Summary
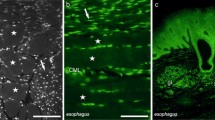
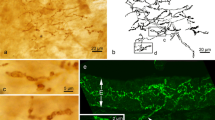
The occurrence and origin of substance P (SP)-immunoreactive (IR) nerves in the lower respiratory tract was studied by means of immunohistochemistry in the guinea-pig, rat, cat and man. In addition, biopsies from human material were also analysed by radioimmunoassay. SP-IR nerves were seen in four principal locations: 1) under or within the lining epithelium, 2) around blood vessels, 3) within the bronchial smooth muscle layer, and 4) around local tracheobronchial ganglion cells. Ligation experiments combined with capsaicin pretreatments indicated that all SP-IR nerves in the respiratory tract are sensory. The trachea seems to be mainly supplied by the vagal nerves, while intrapulmonary bronchi and blood vessels receive SP-IR nerves of both vagal and non-vagal (spinal) origin. SP-IR nerves were also found in the human bronchi with principally similar location as in the guinea-pig. The levels of SP-IR in the trachea and peripheral bronchi of man were about 3–4 pmol/g, which is in the same range as the content of corresponding tissues from the guinea-pig.
In conclusion, the present experimental findings of SP-IR nerves in the lower respiratory tract in both experimental animals and man support the functional evidence for the importance of SP in the vagal and non-vagal (spinal) control of bronchial smooth muscle tone and vascular permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson P, Persson H (1977) Effect of substance P on pulmonary resistance and dynamic pulmonary compliance in the anaesthetized cat and guinea-pig. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 41:444–448
Brimijoin S, Lundberg JM, Brodin E, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G (1980) Axonal transport of substance P in the vagus and sciatic nerves of the guinea-pig. Brain 191:443–457
Coburn RJ, Tomita T (1973) Evidence for nonadrenergic inhibitory nerves in the guinea-pig trachealis muscle. Am J Physiol 224:1072–1080
Cuello AC, Galfree G, Milstein C (1979) Detection of substance P in central nervous system by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Sci Acad, USA, 76:3532–3536
Dahlsgaard CJ, Lundberg JM (1983) Vagal and spinal innervation of the guinea-pig lower respiratory tract as studied by the HRP-technique. Neuroscience letters, in press
Dahlström A (1971) Effects of vinblastine and colchicine on monoamine containing neurons of the rat, with special regard to the axoplasmic transport of amine granules. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) Suppl 5, pp 226–237
Dahlström A (1971) Effects of vinblastine and colchicine on monoamine containing neurons of the rat, with special regard to the axoplasmic transport of amine granules. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) Suppl 5, pp 226–237
Diamond L, Szarek JL, Gillespie MN (1982) Substance P fails to mimic vagally mediated nonadrenergic bronchodilation. Peptides 3:27–29
Gamse R, Lembeck F, Cuello AC (1979a) Substance P in the vagus nerve: immunochemical and immunohistochemical evidence for axoplasmic transport. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs' Arch Pharmacol 306:37–44
Gamse R, Molnar A, Lembeck F (1979b) Substance P release from spinal cord slices by capsaicin. Life Sci 25:629–636
Gamse R, Wax A, Zigmond RE, Leeman SA (1981) Immunoreactive substance P in sympathetic ganglia: distribution and sensitivity towards capsaicin. Neuroscience 6:437–441
Gamse R, Petsche U, Lembeck F, Jancsó G (1982) Capsaicin applied to peripheral nerve inhibits axoplasmic transport of substance P and somatostatin. Brain Res 239:447–462
Grundström N, Andersson RG, Wikberg JES (1981) Pharmacological characterization of the autonomous innervation of the guinea-pig tracheobronchial smooth muscle. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 49:150–157
Helke CJ, Jacobowitz DM, Thoa NB (1981) Capsaicin and potassium evoked substance P release from the nucleus tractus solitarius and spinal trigeminal nucleus in vitro. Life Sci 29:1779–1785
Hökfelt T, Kellerth JO, Nilsson G, Pernow B (1975) Experimental immunohistochemical studies in the localization and distribution of substance P in cat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res 100:235–252
Holmes R, Torrance RW (1959) Afferent fibres of the stellate ganglion. Quart J Exp Physiol 44:271–281
Holzer P, Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1982) Distribution of capsaicinsensitive nerve fibres containing immunoreactive substance P in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neuroscience Letters 31:253–257
Hoyes AD, Barber P (1978) Fine structure and composition of the submucous nerve plexus of the guinea-pig trachea. Cell Tissue Res 190:301–316
Jancsó N, Jancsó-Gábor A, Szolcsanyi J (1967) Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 31:138–151
Jancsó N, Király E, Jancsó-Gábor A (1977) Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurons. Nature (Lond) 270:741–743
Jessell T, Iversen LL, Cuello AC (1978) Capsaicin-induced depletion of substance P from primary sensory neurons. Brain Res 152:183–188
Katz DM, Karten HJ (1980) Substance P in the vagal sensory ganglia. Localization in cell bodies and pericellular arborizations. J Comp Neurol 193:549–564
Konishi S, Otsuka M, Folkers K, Rosell S (1983) A substance P antagonist blocks non-cholinergic slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia. Acta Physiol Scand 117:157–160
Kostreva DR, Zuperku EJ, Hess GC, Coon RL, Kampine J (1975) Pulmonary afferent activity recorded from sympathetic neurons. J Appl Physiol 39:37–40
Lembeck F, Donnerer J, Barthó L (1982) Inhibition of neurogenic vasodilatation and plasma extravasation by substance P antagonists, somatostatin and (D-Met2, Pro5)-enkephalinamide. Eur J Pharmacol 85:171–176
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982a) Vagal substance P nerves involved in control of vascular permeability and smooth muscle tone in the trachea and bronchi. Br J Clin Pharmacol 77:441
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982b) Capsaicin-sensitive vagal neurons involved in control of vascular permeability in rat trachea. Acta Physiol Scand 115:521–523
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982c) Bronchial smooth muscle contraction induced by stimulation of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 116:473–476
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1983) Capsaicin-induced desensitization of the airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature (Lond) 302:251–253
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Elde R, Said S (1978) Peptide neurons in the vagus, splanchnic and sciatic nerves. Acta Physiol Scand 104:499–501
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G, Petterson G, Kewenter J, Ahlman H, Edin R, Dahlström A, Terenius L, Said S, Uvnäs Wallensten K (1979) Substance P, VIP and enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human vagus nerve. Gastroenterology 77:468–471
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Änggård A, Uvnäs-Wallensten K, Brimijoin S, Brodin E, Fahrenkrug J (1980) Peripheral peptide-neuron distribution, axonal transport and some aspects on possible function. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 22:25–36
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Änggård A, Terenius L, Elde R, Markey K, Goldstein M, Kimmel J (1982) Organizational principles in the peripheral sympathetic nervous system: Subdivision by co-existing peptides (somatostatin, avian pancreatic polypeptide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive materials). Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA, 79:1302–1307
Lundberg JM, Brodin E, Saria A (1983a) Effects and distribution of vagal capsaicin-sensitive substance P neurons with special reference to the trachea and lungs. Acta Physiol Scand, in press
Lundberg JM, Martling C-R, Saria A (1983b) Substance P and capsaicin-induced contraction of human bronchi. Acta Physiol Scand, 119:49–53
Lundberg JM, Martling C-R, Saria A, Folkers K, Rosell S (1983c) Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema due to activation of capsaicin-sensitive vagal afferents and substance P release. Neuroscience, in press
Lundberg JM, Saria A, Brodin E, Rosell S, Folkers K (1983d) A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea-pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA, 80:1120–1124
Lundblad L, Änggård A, Lundberg JM (1983) Effects of antidromic trigeminal nerve stimulation in relation to parasympathetic vasodilation in cat nasal mucosa. Acta Physiol Scand, 119:7–13
Molnar A, Makara GB, Byorgy L, Unyi G (1969) The bronchoconstriction action of capsaicin in the guinea-pig. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 36:413–421
Mroz EA, Leeman SE (1979) Substance P. In: Jaffe BM, Behrmann HR (eds) Methods of hormone radioimmunoassay, 2nd ed. New York, Academic Press, pp 121–137
Nilsson G, Dahlberg K, Brodin E, Sundler F, Strandberg K (1977) Distribution and constrictor effect of substance P guinea-pig tracheobronchial tissue. In: Euler US von, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 57–61
Richardson JB, Beland J (1976) Nonadrenergic inhibitory nervous system in human airways. J Appl Physiol 41:764–771
Rosell S, Olgart L, Gazelius B, Panopoulos P, Folkers K, Hörig J (1981) Inhibition of antidromic and substance P-induced vasodilatation by a substance P antagonist. Acta Physiol Scand 111:381–382
Schultzberg M, Hökfelt T, Terenius L, Rehfeld J, Brown M, Elde R, Goldstein M, Said SI (1980) Distribution of peptide and catecholamine containing neurons in the gastrointestinal tract of rat and guinea-pig: Immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin, cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine-β-hydroxylase. Neuroscience 5:689–744
Svensjö E, Lundberg JM, Änggård A, Hökfelt T (1980) Substance P increase in vascular permeability and presence in the hamster cheek pouch. J Microvasc Res 20:38
Wharton J, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Will JA, Brown MR, Pearse AGE (1979) Substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in mammalian lung. Invest Cell Pathol 2:3–10
Widdicombe J (1981) Nervous receptors in the respiratory tract. In: Hornbein T (ed) Lung biology in health and disease. Part I. Regulation of breathing, pp 429–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lundberg, J.M., Hökfelt, T., Martling, C.R. et al. Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res. 235, 251–261 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217848
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217848