Abstract
Rationale
High-fat diet (HFD) has been recently reported to induce sensorimotor gating deficits, but the underlying mechanisms are not well understood.
Objective
The purpose of this study is to determine whether HFD induces long-lasting deficits in sensorimotor gating and to examine the involvement of altered dopamine (DA) function.
Methods
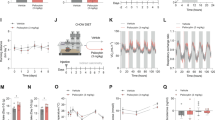
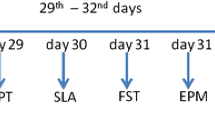
C57BL/6J mice were fed HFD for 10 weeks and then normal diet (ND) for 4 weeks. DA D2 receptor (D2R) knockout (KO) mice were also fed HFD for 10 weeks. The mice were evaluated for prepulse inhibition (PPI) of acoustic startle after HFD and the subsequent 4-week ND. We evaluated the effect of SCH23390, a D1 receptor (D1R) antagonist, on PPI and measured protein expression levels of D1R and D2R in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in HFD mice. The concentrations of monoamines and their metabolites in the cortices of 10-week HFD or ND mice were measured using high performance liquid chromatography.
Results
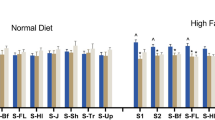
Long-term HFD-induced PPI disruption in WT and D2R KO mice. Even after 4 weeks of subsequent ND, PPI remained to be disrupted. SCH23390 mitigated the PPI disruption. In HFD animals, D1R protein expression in the PFC was significantly decreased, while DA, homovanillic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid levels in the cortex were increased.
Conclusion
This is the first evidence that HFD can induce long-lasting deficits in sensorimotor gating through alteration of cortical levels of DA and its metabolites. Our data suggest that HFD-induced PPI deficits are related to altered D1R signaling and that D1R antagonists may have therapeutic effects on the deficits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Dargham A, Mawlawi O, Lombardo I, Gil R, Martinez D, Huang Y, Hwang DR, Keilp J, Kochan L, Van Heertum R, Gorman JM, Laruelle M (2002) Prefrontal dopamine D1 receptors and working memory in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 22:3708–3719
Abi-Dargham A, Xu X, Thompson JL, Gil R, Kegeles LS, Urban N, Narendran R, Hwang DR, Laruelle M, Slifstein M (2012) Increased prefrontal cortical D1 receptors in drug naive patients with schizophrenia: a PET study with [11C]NNC112. J Psychopharmacol 26:794–805
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Braff D, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer M, Glick I, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Buettner R, Scholmerich J, Bollheimer LC (2007) High-fat diets: modeling the metabolic disorders of human obesity in rodents. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15:798–808
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:117–154
Gould TJ, Bizily SP, Tokarczyk J, Kelly MP, Siegel SJ, Kanes SJ, Abel T (2004) Sensorimotor gating deficits in transgenic mice expressing a constitutively active form of Gsα. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:494–501
Kambeitz J, Abi-Dargham A, Kapur S, Howes OD (2014) Alterations in cortical and extrastriatal subcortical dopamine function in schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis of imaging studies. Br J Psychiatry 204:420–429
Kunugi H, Tanaka M, Hori H, Hashimoto R, Saitoh O, Hironaka N (2007) Prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle in Japanese patients with chronic schizophrenia. Neurosci Res 59:23–28
Labouesse MA, Stadlbauer U, Langhans W, Meyer U (2013) Chronic high fat diet consumption impairs sensorimotor gating in mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:2562–2574
Li XL, Aou S, Oomura Y, Hori N, Fukunaga K, Hori T (2002) Impairment of long-term potentiation and spatial memory in leptin receptor-deficient rodents. Neuroscience 113:607–615
McElroy SL, Keck PE Jr (2014) Metabolic syndrome in bipolar disorder: a review with a focus on bipolar depression. J Clin Psychiatry 75:46–61
McIntyre RS, Rasgon NL, Kemp DE, Nguyen HT, Law CW, Taylor VH, Woldeyohannes HO, Alsuwaidan MT, Soczynska JK, Kim B, Lourenco MT, Kahn LS, Goldstein BI (2009) Metabolic syndrome and major depressive disorder: co-occurrence and pathophysiologic overlap. Curr Diab Rep 9:51–59
Missale C, Nash SR, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Money KM, Stanwood GD (2013) Developmental origins of brain disorders: roles for dopamine. Front Cell Neurosci 7:260
Nozaki S, Kato M, Takano H, Ito H, Takahashi H, Arakawa R, Okumura M, Fujimura Y, Matsumoto R, Ota M, Takano A, Otsuka A, Yasuno F, Okubo Y, Kashima H, Suhara T (2009) Regional dopamine synthesis in patients with schizophrenia using L-[β-11C]DOPA PET. Schizophr Res 108:78–84
Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Yagasaki Y, Izumi A, Kunugi H (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-γ signaling for glutamate release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:647–652
Okubo Y, Suhara T, Suzuki K, Kobayashi K, Inoue O, Terasaki O, Someya Y, Sassa T, Sudo Y, Matsushima E, Iyo M, Tateno Y, Toru M (1997) Decreased prefrontal dopamine D1 receptors in schizophrenia revealed by PET. Nature 385:634–636
Pathan AR, Gaikwad AB, Viswanad B, Ramarao P (2008) Rosiglitazone attenuates the cognitive deficits induced by high fat diet feeding in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 589:176–179
Ralph RJ, Caine SB (2005) Dopamine D1 and D2 agonist effects on prepulse inhibition and locomotion: comparison of Sprague–Dawley rats to Swiss-Webster, 129X1/SvJ, C57BL/6J, and DBA/2J mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:733–741
Ralph-Williams RJ, Lehmann-Masten V, Otero-Corchon V, Low MJ, Geyer MA (2002) Differential effects of direct and indirect dopamine agonists on prepulse inhibition: a study in D1 and D2 receptor knock-out mice. J Neurosci 22:9604–9611
Ralph-Williams RJ, Lehmann-Masten V, Geyer MA (2003) Dopamine D1 rather than D2 receptor agonists disrupt prepulse inhibition of startle in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:108–118
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Garrett TL, Lucot JB (2010) Neurobehavioral deficits in db/db diabetic mice. Physiol Behav 101:381–388
Van De Werd HJ, Uylings HB (2014) Comparison of (stereotactic) parcellations in mouse prefrontal cortex. Brain Struct Funct 219:433–459
Wakabayashi C, Kiyama Y, Kunugi H, Manabe T, Iwakura Y (2011) Age-dependent regulation of depression-like behaviors through modulation of adrenergic receptor α1A subtype expression revealed by the analysis of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist knockout mice. Neuroscience 192:475–484
Wakabayashi C, Numakawa T, Ninomiya M, Chiba S, Kunugi H (2012) Behavioral and molecular evidence for psychotropic effects in L-theanine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 219:1099–1109
Winocur G, Greenwood CE, Piroli GG, Grillo CA, Reznikov LR, Reagan LP, McEwen BS (2005) Memory impairment in obese Zucker rats: an investigation of cognitive function in an animal model of insulin resistance and obesity. Behav Neurosci 119:1389–1395
Yamada N, Katsuura G, Ochi Y, Ebihara K, Kusakabe T, Hosoda K, Nakao K (2011) Impaired CNS leptin action is implicated in depression associated with obesity. Endocrinology 152:2634–2643
Yamaguchi H, Aiba A, Nakamura K, Nakao K, Sakagami H, Goto K, Kondo H, Katsuki M (1996) Dopamine D2 receptor plays a critical role in cell proliferation and proopiomelanocortin expression in the pituitary. Genes Cells 1:253–268
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Intramural Research Grant for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders of NCNP, Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants, and the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. We thank Mr. K. Yamamoto for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(pdf 860 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakabayashi, C., Numakawa, T., Ooshima, Y. et al. Possible role of the dopamine D1 receptor in the sensorimotor gating deficits induced by high-fat diet. Psychopharmacology 232, 4393–4400 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4068-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4068-x