in a mini-brain, the honeybee. Learn Mem 8(2):53–62
Milosevic NJ (1999) Dunce and amnesiac gene effect on signal learning in fruit flies Drosophila melanogaster: experiments with odors. Russ J Genet 35(2):157–163
Müller U (2002) Learning in honeybees: from molecules to behaviour. Zoology 105:313–320
Pascual A, Preat T (2001) Localization of long-term memory within the Drosophila mushroom body. Science 294:1115–1117
Preat T (1999) Testing associative learning in Drosophila. In: Crusio WE, Gerlai RT (eds) Handbook of molecular-genetic techniques for brain and behaviour research (Techniques in the behavioural and neuronal sciences), vol 13. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 79–126
Quinn WG, Harris WA, Benzer S (1974) Conditioned behaviour in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71(3):708–712
Ray S, Ferneyhough B (1999) Behavioral development and olfactory learning in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Dev Psychobiol 34(1):21–27
Riesmensperger T, Völler T, Stock P, Buchner E, Fiala A (2005) Punishment prediction by dopaminergic neurons in Drosophila. Curr Biol 15:1953–1960
Sandoz JC, Roger B, Pham-Delègue MH (1995) Olfactory learning and memory in the honeybee: comparison of different classical procedures of the proboscis extension response. CR Acad Sci III 318:749–755
Sandoz JC, Hammer M, Menzel R (2002) Side-specificity of olfactory learning in the honeybee: US input side. Learn Mem 9(5):337–348
Scheiner R, Barnert M, Erber J (2003) Variation in water and sucrose responsiveness during the foraging season affects proboscis extension learning in honey bees. Apidologie 34:67–72
Schwaerzel M, Monastirioti M, Scholz H, Friggi-Grelin F, Birman S, Heisenberg M (2003) Dopamine and octopamine differentiate between aversive and appetitive olfactory memories in Drosophila. J Neurosci 23(33):10495–10502
Scott K (2005) Taste recognition: food for thought. Neuron 48:455–464
Skiri HT, Stranden M, Sandoz JC, Menzel R, Mustaparta H (2004) Associative learning of plant odorants activating the same or different receptor neurones in the moth Heliothis virescens. J Exp Biol 208:787–7
Tempel BL, Bonini N, Dawson DR, Quinn WG (1983) Reward learning in normal and mutant Drosophila. Psychology 80:1482–1486
Tully T, Quinn WG (1985) Classical conditioning and retention in normal and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J Comp Physiol A 157:263–277
Tully T, Preat T, Boynton SC, Del Vecchio M (1994) Genetic dissection of consolidated memory in Drosophila. Cell 79:35–47
Vargo M, Hirsch J (1982) Central excitation in the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). J Comp Physiol Psychol 96(3):452–459
Vaysse G, Médioni J (1973) Premières expériences sur la gustation tarsale chez Drosophila melanogaster: stimulation par le saccharose. C R Soc Biol 167(3–4):560–564
Vaysse G, Médioni J (1976) Further experiments on the conditioning and pseudoconditioning of the tarsal reflex in the Drosophila (Drosophila melanogaster): effect of low intensity electric shocks. C R Soc Biol 170(6):1290–1304
Vaysse G (1982) Etude du réflexe tarsal et de son inhibition conditionnée chez Drosophila melanogaster: déterminants génétiques et épigénétiques. PhD Thesis, Paul Sabatier University, Toulouse, France
Wang Z, Singhvi A, Kong P, Scott K (2004) Taste representations in the Drosophila brain. Cell 117(7):981–991
Yu D, Ponomarev A, Davis RL (2004) Altered representation of the spatial code for odors after olfactory classical conditioning: memory trace formation by synaptic recruitment. Neuron 42:437–449
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall Uppler Saddle River, NJ, p 663
Zars T, Fischer M, Schulz R, Heisenberg M (2000) Localization of a short-term memory in Drosophila. Science 288(5466):672–675
Acknowledgments
This work was started at the “Laboratoire de Neurobiologie Comparée des Invertébrés”, INRA and completed at the laboratory “Développement, Évolution et Plasticité du Système Nerveux”, CNRS. The authors thank Philippe Vernier for his scientific support to the project, David Laloi, Jean-Christophe Sandoz and Isabelle Bonod for sharing their experience and ideas with the conditioned proboscis activity protocol, Michel Chaminade, Jean-Yves Tiercelin and Pascal Abbas for installation, adaptation and maintenance of the system, Tazu Aoki and Guillaume Isabel for fruitful discussion and Niki Scaplehorn for linguistic advice. This study was supported in part by the “Agence Nationale pour la Recherche” and “the Fondation Bettencourt Schueller”, and Marie-Ange Chabaud was supported by the “Ecole Doctorale Sociétés et Vivant”, option “Biologie du Comportement”, at the University Paris 13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chabaud, MA., Devaud, JM., Pham-Delègue, MH. et al. Olfactory conditioning of proboscis activity in Drosophila melanogaster . J Comp Physiol A 192, 1335–1348 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-006-0160-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-006-0160-3