Abstract
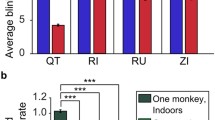
The eyes play an essential role in social communication. Eyeblinks, however, have thus far received minor attention. We previously showed that subjects blink in synchrony while viewing the same video stories (Nakano et al. in Proc R Soc B 276:3635–3644, 2009). We therefore hypothesized that eyeblinks are synchronized between listener and speaker in face-to-face conversation. Here, we show that listeners blinked with a delay of 0.25–0.5 s after the speaker blinked when the listeners viewed close-up video clips (with sound) of the speaker’s face. Furthermore, this entrainment was selectively triggered by speaker’s eyeblinks occurring at the end and during pauses in speech. Eyeblink entrainment was not observed when viewing identical video clips without sound, indicating that blink entrainment was not an automatic imitation. We therefore suggest that eyeblink entrainment reflects smooth communication between interactants.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chartrand TL, Bargh JA (1999) The chameleon effect: the perception-behavior link and social interaction. J Pers Soc Psychol 76:893–910
Condon WS, Ogston WD (1966) Sound film analysis of normal and pathological behavior patterns. J Nerv Ment Dis 143:338–347
Condon WS, Sander LW (1974a) Neonate movement is synchronized with adult speech: interactional participation and language acquisition. Science 183:99–101
Condon WS, Sander LW (1974b) Synchrony demonstrated between movements of the neonate and adult speech. Child Dev 45:456–462
Dittmann AT, Llewellyn LG (1968) Relationship between vocalizations and head nods as listener responses. J Pers Soc Psychol 9:79–84
Drew G (1951) Variations in reflex blink-rate during visual-motor tasks. Q J Exp Psychol 3:73–88
Ekman P (2003) Emotions revealed: recognizing faces and feelings to improve communication and emotional life. Times books
Emery NJ (2000) The eyes have it: the neuroethology, function and evolution of social gaze. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:581–604
Fukuda K (1994) Analysis of eyeblink activity during discriminative tasks. Percept Mot Skills 79:1599–1608
Hall A (1945) The origin and purposes of blinking. Bri J Opthalmol 29:445–467
Karson CN (1983) Spontaneous eye-blink rates and dopaminergic systems. Brain 106(Pt 3):643–653
McFarland DH (2001) Respiratory markers of conversational interaction. J Speech Lang Hear Res 44:128–143
Nakano T, Yamamoto Y, Kitajo K, Takahashi T, Kitazawa S (2009) Synchronization of spontaneous eyeblinks while viewing video stories. Proc Biol Sci 276:3635–3644
Ponder E, Kennedy WP (1927) On the act of blinking. Q J Exp Physiol 18:89–110
Shockley K, Santana MV, Fowler CA (2003) Mutual interpersonal postural constraints are involved in cooperative conversation. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 29:326–332
Stern JA, Walrath LC, Goldstein R (1984) The endogenous eyeblink. Psychophysiology 21:22–33
Theiler J, Eubank S, Longtin A, Galdrikian B, Farmer D (1992) Testing for nonlinearity in time series: the method of surrogate data. Physica D 58:77–94
Tomasello M, Farrar MJ (1986) Joint attention and early language. Child Dev 57:1454–1463
Toyama K, Kimura M, Tanaka K (1981) Cross-correlation analysis of interneuronal connectivity in cat visual cortex. J Neurophysiol 46:191–201
VanderWerf F, Brassinga P, Reits D, Aramideh M, Ongerboer de Visser B (2003) Eyelid movements: behavioral studies of blinking in humans under different stimulus conditions. J Neurophysiol 89:2784–2796
Yuze H, Tada H (1994) A computerized identification and date analysis of eyeblink EOG waves. Jap. J. Ergonom 30:331–337
Zellner B (1994) Pauses and the temporal structure of speech. In: Keller E (ed) Fundamentals of speech synthesis and speech recognition. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 41–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakano, T., Kitazawa, S. Eyeblink entrainment at breakpoints of speech. Exp Brain Res 205, 577–581 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2387-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2387-z