Abstract
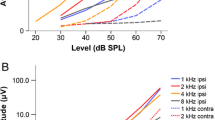
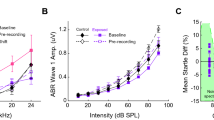
Gross electrical responses to tone bursts were measured in adult barn owls, using a single-ended wire electrode placed onto the round window. Cochlear microphonic (CM) and compound action potential (CAP) responses were evaluated separately. Both potentials were physiologically vulnerable. Selective abolishment of neural responses at high frequencies confirmed that the CAP was of neural origin, while the CM remained unaffected. CAP latencies decreased with increasing stimulus frequency and CAP amplitudes were correlated with known variations in afferent fibre numbers from the different papillar regions. This suggests a local origin of the CAP along the tonotopic gradient within the basilar papilla. The audiograms derived from CAP and CM threshold responses both showed a broad frequency region of optimal sensitivity, very similar to behavioural and single-unit data, but shifted upward in absolute sensitivity. CAP thresholds rose above 8 kHz, while CM responses showed unchanged sensitivity up to 10 kHz.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAP:
-
Compound action potential
- CM:
-
Cochlear microphonic
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- S-AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid
References
Brittan-Powell EF, Dooling RJ, Gleich O (2002) Auditory brainstem responses in adult budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). J Acoust Soc Am 112:999–1008
Brittan-Powell EF, Lohr B, Hahn DC, Dooling RJ (2005) Auditory brainstem responses in the Eastern Screech owl: an estimate of auditory thresholds. J Acoust Soc Am 118:314–321
Chen L, Salvi RJ, Hashino E (1993) Recovery of CAP threshold and amplitude in chickens following kanamycin ototoxicity. Hear Res 69:15–24
Chen L, Trautwein PG, Miller K, Salvi RJ (1995) Effects of kanamycin ototoxicity and hair cell regeneration on the DC endocochlear potential in adult chickens. Hear Res 89:28–34
Chen Z, Kujawa SG, McKenna MJ, Fiering JO, Mescher MJ, Borenstein JT, Swan EEL, Sewell WF (2005) Inner ear drug delivery via a reciprocating perfusion system in the guinea pig. J Control Rel 110:1–19
Coles RB, Guppy A (1988) Directional hearing in the barn owl (Tyto alba). J Comp Physiol A 163:117–133
Dallos P (1973) The auditory periphery: biophysics and physiology. Academic, New York
Dallos R, Harris O, Özdamar Ö, Ryan A (1978) Behavioral, compound action potential, and single unit thresholds: Relationship in normal and abnormal ears. J Acoust Soc Am 64:151–157
Dyson ML, Klump GM, Gauger B (1998) Absolute hearing thresholds and critical masking ratios in the European barn owl: a comparison with other owls. J Comp Physiol A 182:695–702
Fay RR (1988) Hearing in vertebrates: a psychophysics databook. Hill-Fay Associates, Winnetka
Gates GR, Perry DR, Coles RB (1975) Cochlear microphonics in the adult domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol 51A:251–252
Gleich O, Fischer FP, Köppl C, Manley GA (2004) Hearing organ evolution and specialization: Archosaurs. In: Manley GA, Popper A, Fay RR (eds) Evolution of the vertebrate auditory system. Springer, New York, pp 224–255
Gleich O, Klump GM, Dooling RJ (1995) Peripheral basis for the auditory deficit in Belgian Waterslager canaries (Serinus canarius). Hear Res 82:100–108
Gleich O, Manley GA (2000) The hearing organ of birds and crocodilia. In: Dooling RJ, Fay RR, Popper AN (eds) Comparative hearing: birds and reptiles. Springer, New York, pp 70–138
Gummer AW, Smolders JWT, Klinke R (1987) Basilar membrane motion in the pigeon measured with the Mössbauer technique. Hear Res 29:63–92
Henry KR (1995) Auditory nerve neurophonic recorded from the round window of the Mongolian gerbil. Hear Res 90:176–184
Jorgensen F (1977) Cochlear potentials of the pigeon inner ear recorded with microelectrodes. Acta Physiol Scand 100:393–403
Kim YS, Jones TA, Chertoff ME, Nunnally WC (2006) Columella footplate motion and the cochlear microphonic potential in the embryo and hatchling chicken. J Acoust Soc Am 120:3811–3821
Konishi M (1973) How the owl tracks its prey. Am Sci 61:414–424
Köppl C (1997a) Frequency tuning and spontaneous activity in the auditory nerve and cochlear nucleus magnocellularis of the barn owl, Tyto alba. J Neurophysiol 77:364–377
Köppl C (1997b) Number and axon calibres of cochlear afferents in the barn owl. Auditory Neurosci 3:313–334
Köppl C (1997c) Phase locking to high frequencies in the auditory nerve and cochlear nucleus magnocellularis of the barn owl, Tyto alba. J Neurosci 17:3312–3321
Köppl C, Gleich O, Manley GA (1993) An auditory fovea in the barn owl cochlea. J Comp Physiol A 171:695–704
Köppl C, Wegscheider A, Gleich O, Manley GA (2000) A quantitative study of cochlear afferent axons in birds. Hear Res 139:123–143
Özdamar O, Dallos P (1976) Input-output functions of cochlear whole-nerve action potentials: interpretation in terms of one population of units. J Acoust Soc Am 59:143–147
Palmer AR, Russell IJ (1986) Phase-locking in the cochlear nerve of the guinea-pig and its relation to the receptor potential of inner hair-cells. Hear Res 24:1–15
Patuzzi RB, Bull CL (1991) Electrical responses from the chicken basilar papilla. Hear Res 53:57–77
Pickles JO (1982) An introduction to the physiology of hearing. Academic, London
Rajan R, Irvine DRF, Cassell JF (1991) Normative N1 audiogram data for the barbiturate-anaesthetised domestic cat. Hear Res 53:153–158
Rebillard G, Rubel EW (1981) Electrophysiological study of the maturation of auditory responses from the inner ear of the chick. Brain Res 229:15–23
Reng D, Müller M, Smolders JWT (2001) Functional recovery of hearing following AMPA-induced reversible disruption of hair cell afferent synapses in the avian inner ear. Audiol Neuro Otol 6:66–78
Sachs MB, Young ED, Lewis RH (1974) Discharge patterns of single fibers in the pigeon auditory nerve. Brain Res 70:431–447
Salt AN, Ma Y (2001) Quantifcation of solute entry into cochlear perilymph through the round window membrane. Hear Res 154:88–97
Salvi RJ, Saunders SS, Powers NL, Boettcher FA (1992) Discharge patterns of cochlear ganglion neurons in the chicken. J Comp Physiol A 170:227–241
Saunders JC, Coles RB, Gates GR (1973) The development of auditory evoked responses in the cochlea and cochlear nuclei of the chick. Brain Res 63:59–74
Sellick P, Patuzzi R, Robertson D (2003) Primary afferent and cochlear nucleus contributions to extracellular potentials during tone-bursts. Hear Res 176:42–58
Smolders JWT, Ding-Pfennigdorff D, Klinke R (1995) A functional map of the pigeon basilar papilla: correlation of the properties of single auditory nerve fibres and their peripheral origin. Hear Res 92:151–169
Snyder RL, Schreiner CE (1984) The auditory neurophonic: basic properties. Hear Res 15:261–280
Sullivan WE, Konishi M (1984) Segregation of stimulus phase and intensity coding in the cochlear nucleus of the barn owl. J Neurosci 4:1787–1799
Sun H, Salvi RJ, Ding DL, Hashino E, Shero M, Zheng XY (2000) Excitotoxic effect of kainic acid on chicken otoacoustic emissions and cochlear potentials. J Acoust Soc Am 107:2136–2142
van Dijk T (1973) A comparative study of hearing in owls of the family Strigidae. Neth J Zool 23:131–167
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Hermann Wagner for his generous gift of two owls used in this study. Geoff Manley kindly commented on an earlier version of the manuscript. Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft through the SFB 204, a Heisenberg fellowship and an individual grant (Sachbeihilfe Ko 1143/11) to CK. Experiments complied with the “Principles of animal care”, publication No. 86–23, revised 1985 of the National Institute of Health. Animal husbandry and experimental protocols were approved by the Regierung von Oberbayern (AZ 211-2531-28/98).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köppl, C., Gleich, O. Evoked cochlear potentials in the barn owl. J Comp Physiol A 193, 601–612 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-007-0215-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-007-0215-0