Abstract
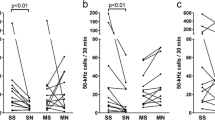
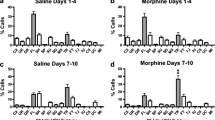
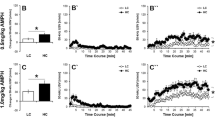
Ultrasounds (US) in rats may communicate affective states, as they occur only in highly significant situations such as maternal care, sex and aggression. Withdrawal from morphine is a manipulation which dramatically alters autonomic, somatic and motor functions; the present experiment demonstrated the production of US in this context and the influence of previous social experience in their production. Sixty male Long-Evans rats with distinct social experiences (social inexperience, defeat or copulation) underwent 72 h of continuous morphine exposure (4 × 75 mg morphine or placebo pellets) and subsequent withdrawal. The rats were observed for 10 min in equally treated pairs and while solitary at 6, 24 and 96 h after pellet removal. US were emitted by all groups and consisted primarily of two distributions of pure tone whistles with little frequency modulation: 1–2 s 21–25 kHz (“low”) signals and the more prevalent 0.02–0.1 s 44–52 kHz (“high”) signals. Morphine withdrawn rats lost weight, displayed wet dog shakes, were hypoactive and emitted threefold more US vocalizations with a fourfold greater duration than placebo controls. Defeat-experienced morphine withdrawn rats were more hypoactive than either socially inexperienced or copulatory experienced rats while increasing vocalization rates and total duration. This increased duration of ultrasounds included a shift in the distribution of individual US durations from less than 0.3 s to greater than 1.0 s. US are readily emitted at high rates in morphine withdrawn laboratory rats, which may implicate an opioid involvement in their generation. Furthermore, relevant social experiences such as copulation and defeat facilitate the emission of US during morphine withdrawal and may serve as an index of the affective components of withdrawal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attila LMJ, Ahtee L (1984) Retardation of cerebral dopamine turnover after morphine withdrawal and its enhanced acceleration by acute morphine administration in rats. Arch Pharmacol 327:201–207
Barfield RJ, Geyer LA (1975) The ultrasonic postejaculatory vocalization and the postejaculatory refractory period of the male rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 88:723–734
Bell RW, Nitschke W, Gorry TH, Zachman TA (1971) Infantile stimulation and ultrasonic signalling: a possible mediator of early handling phenomena. Dev Psychobiol 4[2]:181–191
Bläsig J, Herz A, Reinhold K, Zieglgansberger S (1973) Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia 33:19–38
Blumberg MS, Mennella JA, Moltz H (1987) Hypothalamic temperature and deep body temperature during copulation in the male rat. Physiol Behav 39:367–370
Cagiano R, Sales GD, Renna G, Racagni G, Cuomo V (1986) Ultrasonic vocalization in rat pups: effects of early postnatal exposure to haloperidol. Life Sci 38:1417–1423
Cochin J, Miller JM, Bosow CE, Grell R, Poulsen JL (1979) The influence of the mode of morphine administration on tolerance and dependence. In: Harris L (ed) Problems of drug dependence 1979 (NIDA Monograph) 27:36–47
Cuomo V, Cagiano R, Renna G, De Salvia MA, Racagni G (1987a) Ultrasonic vocalization in rat pups: Effects of early prenatal exposure to SCH 23390 (a DA1-receptor antagonist) and sulpiride (a DA2-receptor antagonist). Neuropharmacology 26:701–705
Cuomo V, De Salvia MA, Maselli MA, Santo L, Cagiano R (1987b) Ultrasonic calling in rodents: A new experimental approach in behavioural toxicology. Neurotoxicol Teratol 9:157–160
Cuomo V, Cagiano R, De Salvia MA, Restani P, Galimberti R, Racagni G, Galli CL (1988a) Ultrasonic vocalization in rat pups as a marker of behavioral development: an investigation of the effects of drugs influencing brain opioid system. Neurotoxicol Teratol 10:465–469
Cuomo V, Cagiano R, De Salvia MA, Maselli MA, Renna G, Racagni G (1988b) Ultrasonic vocalization in response to unavoidable aversive stimuli in rats: effects of benzodiazepines. Life Sci 43:485–491
Elwood RW (1979) Ultrasound and maternal behavior in the Mongolian gerbil. Dev Psychobiol 12[4]:281–284
Floody OR (1979) Behavioral and physiological analyses of ultrasound production by female hamsters(Mesocricetus auratus). Am Zool 19:443–455
Gianutsos G, Hynes MD, Drawbaugh RB, Lal H (1975) Paradoxical absence of aggression during naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal. Psychopharmacologia 43:43–46
Gmerek DE (1988) Physiological dependence on opioids. In: Rodgers RJ, Cooper SJ (eds) Endorphins, opiates and behavioural processes. John Wiley, New York, pp 25–52
Herman BH, Panksepp J (1981) Ascending endorphin inhibition of distress vocalization. Science 211:1060–1062
Insel TR, Harbaugh CR (1989) Central administration of corticotropin releasing factor alters rat pup isolation calls. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:197–201
Jaffe J (1985) Drug addition and drug abuse. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Rall TW, and Murad F (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. MacMillan, New York, pp 532–581
Kachigan SK (1986) Statistical analysis. Radius Press, New York
Kaltwasser M (1990) Acoustic signaling in the Black rat(Rattus rattus). J Comp Psychol 104[3]:227–232
Miczek KA (1979) A new test for aggression in rats without aversive stimulation: differential effects ofd-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology 60:253–259
Miczek KA, Thompson ML, Tornatzky W (1991) Subordinate animals: behavioral and physiological adaptations and opioid tolerance. In: Brown M, Koob G, and Rivier C (eds) Neurobiology of stress. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 323–357
Nyby J, Whitney G (1978) Ultrasonic communication of adult myomorph rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2:1–14
Nyby J, Dizinno GA, Whitney G (1976) Social status and ultrasonic vocalizations of male mice. Behav Biol 18:285–289
Panksepp J, Herman BH, Vilberg T, Bishop P, DeEskinazi FG (1978a) Endogenous opioids and social behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4:473–487
Panksepp J, Vilberg T, Bean NJ, Coy DH, Kastin AJ (1978b) Reduction of distress vocalization in chicks by opiate-like peptides. Brain Res Bull 3:663–667
Panksepp J, Siviy S, Normansell L, White K, Bishop P (1982) Effects of beta-chlornaltrexamine on separation distress in chicks. Life Sci 31:2387–2390
Peters RH, Koch PC, Blythe BL, Sufka KJ (1988) Ultrasonic vocalizations in male rats following acquisition of copulation-illness associations. Physiol Behav 44:749–751
Pontet A, Gyger M, Schenk F (1989) Ontogeny of ultrasonic vocalizations in the woodmouse(Apodemus Sylvaticus L.). In: Temporal organization. Behaviour 108:241–261
Sales GD (1972) Ultrasound and aggressive behaviour in rats and other small mammals. Anim Behav 20:88–100
Siegfried B, Frischknecht H, Waser PG (1982) A new learning model for submissive behavior in mice: Effects of naloxone. Aggress Behav 8:112–115
Siegfried B, Frischknecht H, Külling P, Waser PG (1986) Defeat-induced analgesia and the conditioned display of submissive postures and escape in strains of mice. In: Matthies H (ed) Learning and memory, mechanisms of information storage in the nervous system. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 295–298
Smith WJ (1979) The study of ultrasonic communication. Am Zool 19:531–538
Thiessen DD, Upchurch M (1981) Haloperidol and clonidine increase, and apomorphine decreases ultrasonic vocalizations by gerbils. Psychopharmacology 75:287–290
Thomas DA, Takahashi LK, Barfield RJ (1983) Analysis of ultrasonic vocalizations emitted by intruders during aggressive encounters among rats(Rattus norvegicus). J Comp Psychol 97[3]:201–206
Tonoue T, Ashida Y, Makino H, Hata H (1986) Inhibition of shock-elicited ultrasonic vocalization by opioid peptides in the rat: a psychotropic effect. Psychoneuroendocrinology 11[2]:177–184
van der Poel AM, Noach EJK, Miczek KA (1989) Temporal patterning of ultrasonic distress calls in the adult rat: Effects of morphine and benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacology 97:147–148
Wei E, Way EL (1975) Application of the pellet implantation technique for the assessment of tolerance and physical dependence in the rodent. In: Ehrenpreis S, and Neidle A (eds) Methods in narcotic research. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 243–259
Whitney G, Nyby J (1979) Cues that elicit ultrasounds from adult male mice. Am Zool 19:457–463
Whitney G, Coble JR, Stockton MD, Tilson EF (1973) Ultrasonic emissions: do they facilitate courtship of mice: J Comp Physiol Psychol 34[3]:445–452
Yajima Y, Hayashi Y, Yoshii N (1980) The midbrain central gray as a highly sensitive neural structure for the production of ultrasonic vocalization in the rat. Brain Res 198:446–452
Yajima Y, Hayashi Y, Yoshii N (1981) Identification of ultrasonic vocalization substrates determined by electrical stimulation applied to the medulla oblongata in the rat. Brain Res 229:353–362
Yoburn BC, Chen J, Huang T, Inturrisi CE (1985) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of subcutaneous morphine pellets in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:282–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivian, J.A., Miczek, K.A. Ultrasounds during morphine withdrawal in rats. Psychopharmacology 104, 187–193 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244177
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244177