Abstract
Rationale
The search for novel antipsychotic drugs to treat schizophrenia is driven by the poor treatment efficacy, serious side effects, and poor patient compliance of current medications. Recently, a class of compounds known as tetrahydroprotoberberines, which includes the compound d,l-govadine, have shown promise in preclinical rodent tests relevant to schizophrenia. To date, the effect of govadine on prepulse inhibition (PPI), a test for sensorimotor gating commonly used to assess the effects of putative treatments for schizophrenia, has not been determined.
Objectives
The objective of the present study was to determine the effects of each enantiomer of govadine (d- and l-govadine) on PPI alone and its disruption by the distinct pharmacological compounds apomorphine and MK-801.
Methods
Male Long-Evans rats were treated systemically with d- or l-govadine and apomorphine or MK-801 prior to PPI. The PPI paradigm employed here included parametric manipulations of the prepulse intensity and the interval between the prepulse and pulse.
Results
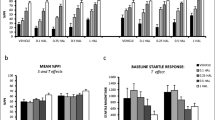
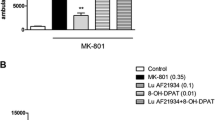
Acute MK-801 (0.15 mg/kg) significantly increased the startle response to startle pulses alone, while both MK-801 and apomorphine (0.2 mg/kg) significantly increased reactivity to prepulse-alone trials. Both MK-801 and apomorphine disrupted PPI. In addition, d-govadine alone significantly disrupted PPI in the apomorphine experiment. Pretreatment with l-, but not d-, govadine (1.0 mg/kg) blocked the effect of apomorphine and MK-801 on PPI. Treatment of rats with l-govadine alone (0.3, 1.0, 3.0 mg/kg) also dose-dependently increased PPI.
Conclusions
Given the high affinity of l-govadine for dopamine D2 receptors, these results suggest that further testing of l-govadine as an antipsychotic is warranted.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Amin HA, Schwarzkopf SB (1996) Effects of the PCP analog dizocilpine on sensory gating: potential relevance to clinical subtypes of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 40:744–754
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1995) Antagonism of phencyclidine-induced deficits in prepulse inhibition by the putative atypical antipsychotic olanzapine. Psychopharmacology 122:198–201
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1994) Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:787–794
Balla A, Koneru R, Smiley J, Sershen H, Javitt DC (2001) Continuous phencyclidine treatment induces schizophrenia-like hyperreactivity of striatal dopamine release. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:157–164
Balla A, Sershen H, Serra M, Koneru R, Javitt DC (2003) Subchronic continuous phencyclidine administration potentiates amphetamine-induced frontal cortex dopamine release. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:34–44
Ballendine SA, Greba Q, Dawicki W, Zhang X, Gordon JR, Howland JG (2015) Behavioral alterations in rat offspring following maternal immune activation and ELR-CXC chemokine receptor antagonism during pregnancy: implications for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 57:155–165
Bast T, Zhang W, Feldon J, White IM (2000) Effects of MK801 and neuroleptics on prepulse inhibition: re-examination in two strains of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:647–658
Bortolato M, Frau R, Aru GN, Orru M, Gessa GL (2004) Baclofen reverses the reduction in prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response induced by dizocilpine, but not by apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 171:322–330
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Braff D, Stone C, Callaway E et al (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Brosda J, Hayn L, Klein C, Koch M, Meyer C, Schallhorn R, Wegener N (2011) Pharmacological and parametrical investigation of prepulse inhibition of startle and prepulse elicited reactions in Wistar rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:22–28
Bubenikova V, Votava M, Horacek J, Palenicek T, Dockery C (2005) The effect of zotepine, risperidone, clozapine and olanzapine on MK-801-disrupted sensorimotor gating. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:591–596
Bubenikova-Valesova V, Svoboda J, Horacek J, Vales K (2009) The effect of a full agonist/antagonist of the D1 receptor on locomotor activity, sensorimotor gating and cognitive function in dizocilpine-treated rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:873–883
Castellanos FX, Fine EJ, Kaysen D, Marsh WL, Rapoport JL, Hallett M (1996) Sensorimotor gating in boys with Tourette’s syndrome and ADHD: preliminary results. Biol Psychiatry 39:33–41
Chandna AR, Kuhlmann N, Bryce CA, Greba Q, Campanucci VA, Howland JG (2015) Chronic maternal hyperglycemia induced during mid-pregnancy in rats increases RAGE expression, augments hippocampal excitability, and alters behavior of the offspring. Neuroscience 303:241–260
Depoortere R, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (1997) Potentiation of prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in rats: pharmacological evaluation of the procedure as a model for detecting antipsychotic activity. Psychopharmacology 132:366–374
Dunah AW, Sirianni AC, Fienberg AA, Bastia E, Schwarzschild MA, Standaert DG (2004) Dopamine D1-dependent trafficking of striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors requires Fyn protein tyrosine kinase but not DARPP-32. Mol Pharmacol 65:121–129
Duncan EJ, Madonick SH, Parwani A, Angrist B, Rajan R, Chakravorty S, Efferen TR, Szilagyi S, Stephanides M, Chappell PB, Gonzenbach S, Ko GN, Rotrosen JP (2001) Clinical and sensorimotor gating effects of ketamine in normals. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:72–83
Fendt M, Li L, Yeomans JS (2001) Brain stem circuits mediating prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex. Psychopharmacology 156:216–224
Geyer MA, Russo PV, Segal DS, Kuczenski R (1987) Effects of apomorphine and amphetamine on patterns of locomotor and investigatory behavior in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 28:393–399
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull 25:485–498
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Gorelova N, Seamans JK, Yang CR (2002) Mechanisms of dopamine activation of fast-spiking interneurons that exert inhibition in rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 88:3150–3166
Grillon C, Ameli R, Charney DS et al (1992) Startle gating deficits occur across prepulse intensities in schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 32:939–943
Hoffman DC, Donovan H, Cassella JV (1993) The effects of haloperidol and clozapine on the disruption of sensorimotor gating induced by the noncompetitive glutamate antagonist MK-801. Psychopharmacology 111:339–344
Homayoun H, Moghaddam B (2007) NMDA receptor hypofunction produces opposite effects on prefrontal cortex interneurons and pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 27:11496–11500
Howland JG, Hannesson DK, Phillips AG (2004) Delayed onset of prepulse inhibition deficits following kainic acid treatment on postnatal day 7 in rats. Eur J Neurosci 20:2639–2648
Howland JG, Cazakoff BN, Zhang Y (2012) Altered object-in-place recognition memory, prepulse inhibition, and locomotor activity in the offspring of rats exposed to a viral mimetic during pregnancy. Neuroscience 201:184–198
Japha K, Koch M (1999) Picrotoxin in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs sensorimotor gating in rats: reversal by haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 144:347–354
Jin GZ, Zhu ZT, Fu Y (2002) (−)-Stepholidine: a potential novel antipsychotic drug with dual D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist actions. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:4–7
Johansson C, Jackson DM, Svensson L (1994) The atypical antipsychotic, remoxipride, blocks phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in the rat. Psychopharmacology 116:437–442
Jones CK, Shannon HE (2000) Muscarinic cholinergic modulation of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1017–1023
Jones NC, Martin S, Megatia I, Hakami T, Salzberg MR, Pinault D, Morris MJ, O'Brien TJ, van den Buuse M (2010) A genetic epilepsy rat model displays endophenotypes of psychosis. Neurobiol Dis 39:116–125
Kegeles LS, Abi-Dargham A, Zea-Ponce Y, Rodenhiser-Hill J, Mann JJ, Van Heertum RL, Cooper TB, Carlsson A, Laruelle M (2000) Modulation of amphetamine-induced striatal dopamine release by ketamine in humans: implications for schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 48:627–640
Keith VA, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Failure of haloperidol to block the effects of phencyclidine and dizocilpine on prepulse inhibition of startle. Biol Psychiatry 30:557–566
Kinney GG, Wilkinson LO, Saywell KL, Tricklebank MD (1999) Rat strain differences in the ability to disrupt sensorimotor gating are limited to the dopaminergic system, specific to prepulse inhibition, and unrelated to changes in startle amplitude or nucleus accumbens dopamine receptor sensitivity. J Neurosci 19:5644–5653
Koch M, Schnitzler HU (1997) The acoustic startle response in rats—circuits mediating evocation, inhibition and potentiation. Behav Brain Res 89:35–49
Lapish CC, Belardetti F, Ashby DM, Ahn S, Butts KA, So K, Macrae CM, Hynd JJ, Miller JJ, Phillips AG (2012) A preclinical assessment of d.l-govadine as a potential antipsychotic and cognitive enhancer. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:1441–1455
Lapish CC, Ahn KC, Chambers RA, Ashby DM, Ahn S, Phillips AG (2014) Selective effects of D- and L-govadine in preclinical tests of positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology.
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Kegeles L, Innis R (1999) Increased dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: relationship to illness phases. Biol Psychiatry 46:56–72
Lins BR, Phillips AG, Howland JG (2015) Effects of d- and l-govadine on the disruption of touchscreen object-location paired associates learning in rats by acute MK-801 treatment. Psychopharmacology 232:4371–4382
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Parametric determinants in pre-stimulus modification of acoustic startle: interaction with ketamine. Psychopharmacology 105:162–168
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
Missale C, Fiorentini C, Busi C, Collo G, Spano PF (2006) The NMDA/D1 receptor complex as a new target in drug development. Curr Top Med Chem 6:801–808
Natesan S, Reckless GE, Barlow KB, Odontiadis J, Nobrega JN, Baker GB, George SR, Mamo D, Kapur S (2008) The antipsychotic potential of l-stepholidine—a naturally occurring dopamine receptor D1 agonist and D2 antagonist. Psychopharmacology 199:275–289
Pezze M, McGarrity S, Mason R et al (2014) Too little and too much: hypoactivation and disinhibition of medial prefrontal cortex cause attentional deficits. J Neurosci 34:7931–7946
Pinnock F, Bosch D, Brown T, Simons N, Yeomans JR, DeOliveira C, Schmid S (2015) Nicotine receptors mediating sensorimotor gating and its enhancement by systemic nicotine. Front Behav Neurosci 9:30
Porsolt RD, Moser PC, Castagne V (2010) Behavioral indices in antipsychotic drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 333:632–638
Qu Y, Saint Marie RL, Breier MR, Ko D, Stouffer D, Parsons LH, Swerdlow NR (2009) Neural basis for a heritable phenotype: differences in the effects of apomorphine on startle gating and ventral pallidal GABA efflux in male Sprague-Dawley and Long-Evans rats. Psychopharmacology 207:271–280
Reijmers L, Peeters B (1994) Effects of acoustic prepulses on the startle reflex in rats: a parametric analysis. Brain Res 661:174–180
Seamans JK, Gorelova N, Durstewitz D, Yang CR (2001) Bidirectional dopamine modulation of GABAergic inhibition in prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 21:3628–3638
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1993) Clozapine and haloperidol in an animal model of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:741–744
Swerdlow NR, Benbow CH, Zisook S, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1993) A preliminary assessment of sensorimotor gating in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 33:298–301
Swerdlow NR, Paulsen J, Braff DL, Butters N, Geyer MA, Swenson MR (1995) Impaired prepulse inhibition of acoustic and tactile startle response in patients with Huntington's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 58:192–200
Swerdlow NR, Bakshi V, Geyer MA (1996) Seroquel restores sensorimotor gating in phencyclidine-treated rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 279:1290–1299
Swerdlow NR, Bakshi V, Waikar M et al (1998) Seroquel, clozapine and chlorpromazine restore sensorimotor gating in ketamine-treated rats. Psychopharmacology 140:75–80
Swerdlow NR, Martinez ZA, Hanlon FM, Platten A, Farid M, Auerbach P, Braff DL, Geyer MA (2000) Toward understanding the biology of a complex phenotype: rat strain and substrain differences in the sensorimotor gating-disruptive effects of dopamine agonists. J Neurosci 20:4325–4336
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2001a) Neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat: current knowledge and future challenges. Psychopharmacology 156:194–215
Swerdlow NR, Platten A, Kim YK, Gaudet I, Shoemaker J, Pitcher L, Auerbach P (2001b) Sensitivity to the dopaminergic regulation of prepulse inhibition in rats: evidence for genetic, but not environmental determinants. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 70:219–226
Swerdlow NR, Talledo J, Shoemaker JM, Codon K, Goins J, Auerbach PP (2004) Weak prepulses inhibit but do not elicit startle in rats and humans. Biol Psychiatry 55:1195–1198
Swerdlow NR, Bonggiovanni MJ, Tochen L, Shoemaker JM (2006) Separable noradrenergic and dopaminergic regulation of prepulse inhibition in rats: implications for predictive validity and Tourette Syndrome. Psychopharm 186:246–254
Swerdlow NR, Weber M, Qu Y, Light GA, Braff DL (2008) Realistic expectations of prepulse inhibition in translational models for schizophrenia research. Psychopharmacology 199:331–388
Swerdlow NR, Bhakta S, Chou HH, Talledo JA, Balvaneda B, Light GA (2016a) Memantine effects on sensorimotor gating and mismatch negativity in patients with chronic psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:419–430
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA (2016b) Sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex: what we said 25 years ago, what has happened since then, and what comes next. J Psychopharmacol. In press.
Trantham-Davidson H, Neely LC, Lavin A, Seamans JK (2004) Mechanisms underlying differential D1 versus D2 dopamine receptor regulation of inhibition in prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 24:10652–10659
van den Buuse M, Gogos A (2007) Differential effects of antipsychotic drugs on serotonin-1A receptor-mediated disruption of prepulse inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1224–1236
Varty GB, Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1999) M100907, a serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist and putative antipsychotic, blocks dizocilpine-induced prepulse inhibition deficits in Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:311–321
Vinson PN, Conn PJ (2012) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as therapeutic targets for schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 62:1461–1472
Vorhees CV, Reed TM, Schilling MS et al (1996) Neonatal methamphetamine-induced long term acoustic startle facilitation in rats as a function of prepulse stimulus intensity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 18:135–139
Weiss IC, Di IL, Feldon J, Domeney AM (2000) Strain differences in the isolation-induced effects on prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response and on locomotor activity. Behav Neurosci 114:364–373
Wiley JL, Harvey SA, Balster RL, Nicholson KL (2003) Affinity and specificity of N-methyl- D-aspartate channel blockers affect their ability to disrupt prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in rats. Psychopharmacology 165:378–385
Yang K, Jin G, Wu J (2007) The neuropharmacology of (−)-stepholidine and its potential applications. Curr Neuropharmacol 5:289–294
Yee BK, Feldon J (2009) Distinct forms of prepulse inhibition disruption distinguishable by the associated changes in prepulse-elicited reaction. Behav Brain Res 204:387–395
Yee BK, Chang DL, Feldon J (2004a) The effects of dizocilpine and phencyclidine on prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex and on prepulse-elicited reactivity in C57BL6 mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1865–1877
Yee BK, Russig H, Feldon J (2004b) Apomorphine-induced prepulse inhibition disruption is associated with a paradoxical enhancement of prepulse stimulus reactivity. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:240–248
Yeomans JS, Lee J, Yeomans MH, Steidl S, Li L (2006) Midbrain pathways for prepulse inhibition and startle activation in rat. Neuroscience 142:921–929
Yeomans JS, Bosch D, Alves N, Daros A, Ure RJ, Schmid S (2010) GABA receptors and prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in mice and rats. Eur J Neurosci 31:2053–2061
Zhai H, Miller J, Sammis G (2012) First enantioselective syntheses of the dopamine D1 and D2 receptor modulators, (+)- and (−)-govadine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:1557–1559
Zhang J, Engel JA, Jackson DM et al (1997) (−)Alprenolol potentiates the disrupting effects of dizocilpine on sensorimotor function in the rat. Psychopharmacology 132:281–288
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by an operating grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR; #125984) and Brain Canada Multi-Investigator Research Initiative Grant (PI: Dr. Terrance Snutch, University of British Columbia) to JGH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JGH is a CIHR New Investigator. BRL received salary support from the University of Saskatchewan. WNM received salary support from the College of Medicine at the University of Saskatchewan and the Saskatchewan Health Research Foundation. AGP holds a patent for the use of the d,l-govadine and its enantiomers as putative antipsychotic drugs. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Brittney R. Lins and Wendie N. Marks contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lins, B.R., Marks, W.N., Phillips, A.G. et al. Dissociable effects of the d- and l- enantiomers of govadine on the disruption of prepulse inhibition by MK-801 and apomorphine in male Long-Evans rats. Psychopharmacology 234, 1079–1091 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4540-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4540-x