Abstract
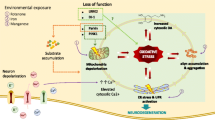
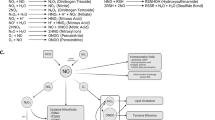
Parkinson disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease of unknown origin that is characterized, mainly, by a significant reduction in the number of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) of the brain and a dramatic reduction in dopamine levels in the corpus striatum. For reasons that we do not know, the dopamine neuron seems to be more vulnerable to damage than any other neuron in the brain. Although hypotheses of damage to the dopamine neuron include oxidative stress, growth factor decline, excitotoxicity, inflammation in the SNpc and protein aggregation, oxidative stress in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system garners a significant amount of attention. In the oxidative stress hypothesis of PD, superoxide, nitric oxide and dopamine all conspire to create an environment that can be detrimental to the dopamine neuron. MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine), the tool of choice for investigations into the mechanisms involved in the death of dopamine neurons in PD, has been used extensively in attempts to sort out what happens in and around the dopamine neuron. Herein, we review the roles of dopamine, superoxide and nitric oxide in the demise of the dopamine neuron in the MPTP model of PD as it relates to the death of the dopamine neuron noted in PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ (1988) Developmental neurobiology. The milieu is the message.Nature 332, 490–491.
Ara J, S Przedborski, AB Naini, V Jackson-Lewis, RR Trifiletti, J Horwitz and H Ischiropoulos (1998) Inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nitration following exposure to peroxynitrite and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 95, 7659–7663.
Babior BM (1999) NADPH oxidase: an update.Blood 93, 1464–1476.
Banati RB, J Gehrmann, P Schubert and GW Kreutzberg (1993) Cytotoxicity of microglia.Glia 7, 111–118.
Beal MF (2003) Mitochondria, oxidative damage, and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 991, 120–131.
Bezard E, CE Gross, MC Fournier, S Dovero, B Bloch and M Jaber (1999) Absence of MPTP-induced neuronal death in mice lacking the dopamine transporter.Exp. Neurol. 155, 268–273.
Bohn MC (1999) A commentary on glial cell line-derived neu-rotrophic factor (GDNF). From a glial secreted molecule to gene therapy.Biochem. Pharmacol. 57, 135–142.
Brooks WJ, MF Jarvis and GC Wagner (1989) Astrocytes as a primary locus for the conversion MPTP into MPP+.J. Neural Transm. 76, 1–12.
Burke WJ, HD Chung and SW Li (1999) Quantitation of 3,4-dihy-droxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylglycolalde-hyde, the monoamine oxidase metabolites of dopamine and nora-drenaline, in human tissues by microcolumn high-performance liquid chromatography.Anal. Biochem. 273, 111–116.
Burke WJ, SW Li, EA Williams, R Nonneman and DS Zahm (2003) 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde is the toxic dopamine metabolitein vivo: implications for Parkinson’s disease patho-genesis.Brain Res. 989, 205–213.
Burke WJ, SW Li, HD Chung, DA Ruggiero, BS Kristal, EM Johnson, P Lampe, VB Kumar, M Franko, EA Williams and DS Zahm (2004) Neurotoxicity of MAO metabolites of cate-cholamine neurotransmitters: role in neurodegenerative diseases.Neurotoxicology 25, 101–115.
Chauhan NB, GJ Siegel and JM Lee (2001) Depletion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in substantia nigra neurons of Parkinson’s disease brain.J. Chem. Neuroanat. 21, 277–288.
Ciesielska A, I Joniec, A Przybylkowski, G Gromadzka, I Kurkowska-Jastrzebska, A Czlonkowska and A Czlonkowski (2003) Dynamics of expression of the mRNA for cytokines and inducible nitric synthase in a murine model of the Parkinson’s disease.Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars.) 63, 117–126.
Cohen G (1984) Oxy-radical toxicity in catecholamine neurons.Neurotoxicology 5, 77–82.
Dauer W and S Przedborski (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models.Neuron 39, 889–909.
Dehmer T, J Lindenau, S Haid, J Dichgans and JB Schulz (2000) Deficiency of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against MPTP toxicityin vivo.J. Neurochem. 74, 2213–2216.
Drachman DB, K Frank, M Dykes-Hoberg, P Teismann, G Almer, S Przedborski and JD Rothstein (2002) Cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition protects motor neurons and prolongs survival in a trans-genic mouse model of ALS.Ann. Neurol. 52, 771–778.
Fahn S (1997) Levodopa-induced neurotoxicity: does it represent a problem for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease?CNS Drugs 8, 376–393.
Fahn S and G Cohen (1992) The oxidant stress hypothesis in Parkinson’s disease: evidence supporting it.Ann. Neurol. 32, 804–812.
Fahn S and S Przedborski (2000) Parkinsonism, In:Merritt’s Neurology (Rowland LP. Ed.) (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: New York, NY), pp 679–693.
Fornai F, FS Giorgi, L Bassi, M Ferrucci, MG Alessandri and GU Corsini (2000) Modulation of dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde extracellular levelsin vivo in the rat striatum after different kinds of pharmacological treatment.Brain Res. 861, 126–134.
Fridovich I (1995) Superoxide radical and superoxide dismutases.Ann. Rev. Biochem. 64, 97–112.
Gainetdinov RR, F Fumagalli, SR Jones and MG Caron (1997) Dopamine transporter is required forin vivo MPTP neurotoxici-ty: evidence from mice lacking the transporter.J.Neurochem. 69, 1322–1325.
Gao HM, B Liu, W Zhang and JS Hong (2003) Critical role of microglial NADPH oxidase-derived free radicals in the in vitro MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease.FASEB J. 17, 1954–1956.
Graham DG (1978) Oxidative pathways for catecholamines in the genesis of neuromelanin and cytotoxic quinones.Mol. Pharmacol.14, 633–643.
Hafler DA (2004) Multiple sclerosis.J. Clin. Invest. 113, 788–794.
Hastings TG (1995) Enzymatic oxidation of dopamine: the role of prostaglandin H synthase.J. Neurochem. 64, 919–924.
Hazell AS, Y Itzhak, H Liu and MD Norenberg (1997) 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes.J. Neurochem. 68, 2216–2219.
Hebert G, J Arsaut, R Dantzer and J Demotes-Mainard (2003) Time-course of the expression of inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in the striatum and mesencephalon of mice injected with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyri-dine, a dopaminergic neurotoxin.Neurosci. Lett. 349, 191–195.
Huang Y, L Cheung, D Rowe and G Halliday (2004) Genetic contributions to Parkinson’s disease.Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 46, 44–70.
Hunot S and EC Hirsch (2003) Neuroinflammatory processes in Parkinson’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 53 Suppl. 3, S49-S58.
Hunot S, F Boissiere, B Faucheux, B Brugg, A Mouatt-Prigent, Y Agid and EC Hirsch (1996) Nitric oxide synthase and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease.Neuroscience 72, 355–363.
Hunot S, N Dugas, B Faucheux, A Hartmann, M Tardieu, P Debre, Y Agid, B Dugas and EC Hirsch (1999) Fc?RII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson’s disease and induces,in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in glial cells.J. Neurosci. 19, 3440–3447.
Ii K, H Ito, K Tanaka and A Hirano (1997) Immunocytochemical co-localization of the proteasome in ubiquitinated structures in neurodegenerative diseases and the elderly.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 125–131.
Ischiropoulos H and AB Al-Mehdi (1995) Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidative protein modifications.FEBS Lett. 364, 279–282.
Jackson-Lewis V, M Jakowec, RE Burke and S Przedborski (1995) Time course and morphology of dopaminergic neuronal death caused by the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahy-dropyridine.Neurodegeneration 4, 257–269.
Jakowec MW, K Nixon, E Hogg, T McNeill and GM Petzinger (2004) Tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine transporter expression following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurodegeneration of the mouse nigrostriatal pathway.J. Neurosci. Res. 76, 539–550.
Javitch JA, RJ D’Amato, SM Strittmatter and SH Snyder (1985) Parkinsonism-inducing neurotoxin,N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine: uptake of the metaboliteN-methyl-4-phenylpyridine by dopamine neurons explains selective toxicity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 82, 2173–2177.
Jeon BS, V Jackson-Lewis and RE Burke (1995) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesion of the rat substantia nigra: time course and morphology of cell death.Neurodegeneration 4, 131–137.
Keller JN, MS Kindy, FW Holtsberg, DK St Clair, HC Yen, A Germeyer, SM Steiner, AJ Bruce-Keller, JB Hutchins and MP Mattson (1998) Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction.J. Neurosci. 18, 687–697.
Klivenyi P, D St Clair, M Wermer, HC Yen, T Oberley, L Yang and MF Beal (1998) Manganese superoxide dismutase overexpres-sion attenuates MPTP toxicity.Neurobiol. Dis. 5, 253–258.
Kopin IJ (1992) Features of the dopaminergic neurotoxin MPTP.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 648, 96–104.
Kostic V, DM Donovan and R Yokoyama (1996) Transgenic mice with increased number of dopamine transporters (DAT) show greater sensitivity to MPTP.Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 22, 722.
Kuhn DM, RE Arthur Jr, DM Thomas and LA Elferink (1999) Tyrosine hydroxylase is inactivated by catechol-quinones and converted to a redox-cycling quinoprotein: possible relevance to Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurochem. 73, 1309–1317.
Lancaster JR Jr (1996) Diffusion of free nitric oxide, In:Nitric Oxide. Source and Detection of NO; NO Synthase (Packer L, Ed.) (Academic Press: New York, NY), pp 31–50.
Langston JW, LS Forno, J Tetrud, AG Reeves, JA Kaplan and D Karluk (1999) Evidence of active nerve cell degeneration in the substantia nigra of humans years after 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine exposure.Ann. Neurol. 46, 598–605.
Lau YS, YK Fung, KL Trobough, JR Cashman and JA Wilson (1991) Depletion of striatal dopamine by theN-oxide of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP).Neurotoxicology 12, 189–199.
Liberatore GT, V Jackson-Lewis, S Vukosavic, AS Mandir, M Vila, WG McAuliffe, VL Dawson, TM Dawson and S Przedborski (1999) Inducible nitric oxide synthase stimulates dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson disease.Nat. Med. 5, 1403–1409.
Marini AM, RH Lipsky, JP Schwartz and IJ Kopin (1992) Accumulation of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in cultured cerebellar astrocytes.J. Neurochem. 58, 1250–1258.
Mizuno Y, N Sone, K Suzuki and T Saitoh (1988) Studies on the toxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) against mitochondria of mouse brain.J. Neurol. Sci. 86, 97–110.
Mizuno Y, S Ohta, M Tanaka, S Takamiya, K Suzuki, T Sato, H Oya, T Ozawa and Y Kagawa (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163, 1450–1455.
Mogi M, A Togari, T Kondo, Y Mizuno, O Komure, S Kuno, H Ichinose and T Nagatsu (1999) Brain-derived growth factor and nerve growth factor concentrations are decreased in the substan-tia nigra in Parkinson’s disease.Neurosci. Lett. 270, 45–48.
Muller HW, U Junghans and J Kappler (1995) Astroglial neu-rotrophic and neurite-promoting factors.Pharmacol. Ther. 65, 1–18.
Nagatsu T, M Mogi, H Ichinose and A Togari (2000) Changes in cytokines and neurotrophins in Parkinson’s disease.J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 277–290.
Nicklas WJ, I Vyas and RE Heikkila (1985) Inhibition of NADH-linked oxidation in brain mitochondria by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridine, a metabolite of the neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine.Life Sci. 36, 2503–2508.
Nicklas WJ, SK Youngster, MV Kindt and RE Heikkila (1987) MPTP, MPP+ and mitochondrial function.Life Sci. 40, 721–729.
O’Banion MK (1999) Cyclooxygenase-2: molecular biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology.Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 13, 45–82.
Olanow CW and WG Tatton (1999) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 123–144.
Przedborski S and V Jackson-Lewis (2000) ROS and Parkinson’s disease: a view to a kill, In:Free Radicals in Brain Pathophysiology (Poli G, E Cadenas and L Packer, Eds.) (Marcel Dekker: New York, NY), pp 273–290.
Przedborski S and M Vila (2003) The 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model: a tool to explore the pathogen-esis of Parkinson’s disease.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 991, 189–198.
Przedborski S, V Kostic, V Jackson-Lewis, AB Naini, S Simonetti, S Fahn, E Carlson, CJ Epstein and JL Cadet (1992) Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity are resistant toN-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 12, 1658–1667.
Przedborski S, M Levivier, H Jiang, M Ferreira, V Jackson-Lewis, D Donaldson and DM Togasaki (1995) Dose-dependent lesions of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway induced by intrastri-atal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine.Neuroscience 67, 631–647.
Przedborski S, V Jackson-Lewis, R Yokoyama, T Shibata, VL Dawson and TM Dawson (1996) Role of neuronal nitric oxide in MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4565–4571.
Przedborski S, V Jackson-Lewis, R Djaldetti, G Liberatore, M Vila, S Vukosavic and G Almer (2000) The parkinsonian toxin MPTP: action and mechanism.Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 16, 135–142.
Radi R, A Cassina, R Hodara, C Quijano and L Castro (2002) Peroxynitrite reactions and formation in mitochondria.Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33, 1451–1464.
Rajput AH (2001a) Levodopa prolongs life expectancy and is non-toxic to substantia nigra.Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord. 8, 95–100.
Rajput AH (2001b) The protective role of levodopa in the human substantia nigra.Adv. Neurol. 86, 327–336.
Ransom BR, DM Kunis, I Irwin and JW Langston (1987) Astrocytes convert the parkinsonism inducing neurotoxin, MPTP, to its active metabolite, MPP+.Neurosci. Lett. 75, 323–328.
Rego AC and CR Oliveira (2003) Mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species in excitotoxicity and apoptosis: implications for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases.Neurochem. Res. 28, 1563–1574.
Schapira AH, JM Cooper, D Dexter, JB Clark, P Jenner and CD Marsden (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurochem. 54, 823–827.
Schmidt CJ, LA Matsuda and JW Gibb (1984)In vitro release of tri-tiated monoamines from rat CNS tissue by the neurotoxic compound 1-methyl-phenyl-tetrahydropyridine.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 103, 255–260.
Snyder H, K Mensah, C Theisler, J Lee, A Matouschek and B Wolozin (2003) Aggregated and monomeric alpha-synuclein bind to the S6’ proteasomal protein and inhibit proteasomal function.J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11753–11759.
Teismann P, K Tieu, DK Choi, DC Wu, A Naini, S Hunot, M Vila, V Jackson-Lewis and S Przedborski (2003a) Cyclooxygenase-2 is instrumental in Parkinson’s disease neurodegeneration.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5473–5478.
Teismann P, K Tieu, O Cohen, DK Choi, DC Wu, D Marks, M Vila, V Jackson-Lewis and S Przedborski (2003b) Pathogenic role of glial cells in Parkinson’s disease.Mov. Disord. 18, 121–129.
Trojanowski JQ, M Goedert, T Iwatsubo and VM Lee (1998) Fatal attractions: abnormal protein aggregation and neuron death in Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia.Cell Death Differ. 5, 832–837.
Vigouroux S, M Briand and Y Briand (2004) Linkage between the proteasome pathway and neurodegenerative diseases and aging.Mol. Neurobiol. 30, 201–221.
Vila M and S Przedborski (2004) Genetic clues to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.Nat. Med. 10 Suppl., S58-S62.
Watanabe H, Y Muramatsu, R Kurosaki, M Michimata, M Matsubara, Y Imai and T Araki (2004) Protective effects of neu-ronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in mouse brain against MPTP neurotoxicity: an immunohistological study.Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 14, 93–104.
Weiner WJ (2000) Is levodopa toxic?Arch. Neurol. 57, 408–410.
Wu DC, P Teismann, K Tieu, M Vila, V Jackson-Lewis, H Ischiropoulos and S Przedborski (2003) NADPH oxidase mediates oxidative stress in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahy-dropyridine model of Parkinson’s disease.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6145–6150.
Youdim MB, E Grunblatt, Y Levites, G Maor and S Mandel (2002) Early and late molecular events in neurodegeneration and neuro-protection in Parkinson’s disease MPTP model as assessed by cDNA microarray; the role of iron.Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 679–689.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson-Lewis, V., Smeyne, R.J. MPTP and SNpc DA neuronal vulnerability: Role of dopamine, superoxide and nitric oxide in neurotoxicity. Minireview.. neurotox res 7, 193–201 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036449
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036449