Abstract
Rationale
Fluoxetine (Prozac®) is the most frequently prescribed drug to battle depression in pregnant women, but its safety in the unborn child has not yet been established. Fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, crosses the placenta, leading to increased extracellular serotonin levels and potentially neurodevelopmental changes in the fetus.
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to elucidate the long-term consequences of prenatal fluoxetine in rats.
Methods
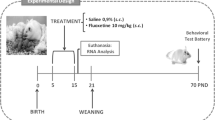
Pregnant rats were injected daily with 12 mg/kg fluoxetine or vehicle from gestational day 11 until birth, and the behavior of the offspring was monitored.
Results
Plasma fluoxetine transfer from mother to pup was 83%, and high levels of fluoxetine (13.0 μg/g) were detected in the pup brain 5 h after the last injection. Fluoxetine-treated dams gave birth to litters 15% smaller than usual and to pups of reduced weight (until postnatal day 7). Furthermore, prenatal fluoxetine exposure significantly increased anxiety in the novelty-suppressed feeding test, the footshock-induced conditioned place aversion test, and the elevated plus maze test (following footshock pre-exposure) during adulthood, and also significantly decreased components of social play behavior at 4 weeks of age, and a strong tendency for increased self-grooming and making less contact in adults. Behavioral despair, anhedonia, and sexual behavior were not different between treatment groups. Finally, the hypothermic response to the 5-HT1A agonist flesinoxan was observed at a lower dose in prenatally fluoxetine-exposed rats than in controls.
Conclusions
Prenatal fluoxetine exposure in rats leads to detrimental behavioral outcomes in later life, which may partly be due to altered 5-HT1A receptor signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-HT:
-
Serotonin
- 5-HTT:
-
Serotonin transporter
- 5-HTT−/− :
-
Serotonin transporter knockout
- CE:
-
Copulatory efficiency
- CPA:
-
Conditioned place aversion
- E:
-
Embryonic day
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- EL:
-
Ejaculatory latency
- GD:
-
Gestational day
- I:
-
Intromission
- I.P.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- M:
-
Mount
- PEL:
-
Postejaculatory latency
- PND:
-
Postnatal day
- SSRI:
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
References
Adamec R, Burton P, Blundell J, Murphy DL, Holmes A (2006) Vulnerability to mild predator stress in serotonin transporter knockout mice. Behav Brain Res 170:126–140
Alexandre C, Popa D, Fabre V, Bouali S, Venault P, Lesch KP et al (2006) Early life blockade of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors normalizes sleep and depression-like behavior in adult knock-out mice lacking the serotonin transporter. J Neurosci 26:5554–5564
Andrade SE, Raebel MA, Brown J, Lane K, Livingston J, Boudreau D et al (2008) Use of antidepressant medications during pregnancy: a multisite study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198:194–195
Ansorge MS, Zhou M, Lira A, Hen R, Gingrich JA (2004) Early-life blockade of the 5-HT transporter alters emotional behavior in adult mice. Science 306:879–881
Ansorge MS, Morelli E, Gingrich JA (2008) Inhibition of serotonin but not norepinephrine transport during development produces delayed, persistent perturbations of emotional behaviors in mice. J Neurosci 28:199–207
Baumann P, Rochat B (1995) Comparative pharmacokinetics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a look behind the mirror. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 10(Suppl 1):15–21
Chambers CD, Johnson KA, Dick LM, Felix RJ, Jones KL (1996) Birth outcomes in pregnant women taking fluoxetine. N Engl J Med 335:1010–1015
Chan JS, Snoeren EM, Cuppen E, Waldinger MD, Olivier B, Oosting RS (2010) The serotonin transporter plays an important role in male sexual behavior: a study in serotonin transporter knockout rats. J Sex Med 8(1):97–108. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.01961.x
Clayton AH, Pradko JF, Croft HA, Montano CB, Leadbetter RA, Bolden-Watson C et al (2002) Prevalence of sexual dysfunction among newer antidepressants. J Clin Psychiatry 63:357–366
Cooper WO, Willy ME, Pont SJ, Ray WA (2007) Increasing use of antidepressants in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 196:544–545
Deave T, Heron J, Evans J, Emond A (2008) The impact of maternal depression in pregnancy on early child development. BJOG 115:1043–1051
DiPietro JA, Novak MF, Costigan KA, Atella LD, Reusing SP (2006) Maternal psychological distress during pregnancy in relation to child development at age two. Child Dev 77:573–587
Duverneuil C, de la Grandmaison GL, de Mazancourt P, Alvarez JC (2003) A high-performance liquid chromatography method with photodiode-array UV detection for therapeutic drug monitoring of the nontricyclic antidepressant drugs. Ther Drug Monit 25:565–573
Evans J, Heron J, Francomb H, Oke S, Golding J (2001) Cohort study of depressed mood during pregnancy and after childbirth. BMJ 323:257–260
File SE (1990) One-trial tolerance to the anxiolytic effects of chlordiazepoxide in the plus-maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:281–282
Forcelli PA, Heinrichs SC (2008) Teratogenic effects of maternal antidepressant exposure on neural substrates of drug-seeking behavior in offspring. Addict Biol 13:52–62
Fricker AD, Rios C, Devi LA, Gomes I (2005) Serotonin receptor activation leads to neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 138:228–235
Gaspar P, Cases O, Maroteaux L (2003) The developmental role of serotonin: news from mouse molecular genetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:1002–1012
Gentile S, Galbally M (2010) Prenatal exposure to antidepressant medications and neurodevelopmental outcomes: a systematic review. J Affect Disord 128(1–2):1–9
Hansen HH, Sanchez C, Meier E (1997) Neonatal administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor Lu 10-134-C increases forced swimming-induced immobility in adult rats: a putative animal model of depression? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1333–1341
Hay DF, Pawlby S, Waters CS, Sharp D (2008) Antepartum and postpartum exposure to maternal depression: different effects on different adolescent outcomes. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 49:1079–1088
Homberg JR, Schiepers OJ, Schoffelmeer AN, Cuppen E, Vanderschuren LJ (2007) Acute and constitutive increases in central serotonin levels reduce social play behaviour in peri-adolescent rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 195:175–182
Homberg JR, Schubert D, Gaspar P (2010) New perspectives on the neurodevelopmental effects of SSRIs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31:60–65
Homberg JR, Olivier JDA, Blom T, Arentsen T, van Brunschot C, Korte-Bouws G et al (2011) Fluoxetine exerts age-dependent effects on behavior and amygdala neuroplasticity in the rat. PLoS ONE 6(1):e16646. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016646
Iniguez SD, Warren BL, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2010) Short- and long-term functional consequences of fluoxetine exposure during adolescence in male rats. Biol Psychiatry 67:1057–1066
Jiang XZ, Liu YQ, Zhang YZ, Zhang LM, Li J, Li YF (2009) Neonatal fluoxetine exposure induced depression-like behaviors in the adult Kunming mice and the antidepressant-like effect of agmatine. Yao Xue Xue Bao 44:716–721
Kalueff AV, Olivier JD, Nonkes LJ, Homberg JR (2010) Conserved role for the serotonin transporter gene in rat and mouse neurobehavioral endophenotypes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:373–386
Kecskemeti V, Rusznak Z, Riba P, Pal B, Wagner R, Harasztosi C et al (2005) Norfluoxetine and fluoxetine have similar anticonvulsant and Ca2+ channel blocking potencies. Brain Res Bull 67:126–132
Kim J, Riggs KW, Misri S, Kent N, Oberlander TF, Grunau RE et al (2006) Stereoselective disposition of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:155–163
Kinney GG, Taber MT, Gribkoff VK (2000) The augmentation hypothesis for improvement of antidepressant therapy: is pindolol a suitable candidate for testing the ability of 5HT1A receptor antagonists to enhance SSRI efficacy and onset latency? Mol Neurobiol 21:137–152
Knutson B, Panksepp J, Pruitt D (1996) Effects of fluoxetine on play dominance in juvenile rats. Aggress Behav 22:297–307
Kumar R, Robson KM (1984) A prospective study of emotional disorders in childbearing women. Br J Psychiatry 144:35–47
Lee LJ (2009) Neonatal fluoxetine exposure affects the neuronal structure in the somatosensory cortex and somatosensory-related behaviors in adolescent rats. Neurotox Res 15:212–223
Lisboa SF, Oliveira PE, Costa LC, Venancio EJ, Moreira EG (2007) Behavioral evaluation of male and female mice pups exposed to fluoxetine during pregnancy and lactation. Pharmacology 80:49–56
Lister RG (1987) The use of a plus-maze to measure anxiety in the mouse. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 92:180–185
Lundmark J, Reis M, Bengtsson F (2001) Serum concentrations of fluoxetine in the clinical treatment setting. Ther Drug Monit 23:139–147
Maciag D, Coppinger D, Paul IA (2006a) Evidence that the deficit in sexual behavior in adult rats neonatally exposed to citalopram is a consequence of 5-HT1 receptor stimulation during development. Brain Res 1125:171–175
Maciag D, Simpson KL, Coppinger D, Lu Y, Wang Y, Lin RC et al (2006b) Neonatal antidepressant exposure has lasting effects on behavior and serotonin circuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:47–57
Maciag D, Williams L, Coppinger D, Paul IA (2006c) Neonatal citalopram exposure produces lasting changes in behavior which are reversed by adult imipramine treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 532:265–269
Manhães de Castro R, Barreto Medeiros JM, Mendes da Silva C, Ferreira LM, Guedes RC, Cabral Filho JE et al (2001) Reduction of intraspecific aggression in adult rats by neonatal treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:121–124
Michelson D, Amsterdam JD, Quitkin FM, Reimherr FW, Rosenbaum JF, Zajecka J et al (1999) Changes in weight during a 1-year trial of fluoxetine. Am J Psychiatry 156:1170–1176
Mirmiran M, van de Poll NE, Corner MA, van Oyen HG, Bour HL (1981) Suppression of active sleep by chronic treatment with chlorimipramine during early postnatal development: effects upon adult sleep and behavior in the rat. Brain Res 204:129–146
Montejo-Gonzalez AL, Llorca G, Izquierdo JA, Ledesma A, Bousono M, Calcedo A et al (1997) SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction: fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and fluvoxamine in a prospective, multicenter, and descriptive clinical study of 344 patients. J Sex Marital Ther 23:176–194
Moses-Kolko EL, Roth EK (2004) Antepartum and postpartum depression: healthy mom, healthy baby. J Am Med Womens Assoc 59:181–191
Narboux-Neme N, Pavone LM, Avallone L, Zhuang X, Gaspar P (2008) Serotonin transporter transgenic (SERTcre) mouse line reveals developmental targets of serotonin specific reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Neuropharmacology 55:994–1005
Neill D, Vogel G, Hagler M, Kors D, Hennessey A (1990) Diminished sexual activity in a new animal model of endogenous depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 14:73–76
Niesink RJ, Van Ree JM (1989) Involvement of opioid and dopaminergic systems in isolation-induced pinning and social grooming of young rats. Neuropharmacology 28:411–418
Noorlander CW, Ververs FF, Nikkels PG, van Echteld CJ, Visser GH, Smidt MP (2008) Modulation of serotonin transporter function during fetal development causes dilated heart cardiomyopathy and lifelong behavioral abnormalities. PLoS ONE 3:e2782
Norcross M, Mathur P, Enoch AJ, Karlsson RM, Brigman JL, Cameron HA et al (2008) Effects of adolescent fluoxetine treatment on fear-, anxiety- or stress-related behaviors in C57BL/6 J or BALB/cJ mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 200:413–424
Nulman I, Rovet J, Stewart DE, Wolpin J, Pace-Asciak P, Shuhaiber S et al (2002) Child development following exposure to tricyclic antidepressants or fluoxetine throughout fetal life: a prospective, controlled study. Am J Psychiatry 159:1889–1895
Oberlander TF, Warburton W, Misri S, Aghajanian J, Hertzman C (2006) Neonatal outcomes after prenatal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and maternal depression using population-based linked health data. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:898–906
O’Connor TG, Heron J, Glover V (2002) Antenatal anxiety predicts child behavioral/emotional problems independently of postnatal depression. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:1470–1477
Oh JE, Zupan B, Gross S, Toth M (2009) Paradoxical anxiogenic response of juvenile mice to fluoxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2197–2207
O’Hara MW, Neunaber DJ, Zekoski EM (1984) Prospective study of postpartum depression: prevalence, course and predictive factors. J Abnorm Psychol 93:158–171
Olivier JD, Cools AR, Olivier B, Homberg JR, Cuppen E, Ellenbroek BA (2008a) Stress-induced hyperthermia and basal body temperature are mediated by different 5-HT(1A) receptor populations: a study in SERT knockout rats. Eur J Pharmacol 590:190–197
Olivier JD, Van Der Hart MG, Van Swelm RP, Dederen PJ, Homberg JR, Cremers T et al (2008b) A study in male and female 5-HT transporter knockout rats: an animal model for anxiety and depression disorders. Neuroscience 152:573–584
Olivier JD, Cools AR, Deen PM, Olivier B, Ellenbroek BA (2010a) Blockade of dopamine, but not noradrenaline, transporters produces hyperthermia in rats that lack serotonin transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 629:7–11
Olivier JDA, Blom T, Arentsen T, Homberg JR (2010b) The age-dependent effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in humans and rodents: a review. Progr Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.09.013
Paulson JF, Keefe HA, Leiferman JA (2009) Early parental depression and child language development. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 50:254–262
Popa D, Lena C, Alexandre C, Adrien J (2008) Lasting syndrome of depression produced by reduction in serotonin uptake during postnatal development: evidence from sleep, stress, and behavior. J Neurosci 28:3546–3554
Ramos SD, Lee JM, Peuler JD (2001) An inexpensive meter to measure differences in electrical resistance in the rat vagina during the ovarian cycle. J Appl Physiol 91:667–670
Ribas VR, Aniceto HK, Martins HA, Ribas KH, Guerra-Ribas RM, Fraga SN et al (2008) Neonatal administration of fluoxetine did not alter the anxiety indicators, but decreased the locomotor activity in adult rats in the elevated plus-maze. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66:844–847
Romijn HJ, Hofman MA, Gramsbergen A (1991) At what age is the developing cerebral cortex of the rat comparable to that of the full-term newborn human baby? Early Hum Dev 26:61–67
Rosen RC, Lane RM, Menza M (1999) Effects of SSRIs on sexual function: a critical review. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19:67–85
Rowland D, McMahon CG, Abdo C, Chen J, Jannini E, Waldinger MD et al (2010) Disorders of orgasm and ejaculation in men. J Sex Med 7:1668–1686
Sikich L, Hickok JM, Todd RD (1990) 5-HT1A receptors control neurite branching during development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 56:269–274
Silva CM, Goncalves L, Manhaes-de-Castro R, Nogueira MI (2010) Postnatal fluoxetine treatment affects the development of serotonergic neurons in rats. Neurosci Lett 483:179–183
Talge NM, Neal C, Glover V (2007) Antenatal maternal stress and long-term effects on child neurodevelopment: how and why? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 48:245–261
van den Hove DL, Blanco CE, Scheepens A, Desbonnet L, Myint AM, Leonard BE et al (2008) Prenatal maternal paroxetine treatment and neonatal mortality in the rat: a preliminary study. Neonatology 93:52–55
van Erp AM, Kruk MR, Meelis W, Willekens-Bramer DC (1994) Effect of environmental stressors on time course, variability and form of self-grooming in the rat: handling, social contact, defeat, novelty, restraint and fur moistening. Behav Brain Res 65:47–55
Ververs T, Kaasenbrood H, Visser G, Schobben F, de Jong-van den Berg L, Egberts T (2006) Prevalence and patterns of antidepressant drug use during pregnancy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:863–870
Vorhees CV, Acuff-Smith KD, Schilling MA, Fisher JE, Moran MS, Buelke-Sam J (1994) A developmental neurotoxicity evaluation of the effects of prenatal exposure to fluoxetine in rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 23:194–205
Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW, Zwinderman AH, Olivier B (1998) Effect of SSRI antidepressants on ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study with fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18:274–281
Acknowledgments
We thank Lars Valke, Mariëlle Winters, Loes Schiphouwer, and Anneke Sloet for their practical assistance. This research was financially supported by the Donders Centre for Neuroscience, Radboud University Nijmegen, The Netherlands, and a grant (no. 433-09-311) from The Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO), awarded to J. Homberg. The Donders Centre for Neuroscience and NWO had no further role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, and in the decision to submit the paper for publication. The experiments comply with the current laws of the Netherlands.
Conflicts
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olivier, J.D.A., Vallès, A., van Heesch, F. et al. Fluoxetine administration to pregnant rats increases anxiety-related behavior in the offspring. Psychopharmacology 217, 419–432 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2299-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2299-z