Summary
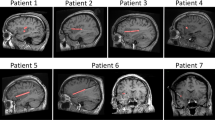
Thalamic EEG recordings were made in 10 patients; the therapeutic goal of the implantation was the electrical stimulation treatment for pain. The patients' ages ranged from 37 to 72 years; seven patients had thalamic pain (Dejerine-Roussy syndrome), two had chronic spinal arachnoiditis and one had facial anaesthesia dolorosa.
Platinum-iridium electrodes were stereotaxically inserted; the ventrobasal complex of the thalamus including the ventral posterior zone was the target of the implant.
Excessive thalamic slowing was found in four of seven patients with Dejerine-Roussy syndrome and also in two of three cases with other causes of pain. One patient had marked rhythmical intermittent delta activity in the thalamus which was often triggered by arousing stimuli. Thalamic spindle activity was sometimes noted without concomitant spindle activity on the scalp and would occasionally occur in states of early drowsiness.
Zusammenfassung
In 10 Patienten mit chronischen Schmerzzuständen wurde das EEG vom Thalamus abgeleitet. Die Tiefenelektroden dienten therapeutisch zur elektrischen Stimulation als Schmerzbehandlung. Das Alter der Patienten lag zwischen 37 und 72 Jahren. In 7 Fällen lag Thalamusschmerz vor (Dejerine-Roussy Syndrome); zwei Patienten litten an chronischer spinaler Arachnoiditis und einer an Anaesthesia dolorosa im Gesichtsbereich.
Die Platin-Iridium-Elektroden wurden stereotaktisch eingeführt; als Zielgebiet diente der ventrobasale Komplex des Thalamus, der die ventralposterioren Kerngebiete einschließt.
Abnorme Verlangsamung im thalamischen EEG bestand bei 4 der 7 Patienten mit Dejerine-Roussy-Syndrome, aber auch bei 2 der 3 Patienten mit Schmerzen anderer Genese. Ein Patient zeigte ausgeprägte rhythmisch-intermittierende Delta-Tätigkeit im Thalamus, oft ausgelöst durch Weckreize. Gelegentlich fand sich Spindelaktivität im Thalamus ohne begleitende Spindeln im Kopfhaut-EEG; solche thalamischen Spindelzüge traten manchmal bereits im Zustand ganz leichter Schläfrigkeit auf.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albe-Fessard, D.: Electrophysiological techniques used to differentiate thalamic nuclei. In: Rémond, A. (Ed.-in-Chief), Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology, Vol. 10, B, pp. 46–58. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1975
Albe-Fessard, D., Arfel, G., Guiot, G., Hardy, J., Vourc'h, G., Hertzog, E., Aleonard, P., Derome, P.: Dérivations d'activités spontanées et évoquées dans les structures cérébrales profondes de l'homme. Rev. neurol. (Paris) 106, 89–105 (1962)
Albe-Fessard, D., Guiot, G., Lamarre, Y., Arfel, G.: Activation of thalamocortical projections related to tremorogenic processes. In: Purpura, D. P., Yahr, M. D. (eds.), The thalamus, pp. 237–253. New York: Columbia University Press 1966
Angeleri, F., Ferro-Milone, F., Parigi, S.: Electrical activity and reactivity of the rhinencephalic, pararhinencephalic and thalamic structures: Prolonged implantation of electrodes in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 16, 100–129 (1964)
Ball, G. J., Gloor, P., Schaul, N.: The cortical electromicrophysiology of pathological delta waves in the electroencephalograms of cats. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 43, 346–361 (1977)
Cobb, W. A.: The E.E.G. of lesions in general. In: Hill, D., Parr, G. (eds.), Electroencephalography, pp. 295–316. New York: MacMillan 1963
Cordeau, J. P.: Monorhythmic frontal delta activity in the human electroencephalogram. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 11, 733–746 (1959)
Crandall, P. H.: Developments in direct recordings from epileptogenic regions in the surgical treatment of partial epilepsies. In: Brazier, M. A. (ed.), Epilepsy. Its phenomena in man, pp. 287–310. New York: Academic Press 1973
Daly, D. D.: Genesis of abnormal activity. In: Rémond, A. (Ed.-in-Chief), Handbook of Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, Vol. 14C, pp. 5–10. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1975
Gibbs, F. A., Gibbs, E. L.: Atlas of electroencephalography, 2nd ed., Vol. 3. Reading: Addison-Wesley 1964
Hayne, R., Belinson, L., Gibs, F. A.: Electrical activity of subcortical areas in epilepsy. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 1, 437–445 (1949)
Hess, R.: The influence of stereotactic lesions on the EEG. In: Magnus, O., Storm van Leeuwen, W., Cobb, W. A. (eds.), Electroencephalography in cerebral tumours, pp. 166–171. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1961
Hosobuchi, Y., Adams, J. E., Linchitz, R.: Pain relief by electrical stimulation of the central gray matter in humans and its reversal by naloxone. Science 197, 183–186 (1977)
Ishikawa, O.: Electroencephalographical study of human thalamus. Folio Psychiat. Neurol. Japon. 11, 128–149 (1957)
Lichtenstein, R. S., Marshall, C., Walker, A. E.: Subcortical recording in temporal lobe epilepsy. Arch. Neurol. (Chicago) 1, 288–302 (1959)
Long, D. M.: External electrical stimulation as a treatment of chronic pain. Minn. Med. 57, 195–198 (1974)
Long, D. M., Hagfors, N.: Electrical stimulation in the nervous system: The current status of electrical stimulation of the nervous system for relief of pain. Pain 1, 109–123 (1975)
Mazars, G., Merienne, L., Cioloca, C.: Stimulations thalamiques intermittentes. Rev. neurol. (Paris) 128, 273–279 (1973)
Melczak, R., Wall, P. D.: Pain mechanisms. A new theory. Science 150, 971–979 (1965)
Niedermeyer, E., Laws, E. R., Jr., Walker, A. E.: Depth EEG findings in epileptics with generalized spike-wave complexes. Arch. Neurol. (Chicago) 21, 51–58 (1969)
Okuma, T., Shimazono, Y., Fakuda, T., Narabayashi, H.: Cortical and subcortical recordings in non-anesthetized and anesthetized periods in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 6, 269–286 (1954)
Richardson, D. E., Akil, H.: Pain reduction by electrical brain stimulation in man. Part 1: Acute administration in periaqueductal and periventricular sites. J. Neurosurg. 47, 179–183 (1977a)
Richardson, D. E., Akil, H.: Pain reduction by electrical brain stimulation in man. Part 2: Chronic self-administration in the periventricular gray matter. J. Neurosurg. 47, 184–194 (1977b)
Sano, K.: The role of the internal medullary lamina in pain. In: Anales del XII Congreso Latinoamericano del Neurocirurgia, pp. 937–952. Lima, Peru, 1967
Shealy, C. N., Mortimer, J. T., Reswick, J. B.: Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns. Anesth. Analg. (Cleveland) 46, 489–491 (1967)
Sweet, W. H.: Lessons on pain control from electrical stimulation. Trans. Stud. Coll. Phys. (Philadelphia) 35, 171–184 (1968)
Umbach, W.: Elektrophysiologische und vegetative Phänomene bei stereotaktischen Hirnoperationen. Berlin: Springer 1966
Van der Drift, J. H. A.: The significance of electro-encephalography for the diagnosis and localization of cerebral tumours. Leiden: Stenfert Kroese 1957
Walker, A. E., Marshall, C.: The contribution of depth recording to clinical medicine. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 16, 88–89 (1964)
Wall, P. D.: Presynaptic control of impulses at the first central synapse in the cutaneous pathway. Prog. Brain Res. 12, 92–118 (1964)
Wall, P. D., Sweet, W. H.: Temporary abolition of pain in man. Science 155, 108–109 (1967)
Williams, D.: A study of thalamic and cortical rhythms in “petit mal”. Brain 76, 50–69 (1953)
Willis, W. D., Haber, H., Martin, R. F.: Inhibition of spinothalamic tract cells and interneurons by brain stem stimulation in the monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 40, 968–981 (1977)
Zobniw, A. M., Yarworth, S., Niedermeyer, E.: Depth electroencephalography. J. Electrophysiol. Tech. 1, 215–240 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gücer, G., Niedermeyer, E. & Long, D.M. Thalamic EEG recordings in patients with chronic pain. J. Neurol. 219, 47–61 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313368
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313368