Abstract
Multisensory integration does not only recruit higher-level association cortex, but also low-level and even primary sensory cortices. Here, we will describe and quantify two types of anatomical pathways, a thalamocortical and a corticocortical that possibly underlie short-latency multisensory integration processes in the primary auditory (A1), somatosensory (S1), and visual cortex (V1). Results were obtained from Mongolian gerbils, a common model-species in neuroscience, using simultaneous injections of different retrograde tracers into A1, S1, and V1. Several auditory, visual, and somatosensory thalamic nuclei project not only to the primary sensory area of their own (matched) but also to areas of other (non-matched) modalities. The crossmodal output ratios of these nuclei, belonging to both core and non-core sensory pathways, vary between 0.4 and 63.5 % of the labeled neurons. Approximately 0.3 % of the sensory thalamic input to A1, 5.0 % to S1, and 2.1 % to V1 arise from non-matched nuclei. V1 has most crossmodal corticocortical connections, projecting strongest to S1 and receiving a similar amount of moderate inputs from A1 and S1. S1 is mainly interconnected with V1. A1 has slightly more projections to V1 than S1, but gets just faint inputs from there. Concerning the layer-specific distribution of the retrogradely labeled somata in cortex, V1 provides the most pronounced feedforward-type outputs and receives (together with S1) most pronounced feedback-type inputs. In contrast, A1 has most pronounced feedback-type outputs and feedforward-type inputs in this network. Functionally, the different sets of thalamocortical and corticocortical connections could underlie distinctive types of integration mechanisms for different modality pairings.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
As reviewed by Driver and Noesselt (2008), multisensory interplay reveals crossmodal influences on sensory-specific brain areas, in particular of the cortex. The authors suggest, that there are at least three possible neuronal pathways mediating this multisensory interplay, which are not mutually exclusive: Account A (for "All multisensory): Direct feedforward influences between A1, V1, and S1, which might either arise subcortically at thalamic levels (account A.I) and/or via corticocortical connections directly between the primary sensory cortices (account A.II). Account B (for new Bimodal brain areas): Some multisensory regions may exist near classic unisensory regions. Account C (for "Critical role of feedback circuitry"): Feedback connections may exist from higher-level multisensory regions back to lower-level areas that are (predominantly) sensory-specific apart from these feedback influences. This feedback can also be mediated by thalamo-cortico-thalamic loops (see also Sherman and Guillery 2011). In the present study, we will largely provide evidence for the first possibility (account A).
Abbreviations
- A1:
-
Primary auditory cortex
- APTV:
-
Anterior pretectal nucleus, ventral division
- AuD:
-
Secondary auditory cortex, dorsal
- AuV:
-
Secondary auditory cortex, ventral
- AV:
-
Anteroventral thalamic nucleus
- BIC:
-
Brachium of the inferior colliculus
- bsc:
-
Brachium of the superior colliculus
- cp:
-
Cerebral peduncle
- CPu:
-
Caudate putamen
- d:
-
Dorsal
- DLG:
-
Dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus
- ec:
-
External capsule
- FDA:
-
Fluorescein-labeled dextran amine
- fi:
-
Fimbria hippocampus
- hbc:
-
Habenular commissure
- HF:
-
Hippocampus
- HL:
-
Hindlimb area
- ic:
-
Internal capsule
- InG:
-
Intermediate gray layer of the superior colliculus
- InWh:
-
Intermediate white layer of the superior colliculus
- l:
-
Lateral
- LD:
-
Laterodorsal thalamic nucleus
- LP:
-
Lateral posterior thalamic nucleus
- m:
-
Medial
- M1/2:
-
Primary/secondary motor cortex
- MGB:
-
Medial geniculate body
- MGD/M/V:
-
MGB, dorsal/medial/ventral division
- ml:
-
Medial lemniscus
- MV:
-
Mean value
- MZMG:
-
Marginal zone of MGB
- Op:
-
Optic nerve layer of the superior colliculus
- opt:
-
Optic tract
- pc:
-
Posterior commissure
- PLi:
-
Posterior limitans thalamic nucleus
- Po:
-
Posterior thalamic nuclear group
- r:
-
Rostral
- RSD:
-
Retrosplenial dysgranular cortex
- Rt:
-
Reticular thalamic nucleus
- S1/2:
-
Primary/secondary somatosensory cortex
- SG:
-
Suprageniculate nucleus
- SNR:
-
Substania nigra, reticular part
- SuG:
-
Superficial gray layer of the superior colliculus
- TMRDA:
-
Tetramethylrhodamine-labeled dextran amine
- v:
-
Ventral
- V1/2:
-
Primary/secondary visual cortex
- VA:
-
Ventral anterior thalamic nucleus
- VL:
-
Ventrolateral thalamic nucleus
- VLG:
-
Ventral lateral geniculate nucleus
- VM:
-
Venteromedial thalalamic nucleus
- VPL:
-
Ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus
- VPM:
-
Ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus
- ZI:
-
Zona incerta
References
Allison T, McCarthy G, Wood CC, Jones SJ (1991) Potentials evoked in human and monkey cerebral cortex by stimulation of the median nerve. A review of scalp and intracranial recordings. Brain 114:2465–2503
Banks MI, Uhlrich DJ, Smith PH, Krause BM, Manning KA (2011) Descending projections from extrastriate visual cortex modulate responses of cells in primary auditory cortex. Cereb Cortex 21:2620–2638
Barnes SJ, Finnerty GT (2010) Sensory experience and cortical rewiring. Neuroscientist 16:186–198
Barone P, Dehay C, Berland M, Bullier J, Kennedy H (1995) Developmental remodeling of primate visual cortical pathways. Cereb Cortex 5:22–38
Benedek G, Pereny J, Kovacs G, Fischer-Szatmari L, Katoh YY (1997) Visual, somatosensory, auditory and nociceptive modality properties in the feline suprageniculate nucleus. Neuroscience 78:179–189
Bezdudnaya T, Keller A (2008) Laterodorsal nucleus of the thalamus: a processor of somatosensory inputs. J Comp Neurol 507:1979–1989
Bizley JK, Nodal FR, Bajo VM, Nelken I, King AJ (2007) Physiological and anatomical evidence for multisensory interactions in auditory cortex. Cereb Cortex 17:2172–2189
Bonath B, Noesselt T, Martinez A, Mishra J, Schwiecker K, Heinze HJ, Hillyard SA (2007) Neural basis of the ventriloquist illusion. Curr Biol 17:1697–1703
Bonath B, Tyll S, Budinger E, Krauel K, Hopf JM, Noesselt T (2013) Task-demands and audio-visual stimulus configurations modulate neural activity in the human thalamus. Neuroimage 66:110–118
Bordi F, LeDoux JE (1994a) Response properties of single units in areas of rat auditory thalamus that project to the amygdala. I. Acoustic discharge patterns and frequency receptive fields. Exp Brain Res 98:261–274
Bordi F, LeDoux JE (1994b) Response properties of single units in areas of rat auditory thalamus that project to the amygdala. II. Cells receiving convergent auditory and somatosensory inputs and cells antidromically activated by amygdala stimulation. Exp Brain Res 98:275–286
Bronchti G, Heil P, Sadka R, Hess A, Scheich H, Wollberg Z (2002) Auditory activation of “visual” cortical areas in the blind mole rat (Spalax ehrenbergi). Eur J Neurosci 16:311–329
Brosch M, Selezneva E, Scheich H (2005) Nonauditory events of a behavioral procedure activate auditory cortex of highly trained monkeys. J Neurosci 25:6797–6806
Brueckner G, Seeger G, Brauer K, Härtig W, Kacza J, Bigl V (1994) Cortical areas are revealed by distribution patterns of proteoglycan components and parvalbumin in the Mongolian gerbil and rat. Brain Res 658:67–86
Budinger E, Scheich H (2009) Anatomical connections suitable for the direct processing of neuronal information of different modalities via the rodent primary auditory cortex. Hear Res 258:16–27
Budinger E, Heil P, Scheich H (2000a) Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). III. Anatomical subdivisions and corticocortical connections. Eur J Neurosci 12:2425–2451
Budinger E, Heil P, Scheich H (2000b) Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). IV. Connections with anatomically characterized subcortical structures. Eur J Neurosci 12:2452–2474
Budinger E, Heil P, Hess A, Scheich H (2006) Multisensory processing via early cortical stages: connections of the primary auditory cortical field with other sensory systems. Neuroscience 143:1065–1083
Budinger E, Laszcz A, Lison H, Scheich H, Ohl FW (2008) Non-sensory cortical and subcortical connections of the primary auditory cortex in Mongolian gerbils: bottom-up and top-down processing of neuronal information via field AI. Brain Res 1220:2–32
Budinger E, Brosch M, Scheich H, Mylius J (2013) The subcortical auditory structures in the Mongolian gerbil: II. Frequency-related topography of the connections with cortical field AI. J Comp Neurol 521:2772–2797
Busse L, Roberts KC, Crist RE, Weissman DH, Woldorff MG (2005) The spread of attention across modalities and space in a multisensory object. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18751–18756
Cahill L, Ohl F, Scheich H (1996) Alteration of auditory cortex activity with a visual stimulus through conditioning: a 2-deoxyglucose analysis. Neurobiol Learn Mem 65:213–222
Calvert GA, Brammer MJ, Bullmore ET, Campbell R, Iversen SD, David AS (1999) Response amplification in sensory-specific cortices during crossmodal binding. NeuroReport 10:2619–2623
Camalier CR, D’Angelo WR, Sterbing-D’Angelo SJ, de la Mothe LA, Hackett TA (2012) Neural latencies across auditory cortex of macaque support a dorsal stream supramodal timing advantage in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18168–18173
Campi KL, Karlen SJ, Bales KL, Krubitzer L (2007) Organization of sensory neocortex in prairie voles (Microtus ochrogaster). J Comp Neurol 502:414–426
Campi KL, Bales KL, Grunewald R, Krubitzer L (2010) Connections of auditory and visual cortex in the prairie vole (Microtus ochrogaster): evidence for multisensory processing in primary sensory areas. Cereb Cortex 20:89–108
Cappe C, Barone P (2005) Heteromodal connections supporting multisensory integration at low levels of cortical processing in the monkey. Eur J Neurosci 22:2886–2902
Cappe C, Morel A, Barone P, Rouiller EM (2009a) The thalamocortical projection systems in primate: an anatomical support for multisensory and sensorimotor interplay. Cereb Cortex 19:2025–2037
Cappe C, Rouiller EM, Barone P (2009b) Multisensory anatomical pathways. Hear Res 258:28–36
Cappe C, Thut G, Romei V, Murray MM (2010) Auditory-visual multisensory interactions in humans: timing, topography, directionality, and sources. J Neurosci 30:12572–12580
Chandler HC, King V, Corwin JV, Reep RL (1992) Thalamocortical connections of rat posterior parietal cortex. Neurosci Lett 143:237–242
Charbonneau V, Laramee ME, Boucher V, Bronchti G, Boire D (2012) Cortical and subcortical projections to primary visual cortex in anophthalmic, enucleated and sighted mice. Eur J Neurosci 36:2949–2963
Clavagnier S, Falchier A, Kennedy H (2004) Long-distance feedback projections to area V1: implications for multisensory integration, spatial awareness, and visual consciousness. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 4:117–126
Clemo HR, Sharma GK, Allman BL, Meredith MA (2008) Auditory projections to extrastriate visual cortex: connectional basis for multisensory processing in ‘unimodal’ visual neurons. Exp Brain Res 191:37–47
Cruikshank SJ, Edeline JM, Weinberger NM (1992) Stimulation at a site of auditory-somatosensory convergence in the medial geniculate nucleus is an effective unconditioned stimulus for fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 106:471–483
De la Mothe LA, Blumell S, Kajikawa Y, Hackett TA (2006) Thalamic connections of the auditory cortex in marmoset monkeys: core and medial belt regions. J Comp Neurol 496:72–96
Donoghue JP, Kerman KL, Ebner FF (1979) Evidence for two organizational plans within the somatic sensory-motor cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 183:647–663
Driver J, Noesselt T (2008) Multisensory interplay reveals crossmodal influences on ‘sensory-specific’ brain regions, neural responses, and judgments. Neuron 57:11–23
Espinosa JS, Stryker MP (2012) Development and plasticity of the primary visual cortex. Neuron 75:230–249
Fabre-Thorpe M, Vievard A, Buser P (1986) Role of the extra-geniculate pathway in visual guidance. II. Effects of lesioning the pulvinar-lateral posterior thalamic complex in the cat. Exp Brain Res 62:596–606
Fabri M, Burton H (1991a) Ipsilateral cortical connections of primary somatic sensory cortex in rats. J Comp Neurol 311:405–424
Fabri M, Burton H (1991b) Topography of connections between primary somatosensory cortex and posterior complex in rat: a multiple fluorescent tracer study. Brain Res 538:351–357
Falchier A, Clavagnier S, Barone P, Kennedy H (2002) Anatomical evidence of multimodal integration in primate striate cortex. J Neurosci 22:5749–5759
Falchier A, Schroeder CE, Hackett TA, Lakatos P, Nascimento-Silva S, Ulbert I, Karmos G, Smiley JF (2010) Projection from visual areas V2 and prostriata to caudal auditory cortex in the monkey. Cereb Cortex 20:1529–1538
Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC (1991) Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 1:1–47
Fishman MC, Michael P (1973) Integration of auditory information in the cat’s visual cortex. Vision Res 13:1415–1419
Foxe JJ, Morocz IA, Murray MM, Higgins BA, Javitt DC, Schroeder CE (2000) Multisensory auditory-somatosensory interactions in early cortical processing revealed by high-density electrical mapping. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 10:77–83
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2008) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Hong Kong
Fu S, Fan S, Chen L (2003) Event-related potentials reveal involuntary processing of orientation changes in the visual modality. Psychophysiology 40:770–775
Ghazanfar AA, Schroeder CE (2006) Is neocortex essentially multisensory? Trends Cogn Sci 10:278–285
Ghazanfar AA, Maier JX, Hoffman KL, Logothetis NK (2005) Multisensory integration of dynamic faces and voices in rhesus monkey auditory cortex. J Neurosci 25:5004–5012
Giard MH, Peronnet F (1999) Auditory-visual integration during multimodal object recognition in humans: a behavioral and electrophysiological study. J Cogn Neurosci 11:473–490
Goldschmidt J, Zuschratter W, Scheich H (2004) High-resolution mapping of neuronal activity by thallium autometallography. Neuroimage 23:638–647
Groenewegen HJ, Witter MP (2004) Thalamus. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 407–453
Hall AJ, Lomber SG (2008) Auditory cortex projections target the peripheral field representation of primary visual cortex. Exp Brain Res 190:413–430
Heimel JA, Van Hooser SD, Nelson SB (2005) Laminar organization of response properties in primary visual cortex of the gray squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis). J Neurophysiol 94:3538–3554
Hensch TK (2005) Critical period plasticity in local cortical circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:877–888
Hess A, Stiller D, Kaulisch T, Heil P, Scheich H (2000) New insights into the hemodynamic blood oxygenation level-dependent response through combination of functional magnetic resonance imaging and optical recording in gerbil barrel cortex. J Neurosci 20:3328–3338
Hicks TP, Stark CA, Fletcher WA (1986) Origins of afferents to visual suprageniculate nucleus of the cat. J Comp Neurol 246:544–554
Hoefer M, Tyll S, Kanowski M, Brosch M, Schoenfeld MA, Heinze HJ, Noesselt T (2013) Tactile stimulation and hemispheric asymmetries modulate auditory perception and neural responses in primary auditory cortex. Neuroimage 79:371–382
Innocenti GM, Price DJ (2005) Exuberance in the development of cortical networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:955–965
Inui K, Kakigi R (2006) Temporal analysis of the flow from V1 to the extrastriate cortex in humans. J Neurophysiol 96:775–784
Inui K, Wang X, Tamura Y, Kaneoke Y, Kakigi R (2004) Serial processing in the human somatosensory system. Cereb Cortex 14:851–857
Inui K, Okamoto H, Miki K, Gunji A, Kakigi R (2006) Serial and parallel processing in the human auditory cortex: a magnetoencephalographic study. Cereb Cortex 16:18–30
Jacobs GH, Deegan JF 2nd (1994) Sensitivity to ultraviolet light in the gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus): characteristics and mechanisms. Vision Res 34:1433–1441
Jaekl PM, Soto-Faraco S (2010) Audiovisual contrast enhancement is articulated primarily via the M-pathway. Brain Res 1366:85–92
Jones B (1995) Reticular formation: cytoarchitecture, transmitters, and projections. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, Sydney, pp 155–172
Jones EG (1998) A new view of specific and nonspecific thalamocortical connections. Adv Neurol 77:49–71 (discussion 72–73)
Jones EG (2007) The thalamus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kaas JH, Hall WC, Diamond IT (1972) Visual cortex of the grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis): architectonic subdivisions and connections from the visual thalamus. J Comp Neurol 145:273–305
Kamishina H, Conte WL, Patel SS, Tai RJ, Corwin JV, Reep RL (2009) Cortical connections of the rat lateral posterior thalamic nucleus. Brain Res 1264:39–56
Karlen SJ, Kahn DM, Krubitzer L (2006) Early blindness results in abnormal corticocortical and thalamocortical connections. Neuroscience 142:843–858
Kayser C, Petkov CI, Augath M, Logothetis NK (2005) Integration of touch and sound in auditory cortex. Neuron 48:373–384
Kayser C, Petkov CI, Logothetis NK (2008) Visual modulation of neurons in auditory cortex. Cereb Cortex 18:1560–1574
Kayser C, Petkov CI, Logothetis NK (2009) Multisensory interactions in primate auditory cortex: fMRI and electrophysiology. Hear Res 258:80–88
Khorevin VI (1978) Responses of the neurons of the magnocellular portion of the medial geniculate body to acoustic and somatosensory stimulation. Neirofiziologiia 10:133–141
Klinge C, Eippert F, Roder B, Buchel C (2010) Corticocortical connections mediate primary visual cortex responses to auditory stimulation in the blind. J Neurosci 30:12798–12805
Kobayasi KI, Suwa Y, Riquimaroux H (2013) Audiovisual integration in the primary auditory cortex of an awake rodent. Neurosci Lett 534:24–29
Komura Y, Tamura R, Uwano T, Nishijo H, Ono T (2005) Auditory thalamus integrates visual inputs into behavioral gains. Nat Neurosci 8:1203–1209
Koralek KA, Jensen KF, Killackey HP (1988) Evidence for two complementary patterns of thalamic input to the rat somatosensory cortex. Brain Res 463:346–351
Kral A, Eggermont JJ (2007) What’s to lose and what’s to learn: development under auditory deprivation, cochlear implants and limits of cortical plasticity. Brain Res Rev 56:259–269
Kurt S, Deutscher A, Crook JM, Ohl FW, Budinger E, Moeller CK, Scheich H, Schulze H (2008) Auditory cortical contrast enhancing by global winner-take-all inhibitory interactions. PLoS One 3:e1735
Lakatos P, Chen CM, O’Connell MN, Mills A, Schroeder CE (2007) Neuronal oscillations and multisensory interaction in primary auditory cortex. Neuron 53:279–292
Laramee ME, Rockland KS, Prince S, Bronchti G, Boire D (2012) Principal component and cluster analysis of layer V pyramidal cells in visual and non-visual cortical areas projecting to the primary visual cortex of the mouse. Cereb Cortex 23:714–728
Larsen DD, Luu JD, Burns ME, Krubitzer L (2009) What are the effects of severe visual impairment on the cortical organization and connectivity of primary visual cortex? Front Neuroanat 3:30
Laurienti PJ, Burdette JH, Wallace MT, Yen YF, Field AS, Stein BE (2002) Deactivation of sensory-specific cortex by cross-modal stimuli. J Cogn Neurosci 14:420–429
Lehmann C, Herdener M, Esposito F, Hubl D, di Salle F, Scheffler K, Bach DR, Federspiel A, Kretz R, Dierks T, Seifritz E (2006) Differential patterns of multisensory interactions in core and belt areas of human auditory cortex. Neuroimage 31:294–300
Lewis R, Noppeney U (2010) Audiovisual synchrony improves motion discrimination via enhanced connectivity between early visual and auditory areas. J Neurosci 30:12329–12339
Liang M, Mouraux A, Hu L, Iannetti GD (2013) Primary sensory cortices contain distinguishable spatial patterns of activity for each sense. Nat Commun 4:1979
Lomber SG, Meredith MA, Kral A (2010) Cross-modal plasticity in specific auditory cortices underlies visual compensations in the deaf. Nat Neurosci 13:1421–1427
Loskota WJ, Lomax P, Verity MA (1974) A stereotaxic atlas of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Ann Arbor Science, Michigan
Lurilli G, Ghezzi D, Olcese U, Lassi G, Nazzaro C, Tonini R, Tucci V, Benfenati F, Medini P (2012) Sound-driven synaptic inhibition in primary visual cortex. Neuron 73:814–828
Macaluso E (2006) Multisensory processing in sensory-specific cortical areas. Neuroscientist 12:327–338
Macaluso E, Driver J (2005) Multisensory spatial interactions: a window onto functional integration in the human brain. Trends Neurosci 28:264–271
MacLean JN, Fenstermaker V, Watson BO, Yuste R (2006) A visual thalamocortical slice. Nat Methods 3:129–134
Martuzzi R, Murray MM, Michel CM, Thiran JP, Maeder PP, Clarke S, Meuli RA (2007) Multisensory interactions within human primary cortices revealed by BOLD dynamics. Cereb Cortex 17:1672–1679
Maunsell JH, Gibson JR (1992) Visual response latencies in striate cortex of the macaque monkey. J Neurophysiol 68:1332–1344
McCarthy G, Wood CC, Allison T (1991) Cortical somatosensory evoked potentials. I. Recordings in the monkey Macaca fascicularis. J Neurophysiol 66:53–63
Mercier MR, Foxe JJ, Fiebelkorn IC, Butler JS, Schwartz TH, Molholm S (2013) Auditory-driven phase reset in visual cortex: human electrocorticography reveals mechanisms of early multisensory integration. Neuroimage 79:19–29
Meredith MA, Kryklywy J, McMillan AJ, Malhotra S, Lum-Tai R, Lomber SG (2011) Crossmodal reorganization in the early deaf switches sensory, but not behavioral roles of auditory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:8856–8861
Meyer K, Kaplan JT, Essex R, Damasio H, Damasio A (2011) Seeing touch is correlated with content-specific activity in primary somatosensory cortex. Cereb Cortex 21:2113–2121
Molholm S, Ritter W, Murray MM, Javitt DC, Schroeder CE, Foxe JJ (2002) Multisensory auditory-visual interactions during early sensory processing in humans: a high-density electrical mapping study. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 14:115–128
Morel A, Garraghty PE, Kaas JH (1993) Tonotopic organization, architectonic fields, and connections of auditory cortex in macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol 335:437–459
Morrell F (1972) Visual system’s view of acoustic space. Nature 238:44–46
Murata K, Cramer H, Bach-y-Rita P (1965) Neuronal convergence of noxious, acoustic, and visual stimuli in the visual cortex of the cat. J Neurophysiol 28:1223–1239
Murray MM, Molholm S, Michel CM, Heslenfeld DJ, Ritter W, Javitt DC, Schroeder CE, Foxe JJ (2005) Grabbing your ear: rapid auditory-somatosensory multisensory interactions in low-level sensory cortices are not constrained by stimulus alignment. Cereb Cortex 15:963–974
Mylius J, Brosch M, Scheich H, Budinger E (2013) Subcortical auditory structures in the Mongolian gerbil: I. Golgi architecture. J Comp Neurol 521:1289–1321
Naue N, Rach S, Struber D, Huster RJ, Zaehle T, Korner U, Herrmann CS (2011) Auditory event-related response in visual cortex modulates subsequent visual responses in humans. J Neurosci 31:7729–7736
Nauta WJ, Bucher VM (1954) Efferent connections of the striate cortex in the albino rat. J Comp Neurol 100:257–285
Noesselt T, Rieger JW, Schoenfeld MA, Kanowski M, Hinrichs H, Heinze HJ, Driver J (2007) Audiovisual temporal correspondence modulates human multisensory superior temporal sulcus plus primary sensory cortices. J Neurosci 27:11431–11441
Noesselt T, Tyll S, Boehler CN, Budinger E, Heinze HJ, Driver J (2010) Sound-induced enhancement of low-intensity vision: multisensory influences on human sensory-specific cortices and thalamic bodies relate to perceptual enhancement of visual detection sensitivity. J Neurosci 30:13609–13623
Nothias F, Peschanski M, Besson JM (1988) Somatotopic reciprocal connections between the somatosensory cortex and the thalamic Po nucleus in the rat. Brain Res 447:169–174
Nowak LG, Munk MH, Nelson JI, James AC, Bullier J (1995) Structural basis of cortical synchronization. I. Three types of interhemispheric coupling. J Neurophysiol 74:2379–2400
Ohl FW, Scheich H, Freeman WJ (2001) Change in pattern of ongoing cortical activity with auditory category learning. Nature 412:733–736
Palomero-Gallagher N, Zilles K (2004) Isocortex. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 729–757
Paperna T, Malach R (1991) Patterns of sensory intermodality relationships in the cerebral cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 308:432–456
Paxinos G (1995) The rat nervous system. Academic Press, Sydney
Paxinos G (2004) The rat nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Sydney
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Carrive P, Wang H, Wang P-Y (1999a) Chemoarchitectonic atlas of the rat brainstem. Academic Press, San Diego
Paxinos G, Kus L, Ashwell KWS, Watson C (1999b) Chemoarchitectonic atlas of the rat forebrain. Academic Press, San Diego
Pekkola J, Ojanen V, Autti T, Jaaskelainen IP, Mottonen R, Tarkiainen A, Sams M (2005) Primary auditory cortex activation by visual speech: an fMRI study at 3 T. NeuroReport 16:125–128
Peters A, Feldman ML (1976) The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat cerebral cortex. I. General description. J Neurocytol 5:63–84
Price DJ, Kennedy H, Dehay C, Zhou L, Mercier M, Jossin Y, Goffinet AM, Tissir F, Blakey D, Molnar Z (2006) The development of cortical connections. Eur J Neurosci 23:910–920
Radtke-Schuller S, Angenstein F, Goldschmidt J, Grosser OS, Schuller G, Budinger E (2011) Reconstructing the in vivo brain: A CT/MRT aided stereotaxic atlas of the Mongolian brain (Meriones unguiculatus) In: Proceedings of the 33rd Göttingen neurobiology conference and ninth Göttingen meeting of the German Neuroscience Society, p 1340
Raij T, Ahveninen J, Lin FH, Witzel T, Jaaskelainen IP, Letham B, Israeli E, Sahyoun C, Vasios C, Stufflebeam S, Hamalainen M, Belliveau JW (2010) Onset timing of cross-sensory activations and multisensory interactions in auditory and visual sensory cortices. Eur J Neurosci 31:1772–1782
Recanzone GH, Guard DC, Phan ML (2000) Frequency and intensity response properties of single neurons in the auditory cortex of the behaving macaque monkey. J Neurophysiol 83:2315–2331
Ro T, Ellmore TM, Beauchamp MS (2013) A neural link between feeling and hearing. Cereb Cortex 23:1724–1730
Rockland KS, Ojima H (2003) Multisensory convergence in calcarine visual areas in macaque monkey. Int J Psychophysiol 50:19–26
Romo R, Merchant H, Zainos A, Hernandez A (1996) Categorization of somaesthetic stimuli: sensorimotor performance and neuronal activity in primary somatic sensory cortex of awake monkeys. NeuroReport 7:1273–1279
Rouiller EM (1997) Functional organization of the auditory pathways. In: Ehret G, Romand R (eds) The central auditory system, pp 3–96
Rouiller EM, Simm GM, Villa AE, de Ribaupierre Y, de Ribaupierre F (1991) Auditory corticocortical interconnections in the cat: evidence for parallel and hierarchical arrangement of the auditory cortical areas. Exp Brain Res 86:483–505
Roy NC, Bessaih T, Contreras D (2011) Comprehensive mapping of whisker-evoked responses reveals broad, sharply tuned thalamocortical input to layer 4 of barrel cortex. J Neurophysiol 105:2421–2437
Ryan A (1976) Hearing sensitivity of the mongolian gerbil, Meriones unguiculatis. J Acoust Soc Am 59:1222–1226
Scheich H, Heil P, Langner G (1993) Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). II. Tonotopic 2-deoxyglucose. Eur J Neurosci 5:898–914
Schmahmann JD (2003) Vascular syndromes of the thalamus. Stroke 34:2264–2278
Schroeder CE, Foxe J (2005) Multisensory contributions to low-level, ‘unisensory’ processing. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:454–458
Schroeder CE, Lindsley RW, Specht C, Marcovici A, Smiley JF, Javitt DC (2001) Somatosensory input to auditory association cortex in the macaque monkey. J Neurophysiol 85:1322–1327
Schroeder CE, Smiley J, Fu KG, McGinnis T, O’Connell MN, Hackett TA (2003) Anatomical mechanisms and functional implications of multisensory convergence in early cortical processing. Int J Psychophysiol 50:5–17
Sears LL, Logue SF, Steinmetz JE (1996) Involvement of the ventrolateral thalamic nucleus in rabbit classical eyeblink conditioning. Behav Brain Res 74:105–117
Seto-Ohshima A, Ito M, Katoh M, Kitajima S, Kishikawa M (2001) Manipulation of the somatosensory cortex modulates stimulus-induced repetitive ear movements in a seizure-sensitive strain of gerbil. Zool Sci 18:1217–1223
Shankar S, Ellard C (2000) Visually guided locomotion and computation of time-to-collision in the mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus): the effects of frontal and visual cortical lesions. Behav Brain Res 108:21–37
Sherman SM, Guillery RW (2011) Distinct functions for direct and transthalamic corticocortical connections. J Neurophysiol 106:1068–1077
Shires KL, Hawthorne JP, Hope AM, Dudchenko PA, Wood ER, Martin SJ (2013) Functional connectivity between the thalamus and postsubiculum: analysis of evoked responses elicited by stimulation of the laterodorsal thalamic nucleus in anesthetized rats. Hippocampus 23:559–569
Sieben K, Roder B, Hanganu-Opatz IL (2013) Oscillatory entrainment of primary somatosensory cortex encodes visual control of tactile processing. J Neurosci 33:5736–5749
Smiley JF, Falchier A (2009) Multisensory connections of monkey auditory cerebral cortex. Hear Res 258:37–46
Smith PH, Manning KA, Uhlrich DJ (2010) Evaluation of inputs to rat primary auditory cortex from the suprageniculate nucleus and extrastriate visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 518:3679–3700
Spinelli DN, Starr A, Barrett TW (1968) Auditory specificity in unit recordings from cat’s visual cortex. Exp Neurol 22:75–84
Spreafico R, Hayes NL, Rustioni A (1981) Thalamic projections to the primary and secondary somatosensory cortices in cat: single and double retrograde tracer studies. J Comp Neurol 203:67–90
Stein BE, Stanford TR (2008) Multisensory integration: current issues from the perspective of the single neuron. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:255–266
Strick PL (1973) Light microscopic analysis of the cortical projection of the thalamic ventrolateral nucleus in the cat. Brain Res 55:1–24
Swanson L (2004) Brain maps. III. Structure of the rat brain. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Talsma D, Woldorff MG (2005) Selective attention and multisensory integration: multiple phases of effects on the evoked brain activity. J Cogn Neurosci 17:1098–1114
Teder-Salejarvi WA, McDonald JJ, Di Russo F, Hillyard SA (2002) An analysis of audio-visual crossmodal integration by means of event-related potential (ERP) recordings. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 14:106–114
Thiessen DD, Yahr P (1977a) A stereotaxic brain atlas of the gerbil. In: Thiessen DD, Yahr P (eds) The gerbil in behavioral investigations. Mechanisms of territoriality and olfactory communication. University of Texas Press, Austin, pp 118–157
Thiessen DD, Yahr P (1977b) The gerbil in behavioral investigations. Mechanisms of territoriality and olfactory communication. University of Texas Press, Austin
Thomas O (1908) The Duke of Bedford’s zoological exploration in Eastern Asia. XI List of mammals from the Mongolian plateau. Proc Zool Soc Lond:104–110
Thomas H, Tillein J, Heil P, Scheich H (1993) Functional organization of auditory cortex in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). I. Electrophysiological mapping of frequency representation and distinction of fields. Eur J Neurosci 5:882–897
Thorne JD, De Vos M, Viola FC, Debener S (2011) Cross-modal phase reset predicts auditory task performance in humans. J Neurosci 31:3853–3861
Tlamsa AP, Brumberg JC (2010) Organization and morphology of thalamocortical neurons of mouse ventral lateral thalamus. Somatosens Motor Res 27:34–43
Towns LC, Burton SL, Kimberly CJ, Fetterman MR (1982) Projections of the dorsal lateral geniculate and lateral posterior nuclei to visual cortex in the rabbit. J Comp Neurol 210:87–98
Tyll S, Budinger E, Noesselt T (2011) Thalamic influences on multisensory integration. Commun Integr Biol 4:378–381
Tyll S, Bonath B, Schoenfeld MA, Heinze HJ, Ohl FW, Noesselt T (2013) Neural basis of multisensory looming signals. Neuroimage 65:13–22
Vallejo LA, Garrosa M, Al-Majdalawi A, Mayo A, Gayoso MJ (2000) Effects of unilateral deprivation in postnatal development of the olfactory bulb in an altricial rodent, the gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Brain Res Dev Brain Res 122:35–46
Van Groen T, Wyss JM (1992) Projections from the laterodorsal nucleus of the thalamus to the limbic and visual cortices in the rat. J Comp Neurol 324:427–448
Van Groen T, Kadish I, Wyss JM (2002) The role of the laterodorsal nucleus of the thalamus in spatial learning and memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 136:329–337
Vaudano E, Legg CR, Glickstein M (1991) Afferent and efferent connections of temporal association cortex in the rat: a horseradish peroxidase study. Eur J Neurosci 3:317–330
Wallace MT, Ramachandran R, Stein BE (2004) A revised view of sensory cortical parcellation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2167–2172
Wang Q, Burkhalter A (2007) Area map of mouse visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 502:339–357
Wang Y, Celebrini S, Trotter Y, Barone P (2008) Visuo-auditory interactions in the primary visual cortex of the behaving monkey: electrophysiological evidence. BMC Neurosci 9:79
Wang Q, Sporns O, Burkhalter A (2012) Network analysis of corticocortical connections reveals ventral and dorsal processing streams in mouse visual cortex. J Neurosci 32:4386–4399
Watson C, Paxinos G, Pulles L (2012) The mouse nervous system. Elsevier, Sydney
Wepsic JG (1966) Multimodal sensory activation of cells in the magnocellular medial geniculate nucleus. Exp Neurol 15:299–318
Werner S, Noppeney U (2011) The contributions of transient and sustained response codes to audiovisual integration. Cereb Cortex 21:920–931
Werner-Reiss U, Kelly KA, Trause AS, Underhill AM, Groh JM (2003) Eye position affects activity in primary auditory cortex of primates. Curr Biol 13:554–562
Winer JA (1992) The functional architecture of the medial geniculate body and the primary auditory cortex. In: Webster DB, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) The mammalian auditory pathway: neuroanatomy. Springer, New York, pp 222–409
Winer JA, Diamond IT, Raczkowski D (1977) Subdivisions of the auditory cortex of the cat: the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase to the medial geniculate body and posterior thalamic nuclei. J Comp Neurol 176:387–417
Winer JA, Sally SL, Larue DT, Kelly JB (1999) Origins of medial geniculate body projections to physiologically defined zones of rat primary auditory cortex. Hear Res 130:42–61
Wise SP, Jones EG (1977) Cells of origin and terminal distribution of descending projections of the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol 175:129–157
Woldorff MG, Gallen CC, Hampson SA, Hillyard SA, Pantev C, Sobel D, Bloom FE (1993) Modulation of early sensory processing in human auditory cortex during auditory selective attention. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8722–8726
Zilles K (1985) The cortex of the rat. A stereotaxic atlas. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgments
We thank Anja Gürke and Janet Stallmann for their excellent histological assistance and Alexander Waite for editorial help. This work was supported by the State Sachsen-Anhalt, Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, and Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (grants of Sonderforschungsbereich Transregio 31 to T.N., H.S., E.B.), Germany.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
We declare that all animal studies have been approved by the appropriate ethics committee (see “Materials and methods”) and have, therefore, been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material
For those who are red-green color blind, Figures 1, 3 and 5 are provided in magenta-green (Suppl. Figures 1–3).
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
429_2013_694_MOESM1_ESM.tif
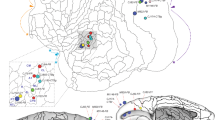
Supplementary Figure 1 (Fig. 1 magenta/green). (A-C) Frontal sections showing the cytoarchitecture (blue-fluorescent Nissl-stain) of the primary auditory (A1), somatosensory (S1), and visual cortex (V1). (D-F) Frontal sections showing a representative injection site of tetramethylrhodamine-dextranamine (TMRDA) (magenta) into A1 (D), of fluorescein-dextran amine (FDA) (green) into S1/HL (E), and of FDA into V1 (F). (G) Horizontal section illustrating the anterograde and retrograde labeling in the medial geniculate body (MGV, MGM), brachium of the inferior colliculus (BIC), reticular thalamic (Rt), ventrolateral thalamic (VL), and ventral posterorlateral thalamic nucleus (VPL) following an injection of TMRDA into A1 and of FDA into S1. Note the TMRDA and FDA labeling in the MGM (arrows). (H) Frontal section illustrating the anterograde and retrograde labeling in the dorsal, ventral, and medial divisions of the medial geniculate body (MGD, MGV, MGM), marginal zone of medial geniculate body (MZMG), and suprageniculate thalamic nucleus (SG) following an injection of TMRDA into A1 and of FDA into S1. Note the retrograde TMRDA and FDA labeling in the MZMG (arrows). (I) Frontal section illustrating the anterograde and retrograde labeling in the MGD, SG, posterior limitans thalamic nucleus (PLi), and BIC following an injection of TMRDA into A1 and of FDA into S1. Within the SG, a double-labeled neuron (yellow fluorescent, enlarged in inset) can be seen. (K) Horizontal section illustrating the anterograde and retrograde labeling in the dorsal division of lateral geniculate body (DLG), lateral posterior (LP), posterior thalamic nucleus (Po), and Rt following an injection of TMRDA into V1 and of FDA into S1. Note the retrograde TMRDA and FDA labeling in Po (arrow). Scale bars 1 mm (D-G, K) and 500 μm (A-C, H, I). For other abbreviations see list. (TIFF 19973 kb)
429_2013_694_MOESM2_ESM.tif
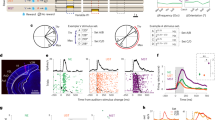
Supplementary Figure 2 (Fig. 3 magenta/green). Serial reconstructions of sections through the thalamus showing retrograde labeling after injections of TMRDA into A1 and FDA into V1 (A, D), TMRDA into A1 and FDA into S1 (B, E), and TMRDA into V1 and FDA into S1 (C, F). Note the TMRDA and FDA labeling in the suprageniculate (SG), laterodorsal (LD), posterior thalamic nucleus (Po), and medial division of the medial geniculate body (MGM). Horizontal (A-C) and frontal sections (D-F), respectively. Scale bars 1 mm. For other abbreviations see list. (TIFF 16710 kb)
429_2013_694_MOESM3_ESM.tif
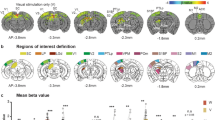
Supplementary Figure 3 (Fig. 5 magenta/green). Frontal sections showing retrogradely labeled somata (insets A, B, D, F and arrows in C, E) in the primary somatosensory (A, B), visual (C, D), and auditory cortex (E, F) following injections of FDA (green) and TMRDA (magenta) into A1 (B, D), S1 (C, F), and V1 (A, E). Scale bars 1 mm (A, B, D, F and insets C, E), 500 μm (C, E), 100 μm (inset A, B, D, F). For abbreviations see list. (TIFF 14166 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henschke, J.U., Noesselt, T., Scheich, H. et al. Possible anatomical pathways for short-latency multisensory integration processes in primary sensory cortices. Brain Struct Funct 220, 955–977 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0694-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-013-0694-4