Abstract
Rationale
Conditioned cues can elicit relapse to drug- and food-seeking behavior over prolonged periods of abstinence. If seeking behavior depends on mesolimbic dopamine D1 receptors, blocking these receptors should reduce seeking behavior.
Objectives
We examined the effects of either systemic or intra-nucleus accumbens administration of the D1 antagonist SCH 23390 on extinction responding (sucrose seeking) by rats either 1 or 30 days into forced abstinence.
Materials and methods
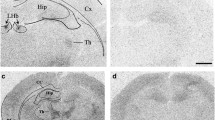
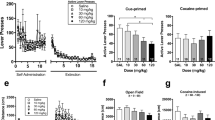
Rats self-administered 10% sucrose paired with a tone + light cue for 10 days. After either 1 or 30 days of forced abstinence, rats received systemic (0, 1, 5, or 25 μg/kg IP) or bilateral nucleus accumbens core or shell (0.3 or 0.6 μg/site) injections of SCH 23390 prior to extinction testing.
Results
Saline-treated rats responded more during extinction following 30 vs. 1 day of forced abstinence (“incubation of craving”). Systemic SCH 23390 reduced sucrose seeking after 1 day of forced abstinence, significantly reducing responding following pretreatment with 1, 5, and 25 μg/kg SCH 23390, but only 25 μg/kg significantly reduced sucrose seeking after 30 days of forced abstinence. SCH 23390 (0.3 or 0.6 μg/site) in the core or shell of the nucleus accumbens reduced sucrose seeking in all groups.
Conclusion
Nucleus accumbens D1 receptors are involved in sucrose seeking, but it is not clear if they are involved in the incubation of craving. The fact that D1 antagonism reduced sucrose seeking across an extended period of abstinence may be of use for development of treatment strategies for relapse.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alleweireldt AT, Hobbs RJ, Taylor AR, Neisewander JL (2006) Effects of SCH-23390 infused into the amygdala or adjacent cortex and basal ganglia on cocaine seeking and self-administration in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:363–374
Alleweireldt AT, Weber SM, Kirschner KF, Bullock BL, Neisewander JL (2002) Blockade or stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors attenuates cue reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159:284–293
Bachtell RK, Whisler K, Karanian D, Self DW (2005) Effects of intra-nucleus accumbens shell administration of dopamine agonists and antagonists on cocaine-taking and cocaine-seeking behaviors in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:41–53
Baldo BA, Sadeghian K, Basso AM, Kelley AE (2002) Effects of selective dopamine D1 or D2 receptor blockade within nucleus accumbens subregions on ingestive behavior and associated motor activity. Behav Brain Res 137:165–177
Bari AA, Pierce RC (2005) D1-like and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists administered into the shell subregion of the rat nucleus accumbens decrease cocaine, but not food, reinforcement. Neuroscience 135:959–968
Belin D, Jonkman S, Dickinson A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2009) Parallel and interactive learning processes within the basal ganglia: relevance for the understanding of addiction. Behav Brain Res 199:89–102
Bossert JM, Poles GC, Wihbey KA, Koya E, Shaham Y (2007) Differential effects of blockade of dopamine D1-family receptors in nucleus accumbens core or shell on reinstatement of heroin seeking induced by contextual and discrete cues. J Neurosci 27:12655–12663
Bossert JM, Wihbey KA, Pickens CL, Nair SG, Shaham Y (2009) Role of dopamine D(1)-family receptors in dorsolateral striatum in context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206:51–60
Brownell KD, Wadden TA (1992) Etiology and treatment of obesity: understanding a serious, prevalent, and refractory disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 60:505–517
Cador M, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1989) Involvement of the amygdala in stimulus–reward associations: interaction with the ventral striatum. Neuroscience 30:77–86
Caine SB, Heinrichs SC, Coffin VL, Koob GF (1995) Effects of the dopamine D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 microinjected into the accumbens, amygdala or striatum on cocaine self-administration in the rat. Brain Res 692:47–56
Carter BL, Tiffany ST (1999) Meta-analysis of cue-reactivity in addiction research. Addiction 94:327–340
Chaudhri N, Sahuque LL, Janak PH (2009) Ethanol seeking triggered by environmental context is attenuated by blocking dopamine D1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 207:303–314
Childress AR, Mozley PD, McElgin W, Fitzgerald J, Reivich M, O'Brien CP (1999) Limbic activation during cue-induced cocaine craving. Am J Psychiatry 156:11–18
Choi WY, Morvan C, Balsam PD, Horvitz JC (2009) Dopamine D1 and D2 antagonist effects on response likelihood and duration. Behav Neurosci 123:1279–1287
Ciccocioppo R, Sanna PP, Weiss F (2001) Cocaine-predictive stimulus induces drug-seeking behavior and neural activation in limbic brain regions after multiple months of abstinence: reversal by D(1) antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1976–1981
Crombag HS, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Effect of dopamine receptor antagonists on renewal of cocaine seeking by reexposure to drug-associated contextual cues. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:1006–1015
Di Ciano P, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2008) Differential effects of nucleus accumbens core, shell, or dorsal striatal inactivations on the persistence, reacquisition, or reinstatement of responding for a drug-paired conditioned reinforcer. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1413–1425
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189:1–16
Epstein DH, Willner-Reid J, Vahabzadeh M, Mezghanni M, Lin JL, Preston KL (2009) Real-time electronic diary reports of cue exposure and mood in the hours before cocaine and heroin craving and use. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:88–94
Floresco SB, Blaha CD, Yang CR, Phillips AG (2001) Modulation of hippocampal and amygdalar-evoked activity of nucleus accumbens neurons by dopamine: cellular mechanisms of input selection. J Neurosci 21:2851–2860
Gonzalez FA, Goldberg SR (1977) Effects of cocaine and d-amphetamine on behavior maintained under various schedules of food presentation in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:33–43
Grimm JW, Fyall AM, Osincup DP (2005) Incubation of sucrose craving: effects of reduced training and sucrose pre-loading. Physiol Behav 84:73–79
Grimm JW, Hope BT, Wise RA, Shaham Y (2001) Neuroadaptation. Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal. Nature 412:141–142
Grimm JW, Kruzich PJ, See RE (2000) Contingent access to stimuli associated with cocaine self-administration is required for reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. Psychobiology 28:383–386
Grimm JW, Manaois M, Osincup D, Wells B, Buse C (2007) Naloxone attenuates incubated sucrose craving in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 194:537–544
Grimm JW, Osincup D, Wells B, Manaois M, Fyall A, Buse C, Harkness JH (2008) Environmental enrichment attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of sucrose seeking in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:777–785
Grodstein F, Levine R, Troy L, Spencer T, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ (1996) Three-year follow-up of participants in a commercial weight loss program. Can you keep it off? Arch Intern Med 156:1302–1306
Groenewegen HJ, Wright CI, Beijer AV, Voorn P (1999) Convergence and segregation of ventral striatal inputs and outputs. Ann NY Acad Sci 877:49–63
Haile CN, Kosten TA (2001) Differential effects of D1- and D2-like compounds on cocaine self-administration in Lewis and Fischer 344 inbred rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:509–518
Hamlin AS, Blatchford KE, McNally GP (2006) Renewal of an extinguished instrumental response: neural correlates and the role of D1 dopamine receptors. Neuroscience 143:25–38
Hamlin AS, Clemens KJ, McNally GP (2007) Renewal of extinguished cocaine-seeking. Neuroscience 151:659–670
Harkness JH, Webb S, Grimm JW (2009) Abstinence-dependent transfer of lithium chloride-induced sucrose aversion to a sucrose-paired cue in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 208:521–530
Holland PC, Lasseter H, Agarwal I (2008) Amount of training and cue-evoked taste-reactivity responding in reinforcer devaluation. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 34:119–132
Ito R, Robbins TW, McNaughton BL, Everitt BJ (2006) Selective excitotoxic lesions of the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala have dissociable effects on appetitive cue and place conditioning based on path integration in a novel Y-maze procedure. Eur J Neurosci 23:3071–3080
Jansen A, Theunissen N, Slechten K, Nederkoorn C, Boon B, Mulkens S, Roefs A (2003) Overweight children overeat after exposure to food cues. Eat Behav 4:197–209
Kilts CD, Dew KL, Ely TD, Mailman RB (1985) Quantification of R-(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydro-1H-3-methyl-3-benzazepine in brain and blood by use of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr 342:452–457
Koya E, Uejima JL, Wihbey KA, Bossert JM, Hope BT, Shaham Y (2009) Role of ventral medial prefrontal cortex in incubation of cocaine craving. Neuropharmacology 56:177–185
Lex B, Hauber W (2010) The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in outcome encoding in instrumental and Pavlovian conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:283–290
Li YQ, Li FQ, Wang XY, Wu P, Zhao M, Xu CM, Shaham Y, Lu L (2008) Central amygdala extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway is critical to incubation of opiate craving. J Neurosci 28:13248–13257
Liu X, Jernigen C, Gharib M, Booth S, Caggiula AR, Sved AF (2010) Effects of dopamine antagonists on drug cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking behavior in rats. Behav Pharmacol 21:153–160
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Reversal of ethanol-seeking behavior by D1 and D2 antagonists in an animal model of relapse: differences in antagonist potency in previously ethanol-dependent versus nondependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:882–889
Lu L, Hope BT, Dempsey J, Liu SY, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2005) Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat Neurosci 8:212–219
Markou A, Weiss F, Gold LH, Caine B, Schulteis G, Koob GF (1993) Animal models of drug craving. Psychopharmacology 112:163–182
Mashhoon Y, Tsikitas LA, Kantak KM (2009) Dissociable effects of cocaine-seeking behavior following D1 receptor activation and blockade within the caudal and rostral basolateral amygdala in rats. Eur J Neurosci 29:1641–1653
Mendelson JH, Mello NK (1996) Management of cocaine abuse and dependence. N Engl J Med 334:965–972
Nair SG, Adams-Deutsch T, Epstein DH, Shaham Y (2009) The neuropharmacology of relapse to food seeking: methodology, main findings, and comparison with relapse to drug seeking. Prog Neurobiol 89:18–45
Nann-Vernotica E, Donny EC, Bigelow GE, Walsh SL (2001) Repeated administration of the D1/5 antagonist ecopipam fails to attenuate the subjective effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 155:338–347
Novak M, Halbout B, O'Connor EC, Rodriguez Parkitna J, Su T, Chai M, Crombag HS, Bilbao A, Spanagel R, Stephens DN, Schutz G, Engblom D (2010) Incentive learning underlying cocaine-seeking requires mGluR5 receptors located on dopamine D1 receptor-expressing neurons. J Neurosci 30:11973–11982
Nunes EJ, Randall PA, Santerre JL, Given AB, Sager TN, Correa M, Salamone JD (2010) Differential effects of selective adenosine antagonists on the effort-related impairments induced by dopamine D1 and D2 antagonism. Neuroscience 170:268–280
O'Brien CP, Childress AR, Arndt IO, McLellan AT, Woody GE, Maany I (1988) Pharmacological and behavioral treatments of cocaine dependence: controlled studies. J Clin Psychiatry 49:17–22
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Elsevier Academic, San Diego
Phillips G, Willner P, Sampson D, Nunn J, Muscat R (1991) Time-, schedule-, and reinforcer-dependent effects of pimozide and amphetamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 104:125–131
Reichel CM, Bevins RA (2009) Forced abstinence model of relapse to study pharmacological treatments of substance use disorder. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 2:184–194
Rusk IN, Cooper SJ (1994) Parametric studies of selective D1 or D2 antagonists: effects on appetitive and feeding behaviour. Behav Pharmacol 5:615–622
Sanger DJ (1987) The actions of SCH 23390, a D1 receptor antagonist, on operant and avoidance behavior in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:509–513
See RE (2009) Dopamine D1 receptor antagonism in the prelimbic cortex blocks the reinstatement of heroin-seeking in an animal model of relapse. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:431–436
See RE, Elliott JC, Feltenstein MW (2007) The role of dorsal vs ventral striatal pathways in cocaine-seeking behavior after prolonged abstinence in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 194:321–331
See RE, Kruzich PJ, Grimm JW (2001) Dopamine, but not glutamate, receptor blockade in the basolateral amygdala attenuates conditioned reward in a rat model of relapse to cocaine-seeking behavior. Psychopharmacology 154:301–310
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Sobik L, Hutchison K, Craighead L (2005) Cue-elicited craving for food: a fresh approach to the study of binge eating. Appetite 44:253–261
Tobin S, Newman AH, Quinn T, Shalev U (2009) A role for dopamine D1-like receptors in acute food deprivation-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:217–226
Tye KM, Stuber GD, De Ridder B, Bonci A, Janak PH (2008) Rapid strengthening of thalamo-amygdala synapses mediates cue-reward learning. Nature 453:1253–1257
Uejima JL, Bossert JM, Poles GC, Lu L (2007) Systemic and central amygdala injections of the mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 attenuate the expression of incubation of sucrose craving in rats. Behav Brain Res 181:292–296
Volkow ND, Wise RA (2005) How can drug addiction help us understand obesity? Nat Neurosci 8:555–560
Wadden TA (1993) Treatment of obesity by moderate and severe caloric restriction. Results of clinical research trials. Ann Intern Med 119:688–693
Wakabayashi KT, Fields HL, Nicola SM (2004) Dissociation of the role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in responding to reward-predictive cues and waiting for reward. Behav Brain Res 154:19–30
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Thanos PK, Fowler JS (2004) Similarity between obesity and drug addiction as assessed by neurofunctional imaging: a concept review. J Addict Dis 23:39–53
Weiss F, Martin-Fardon R, Ciccocioppo R, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O (2001) Enduring resistance to extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior induced by drug-related cues. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:361–372
Weissenborn R, Deroche V, Koob GF, Weiss F (1996) Effects of dopamine agonists and antagonists on cocaine-induced operant responding for a cocaine-associated stimulus. Psychopharmacology 126:311–322
Wheeler RA, Carelli RM (2009) Dissecting motivational circuitry to understand substance abuse. Neuropharmacology 56:149–159
Wise RA (2004) Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:483–494
Wise RA, Spindler J, deWit H, Gerberg GJ (1978) Neuroleptic-induced "anhedonia" in rats: pimozide blocks reward quality of food. Science 201:262–264
Yun IA, Nicola SM, Fields HL (2004) Contrasting effects of dopamine and glutamate receptor antagonist injection in the nucleus accumbens suggest a neural mechanism underlying cue-evoked goal-directed behavior. Eur J Neurosci 20:249–263
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse/National Institutes of Health grant R15 DA016285-02 and the Western Washington University Biomedical Research Activities in Neuroscience Initiative. The authors wish to thank Addison Tice, David Goodman, and Jon Koerber for helping with data collection.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimm, J.W., Harkness, J.H., Ratliff, C. et al. Effects of systemic or nucleus accumbens-directed dopamine D1 receptor antagonism on sucrose seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 216, 219–233 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2210-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2210-y