Abstract
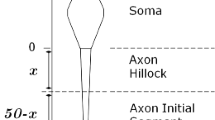
Action potentials elicited in the axon actively back-propagate into the dendritic tree. During this process their amplitudes can be modulated by internal and external factors. We used a compartmental model of a hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neuron to illustrate how this modulation could depend on (1) the properties of an A-type K+ conductance that is expressed at high density in hippocampal dendrites and (2) the relative timing of synaptic activation. The simulations suggest that the time relationship between pre- and postsynaptic activity could help regulate the amplitude of back-propagating action potentials, especially in the distal portion of the dendritic tree.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrionuevo G, Brown TH (1983) Associative long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80: 7347–7351.
Bekkers JM, Stevens CF (1990) Computational implications of NMDA receptor channels. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 55: 131–135.
Bernander Ö, Koch C, Douglas RJ (1994) Amplification and linearization of distal synaptic input to cortical pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 72: 2743–2753.
Bi GQ, Poo MM (1998) Synaptic modification in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type. J. Neurosci. 18: 10464–10472.
Cash S, Yuste R (1998) Input summation by cultured pyramidal neurons is linear and position-independent. J. Neurosci. 18: 10–15.
Cash S, Yuste R (1999) Linear summation of excitatory inputs by CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuron 22: 383–394.
Colbert CM, Johnston D (1996) Axonal action-potential initiation and NaC channel densities in the soma and axon initial segment of subicular pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 16: 6676–6686.
Colbert CM, Johnston D (1998) Protein Kinase C activation decreases activity-dependent attenuation of dendritic NaC current in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 79: 491–495.
Colbert CM, Magee JC, Hoffman DA, Johnston D (1997) Slow recovery from inactivation of NaC channels underlie the activity dependent attenuation of dendritic action potentials in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 17: 6512–6521.
Covarrubias M, Wei A, Salkoff L, Vyas TB (1994) Elimination of rapid potassium channel inactivation by phosphorylation of the inactivation gate. Neuron 13: 1403–1412.
Debanne D, Gähwiler BH, Thompson SM(1998) Long-term synaptic plasticity between pairs of individual CA3 pyramidal cells in rat hippocampal slice cultures. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 507: 237–247.
Drain P, Dubin AE, Aldrich RW (1994) Regulation of Shaker KC channel inactivation gating by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Neuron 12: 1097–1109.
Gustafsson B, Asztely F, Hanse E, Wigström H (1989) Onset characteristics of long-term potentiation in the guinea-pig hippocampal CA1 region in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1: 382–394.
Hines M, Carnevale NT (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comp. 9: 1178–1209.
Hoffman DA, Johnston D (1998) Down-regulation of transient KC channels in dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons by activation of PKA and PKC. J. Neurosci. 18: 3521–3528.
Hoffman DA, Johnston D (1999) Neuromodulation of dendritic action potentials. J. Neurophysiol. 81: 408–411.
Hoffman DA, Magee JC, Colbert CM, Johnston D (1997) Potassium channel regulation of signal propagation in dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nature 387: 869–875.
Holmes WR (1986) Cable theory modeling of the effectiveness of synaptic inputs in cortical pyramidal cells. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
Johnston D, Amaral DG (1998) Hippocampus. In: GM Shepherd, ed. The Synaptic Organization of the Brain, 4th ed. Oxford University Press, New York. pp. 417–458.
Jefferys JG (1975) Propagation of action potentials into the dendrites of hippocampal granule cells in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 249: 16P–18P.
Jung H, Mickus T, Spruston N (1997) Prolonged sodium channel inactivation contributes to dendritic action potential attenuation in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 17: 6639–6646.
Kelso SR, Brown TH (1986) Differential conditioning of associative synaptic enhancement in hippocampal brain slices. Science 232: 85–87.
Koester HJ, Sakmann B (1998) Calcium dynamics in single spines during coincident pre-and postsynaptic activity depend on relative timing of back-propagating action potentials and subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic potentials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 9596–9601.
Levy WB, Steward O (1983) Temporal contiguity requirements for long-term associative potentiation/depression in the hippocampus. Neurosci. 8: 791–797.
Magee, JC (1998) Dendritic hyperpolarization-activated currents modify the integrative properties of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci.
Magee JC (1999) Dendritic l-h normalizes temporal summation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Nature Neurosci. 2: 508–514.
Magee JC, Johnston D (1995) Characterization of single voltage gated NaC and Ca2C channels in apical dendrites of rat CA1 pyramidal neurons. J. Physiol. 487: 67–90.
Magee JC, Johnston D (1997) A synaptically controlled, associative signal for Hebbian plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Science 275: 209–213.
Mainen ZF, Joerges J, Huguenard JR, Sejnowski TJ (1995) A model of spike initiation in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron 15: 1427–1439.
Markram H, Lübke J, Frotscher M, Sakmann B (1997) Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275: 213–215.
Mickus T, Jung HY, Spruston N (1999) Properties of slow, cumulative sodium channel inactivation in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Biophys. J. 76: 846–860.
Migliore M (1996) Modeling the attenuation and failure of action potentials in the dendrites of hippocampal neurons. Biophys. J. 71: 2394–2403.
Migliore M, Culotta M (1998) Energy efficient modulation of dendritic processing functions. Biosystems 48: 157–163.
Rapp M, Yarom Y, Segev I (1996) Modeling back propagating action potential in weakly excitable dendrites of neocortical pyramidal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 11985–11990.
Rockland KS, Virga A (1989) Terminal arbors of individual feedback axons projecting from area V2 to V1 in the macaque monkey: A study using immunocitochemistry of anterogradely transported phaseoulus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J. Comp. Neurol. 285: 54–72.
Schiller J, Schiller Y, and Clapham DE (1998). NMDA receptors amplify calcium influx into dendritic spines during associative pre-and postsynaptic activation. Nature Neurosci. 1: 114–118.
Spruston N, Schiller Y, Stuart G, Sakmann B (1995) Activitydependent action potential invasion and Ca2C influx into hippocampal CA1 dendrites. Science 268: 297–300.
Stuart G, Häusser M (1992) Initiation and spread of sodium action potentials in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron 13: 703–712.
Stuart G, Sakmann B (1994) Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature 367: 69–72.
Tongiorgi E, Righi M, Cattaneo A (1997) Activity-dependent dendritic targeting of BDNF and TrkB mRNAs in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 17: 9492–9505.
Zador A, Koch C, Brown TH (1990) Biophysical model of a Hebbian synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 6718–6722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Migliore, M., Hoffman, D., Magee, J. et al. Role of an A-Type K+ Conductance in the Back-Propagation of Action Potentials in the Dendrites of Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons. J Comput Neurosci 7, 5–15 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008906225285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008906225285